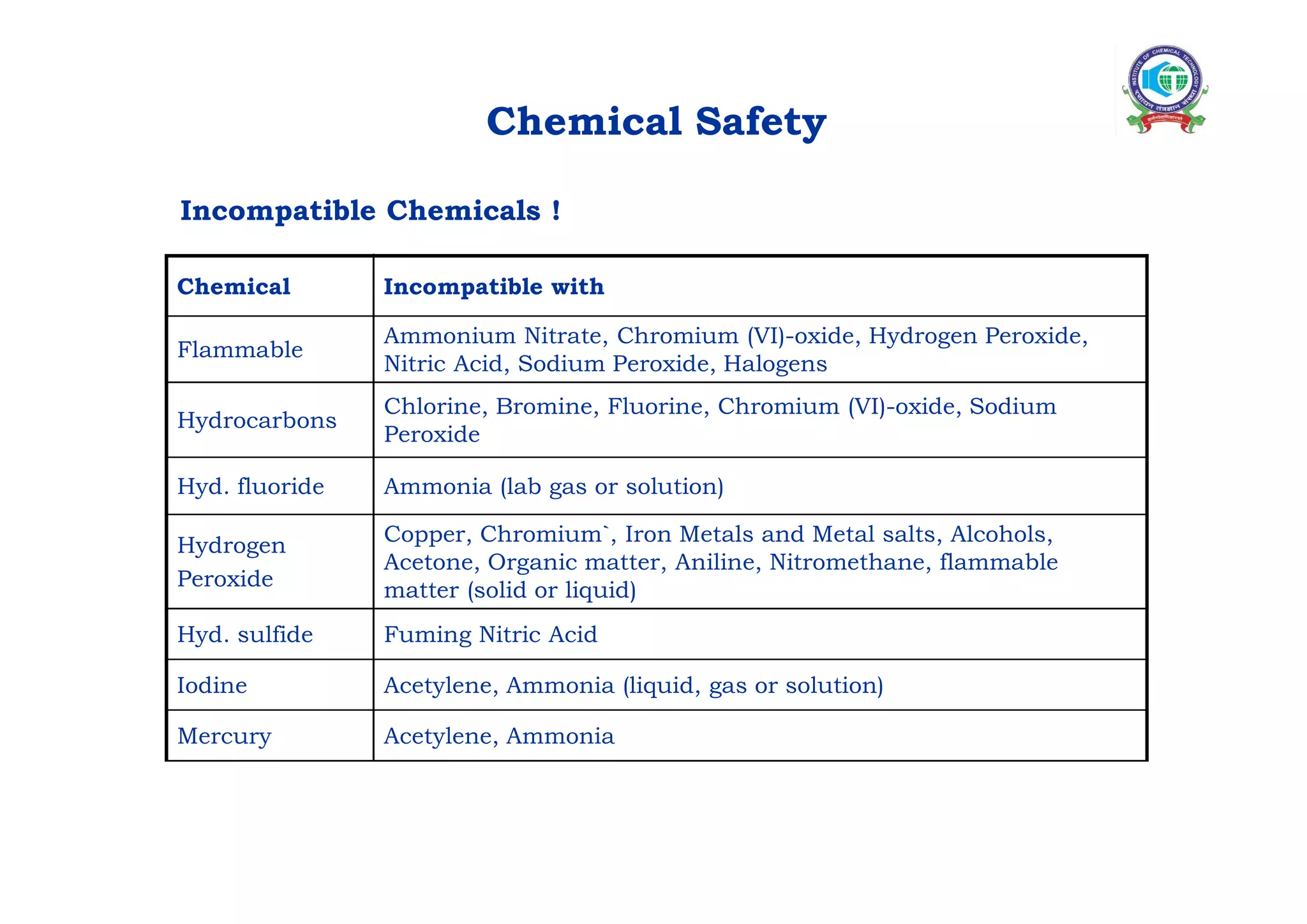
This document outlines various laboratory safety guidelines and procedures. It discusses the benefits of safety, as well as general safety practices regarding glassware, chemicals, electricity, heating, personal protective equipment, fire safety, first aid, chemical storage, and waste disposal. Specific hazards are identified, such as incompatible chemicals. The document emphasizes that following safety regulations and having proper training are essential for preventing accidents in the laboratory.