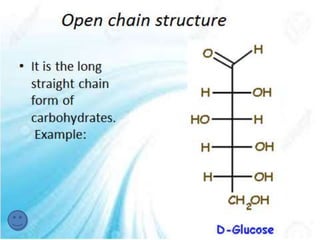
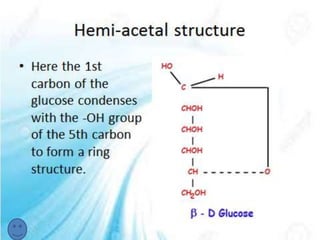
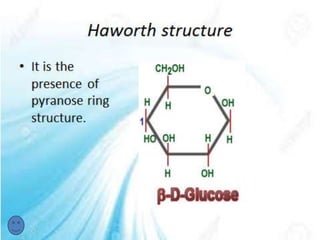
Carbohydrates, which include sugars, starches, and fibers, serve as a key energy source for the body and are vital for a healthy life. They are classified as macronutrients, with functions ranging from energy storage to supporting structural components in organisms. Furthermore, carbohydrates play significant roles in biological processes, including cell communication and immune modulation.