Embed presentation
Downloaded 625 times






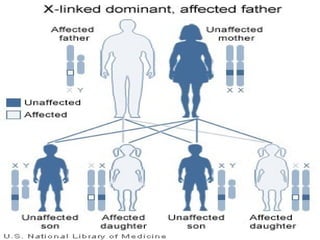




The document explains sex-linked inheritance, focusing on x-linked dominant and recessive inheritance patterns and their effects on males and females. It details how traits are passed down, especially under conditions when either parent is a carrier of a mutated gene. Additionally, it mentions y-linked inheritance, which is rare and specifically affects males, occurring from father to son.










