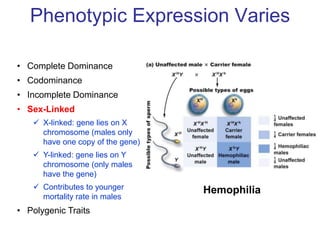
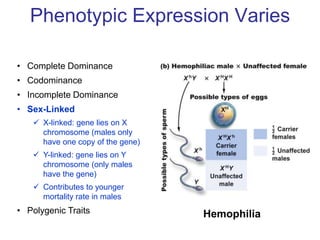
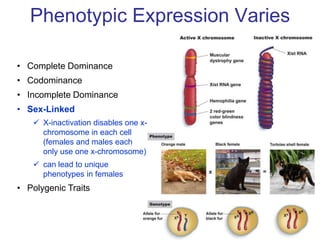
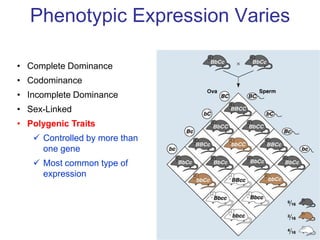
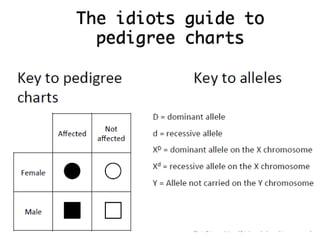
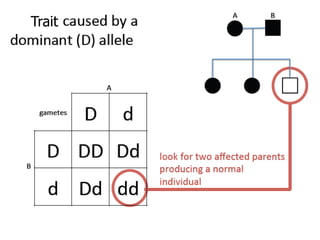
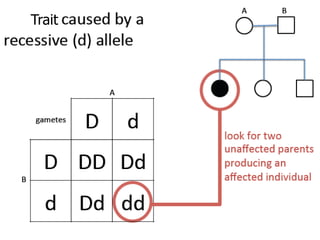
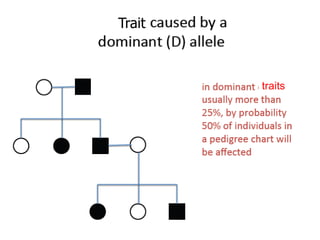
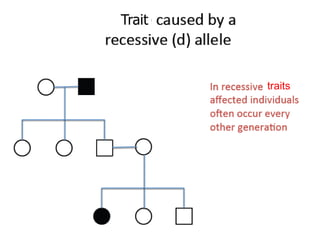
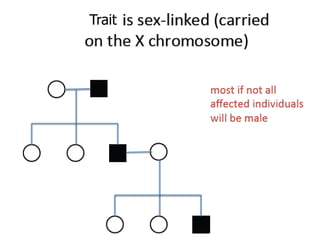
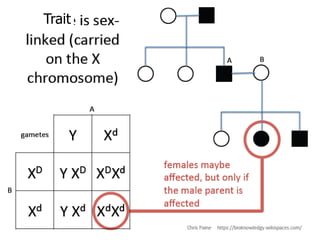
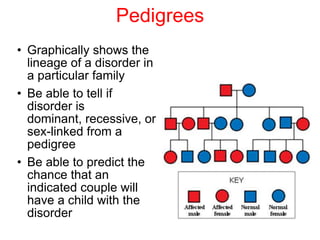
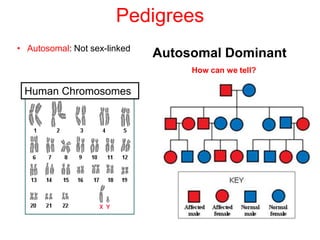
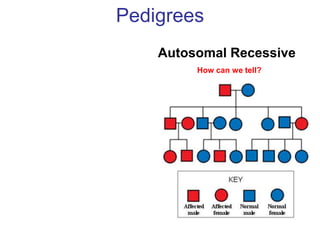
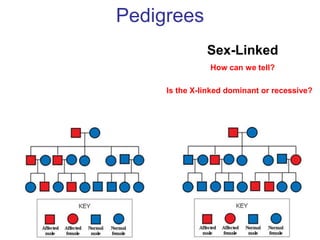
Sex-linked traits are caused by genes located on the X or Y chromosomes, with X-linked traits more common. Males typically only have one copy of the X chromosome and are thus more likely to exhibit sex-linked traits. Females have two X chromosomes and one trait can be compensated for by the other chromosome through X-inactivation.