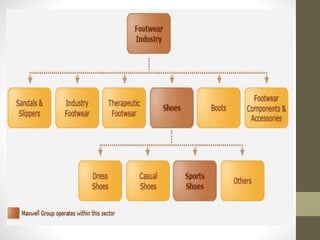
Shoe technology involves several steps in the manufacturing process. Materials like leather, plastic, rubber and jute are used to make different parts of the shoe. Over 200 operations are required to make a modern shoe using machines. The major steps include cutting the materials, closing and sewing the pieces together, lasting to form the shoe shape around a last, finishing, and packaging. Different machines are used at each step to efficiently produce shoes on a large scale. The primary parts of a shoe are the sole, insole, outsole, midsole, heel and vamp, along with secondary parts that hold the shoe together and provide style and comfort.