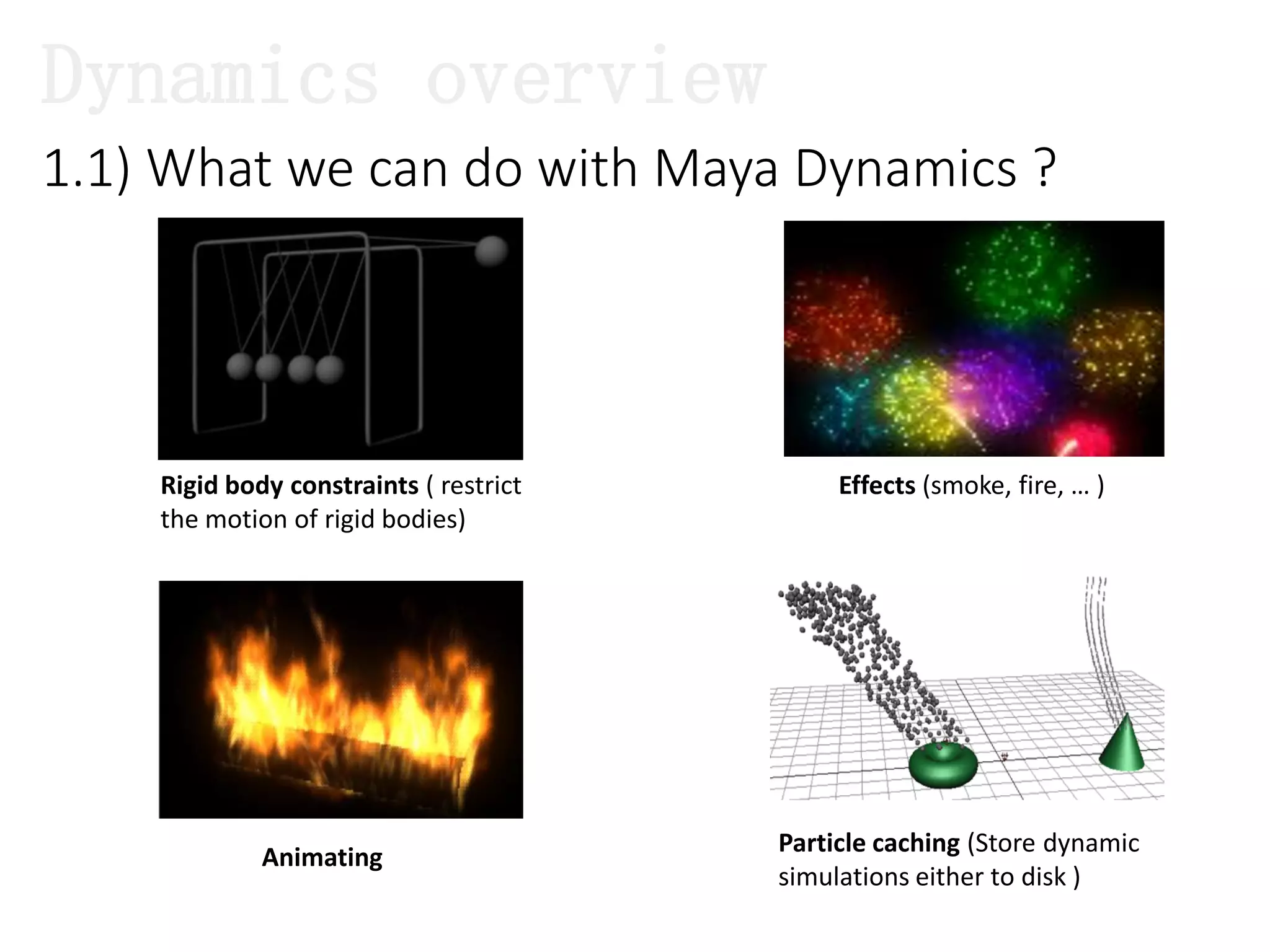
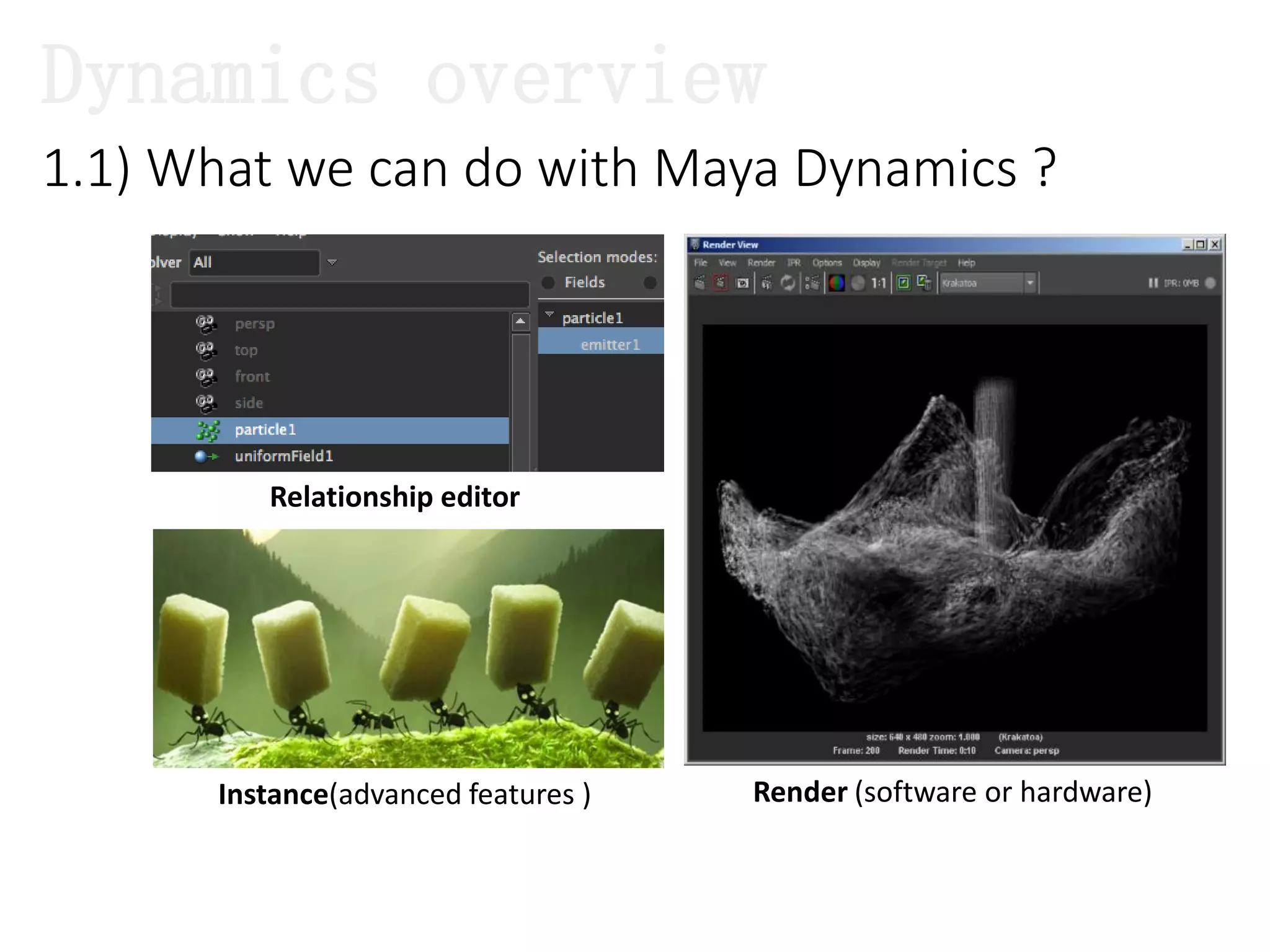
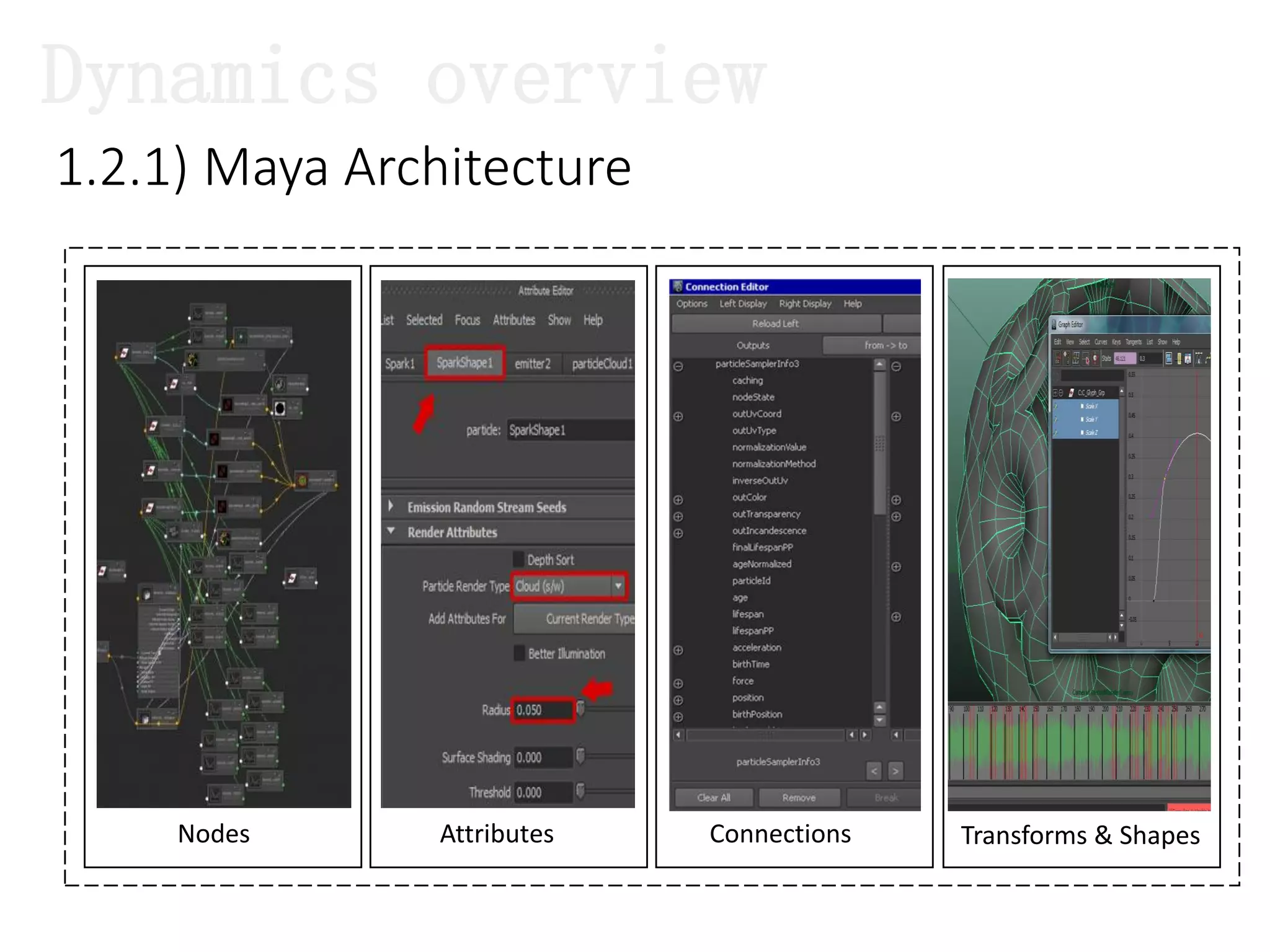
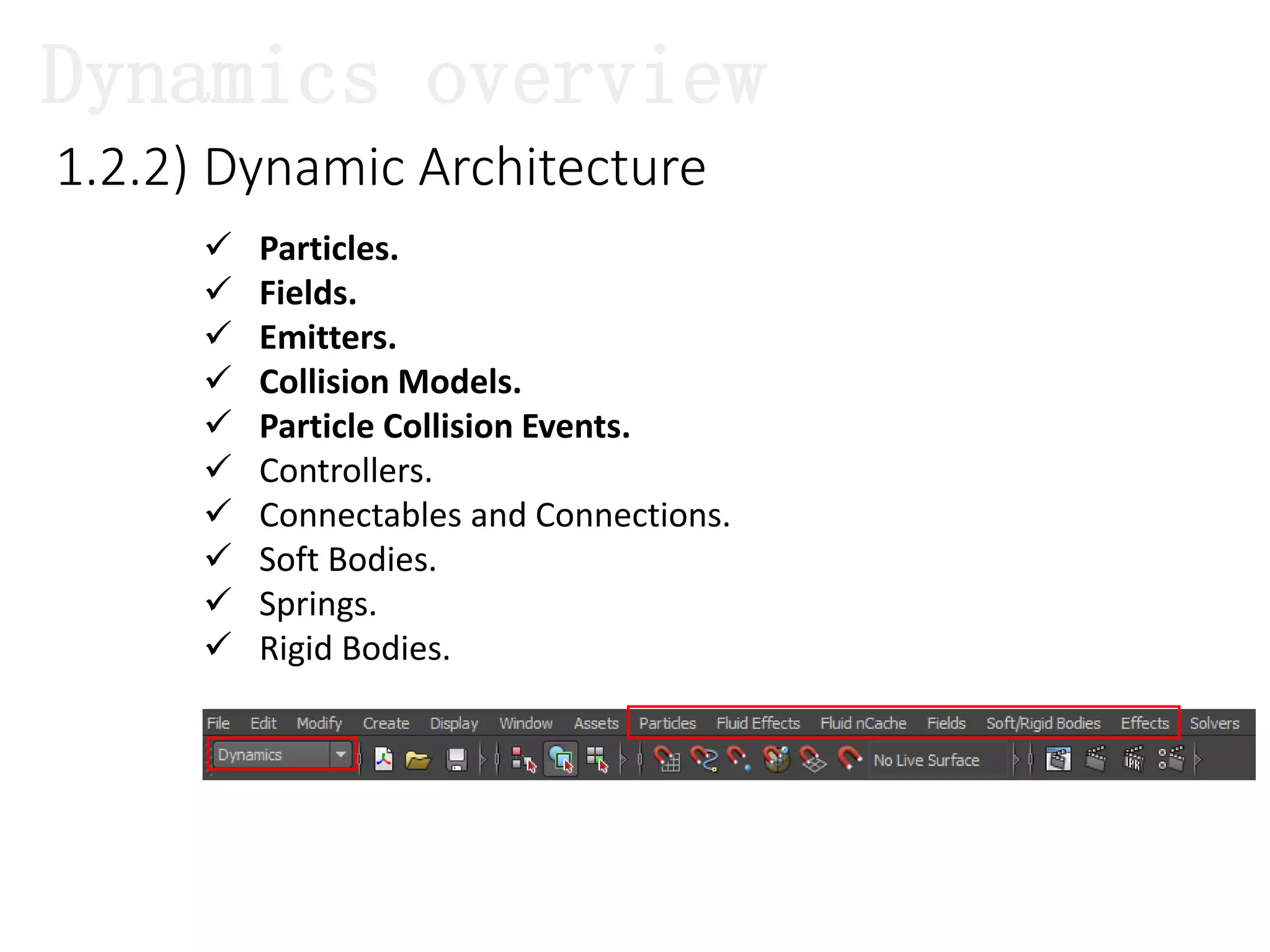
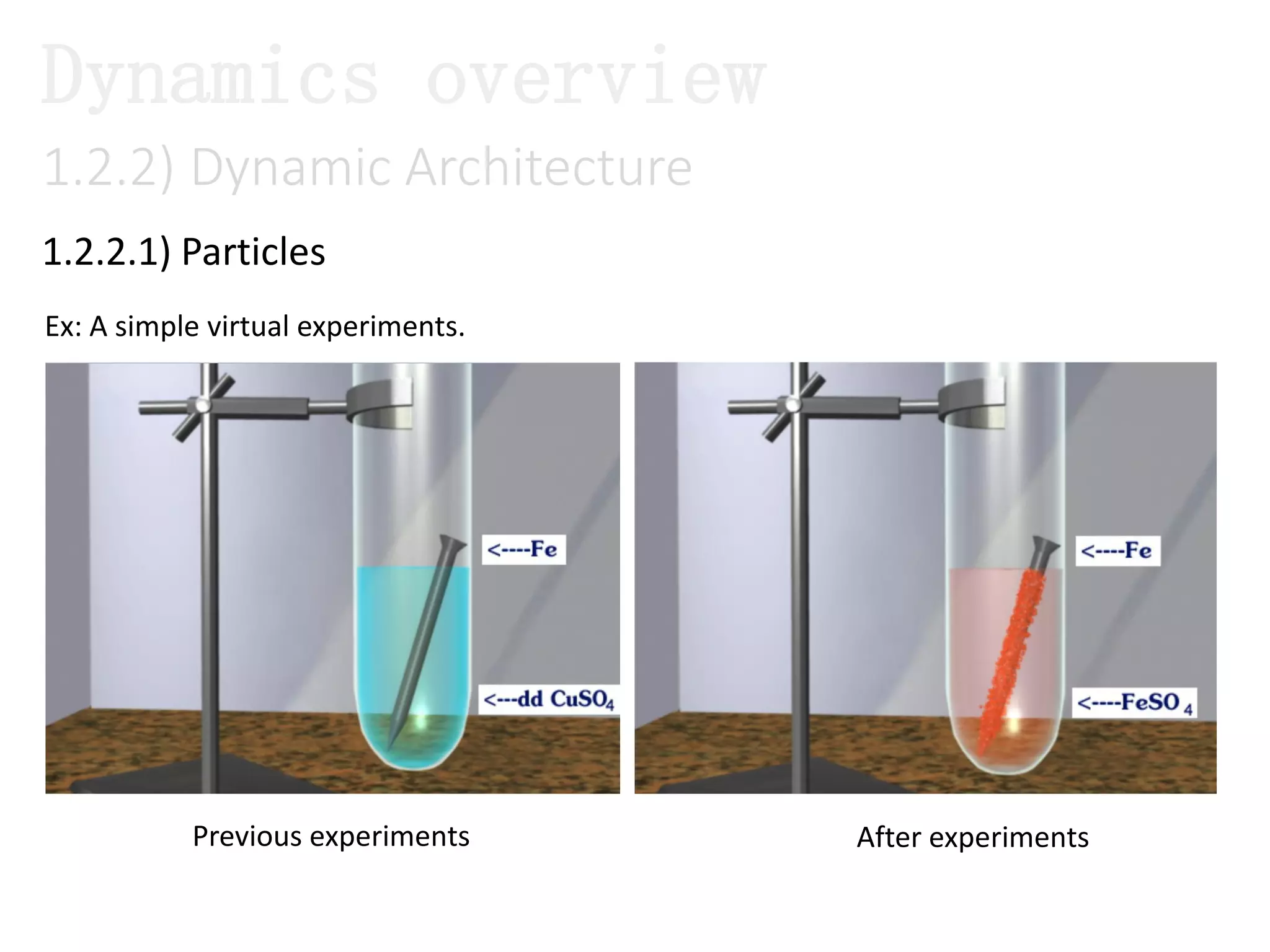
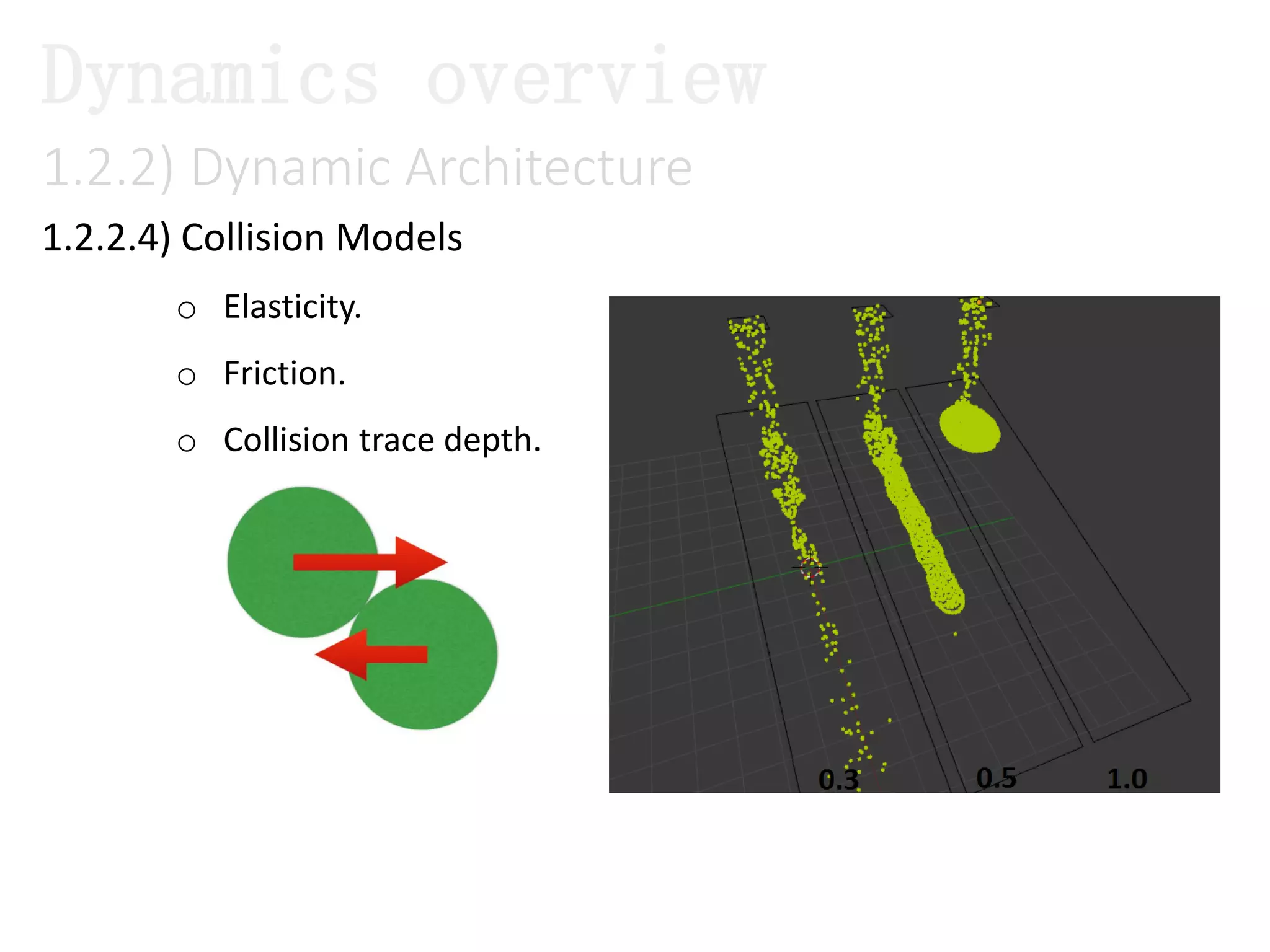
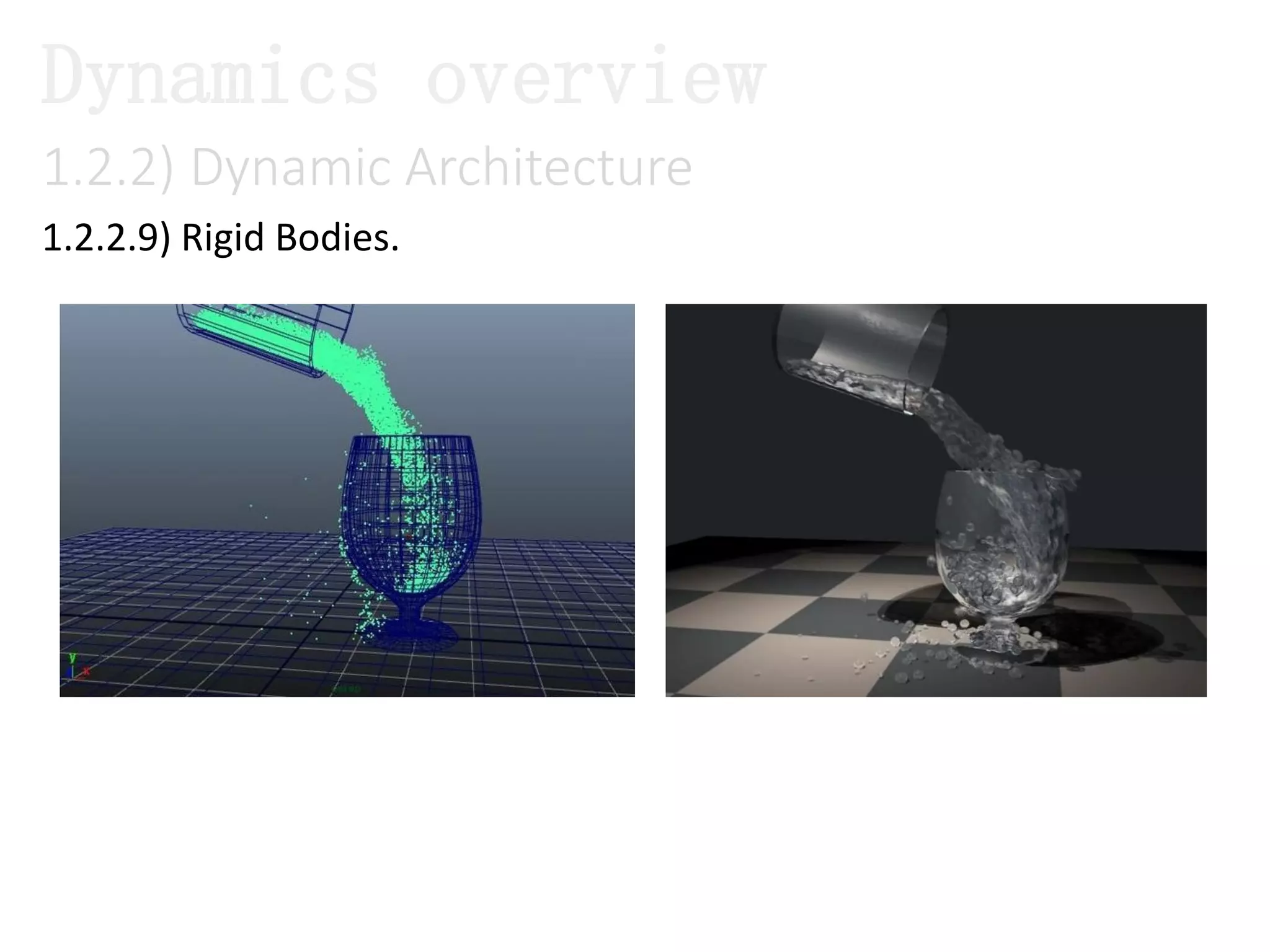
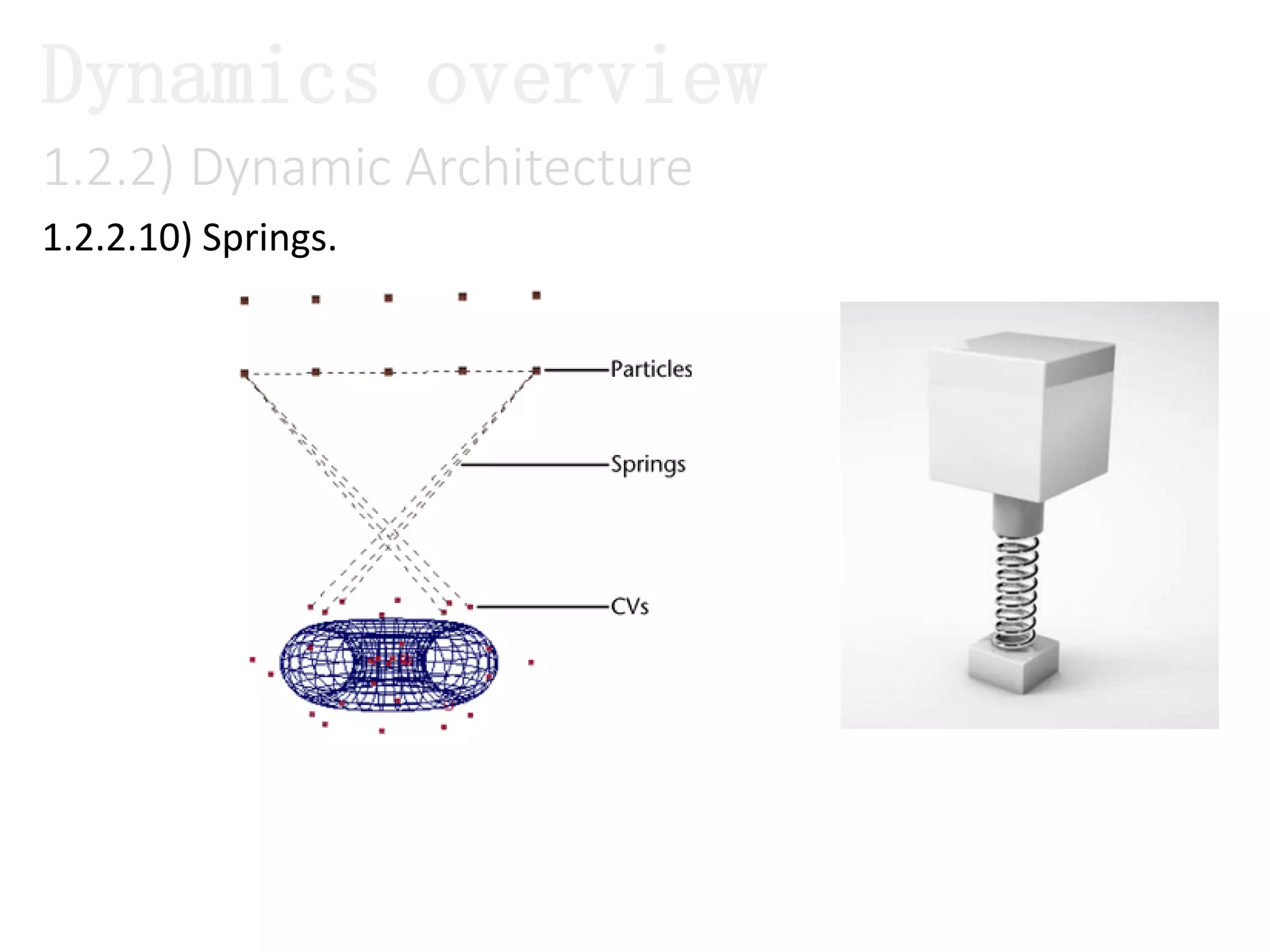
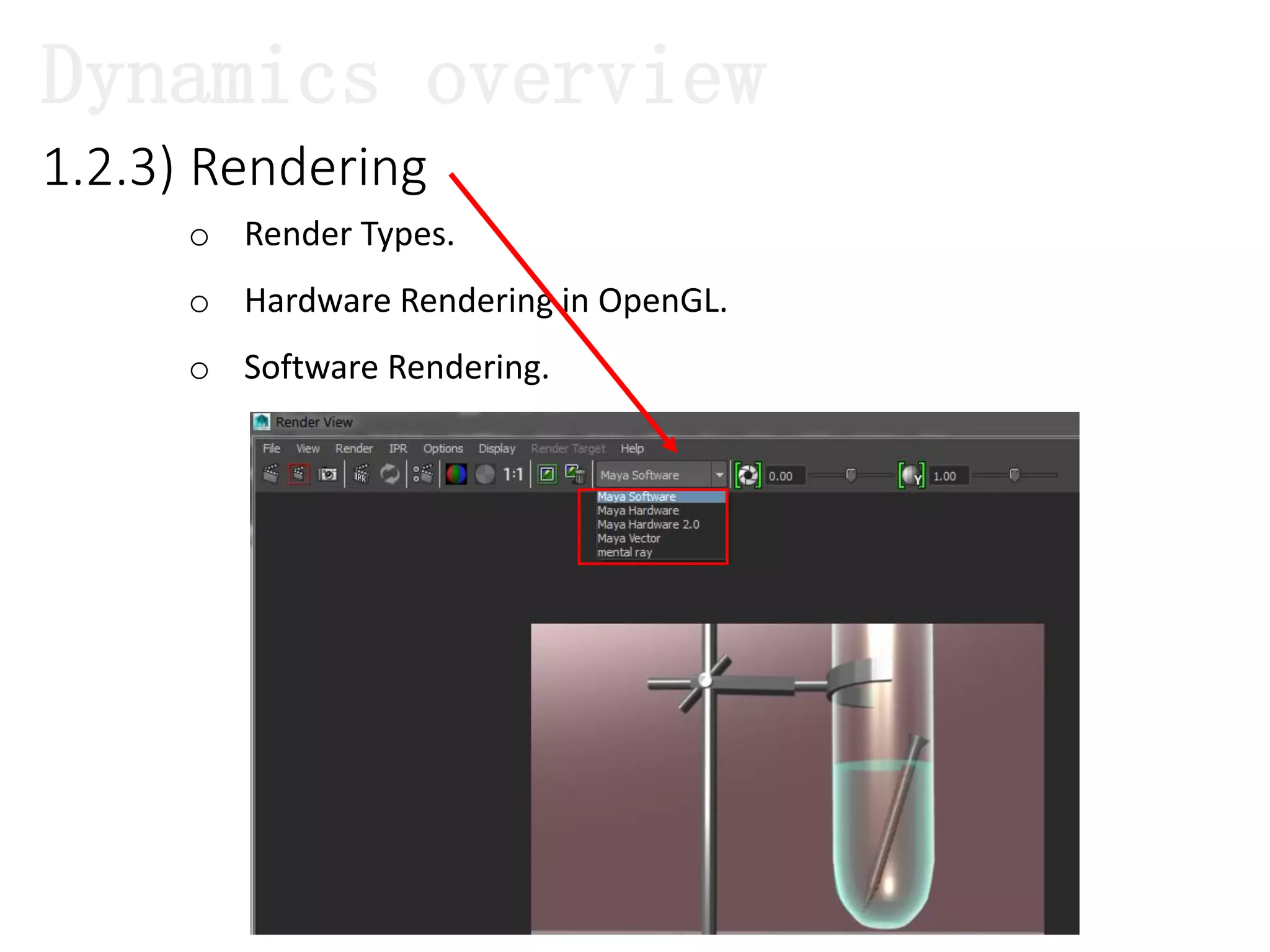
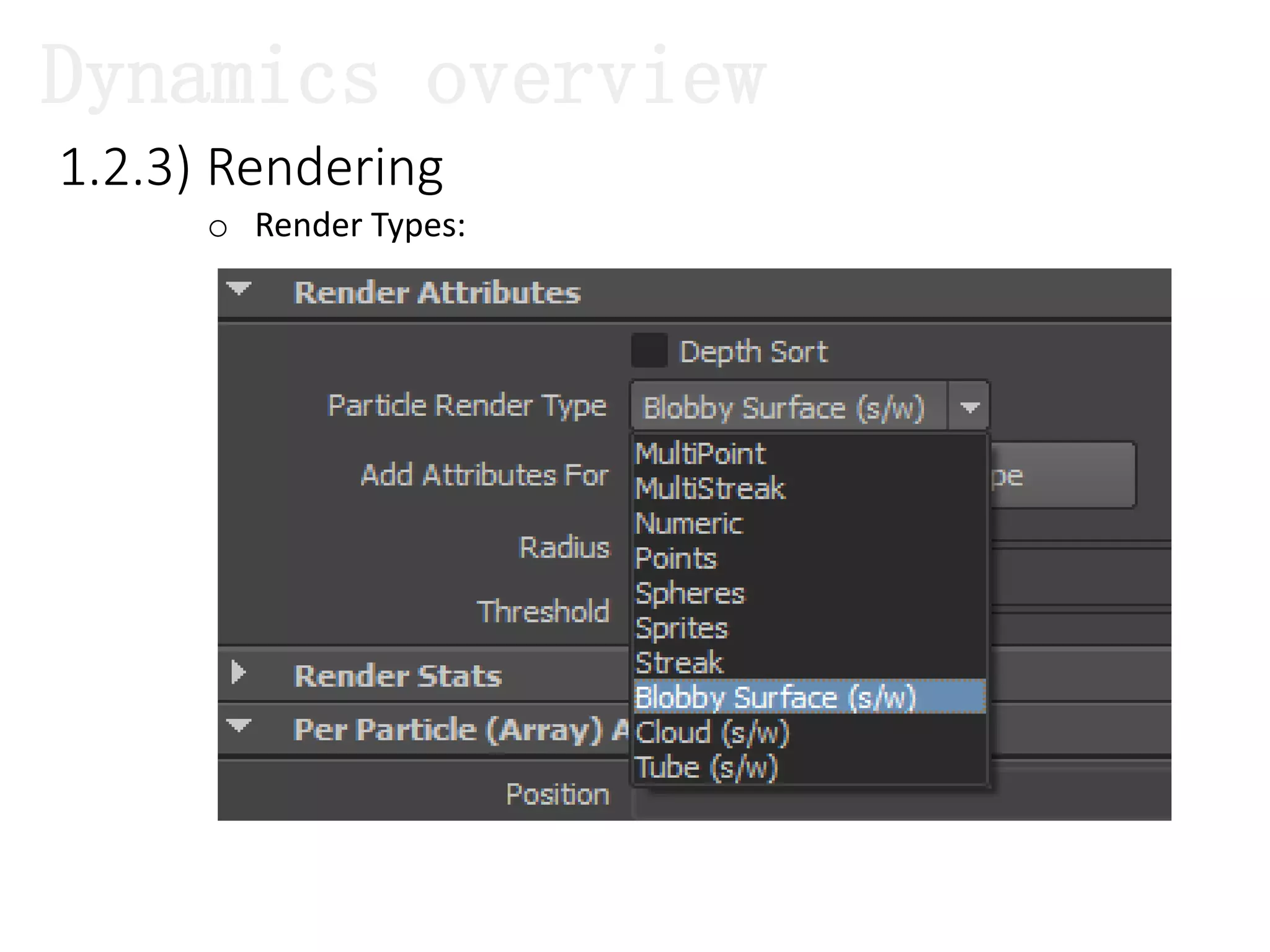
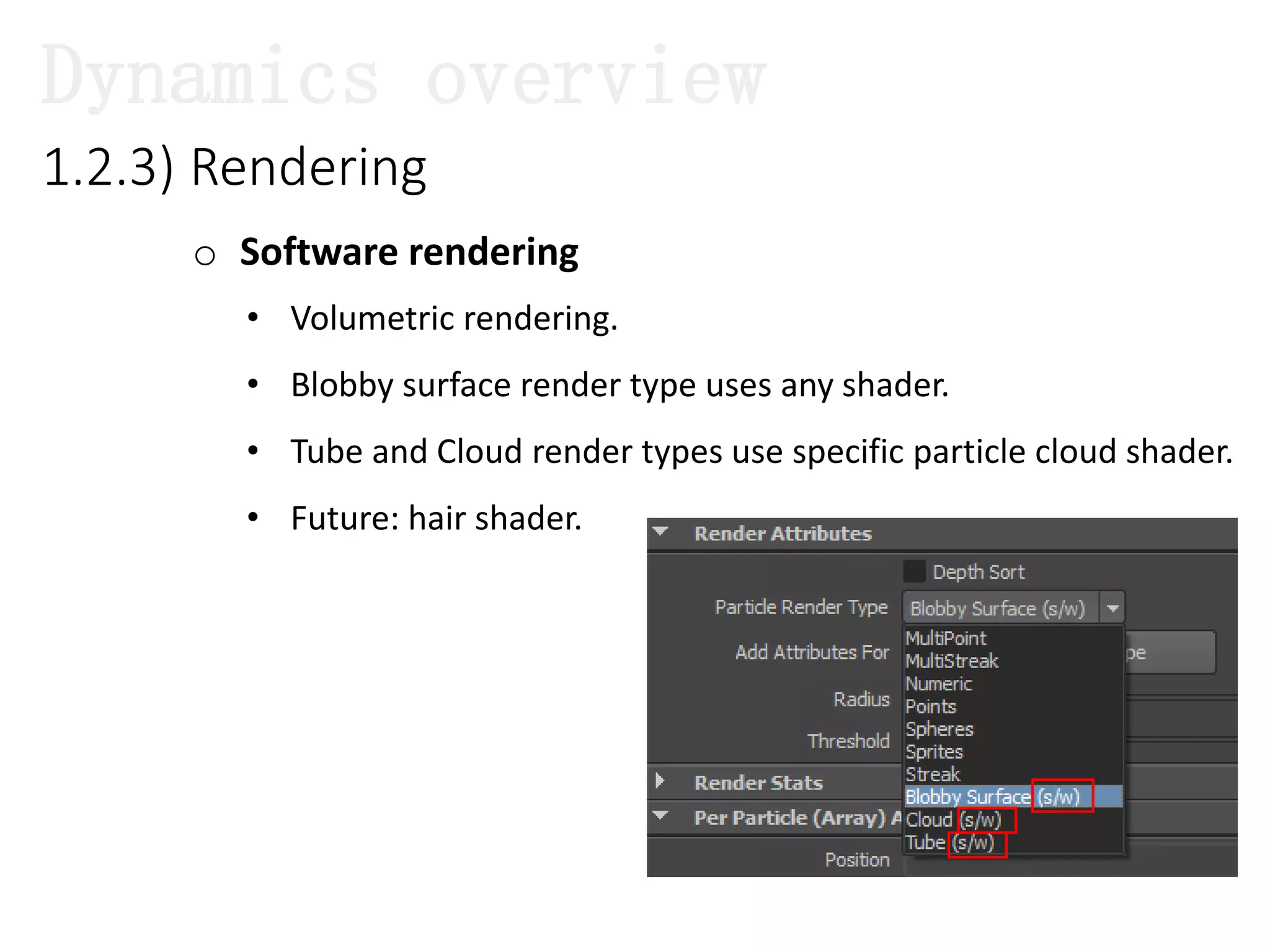
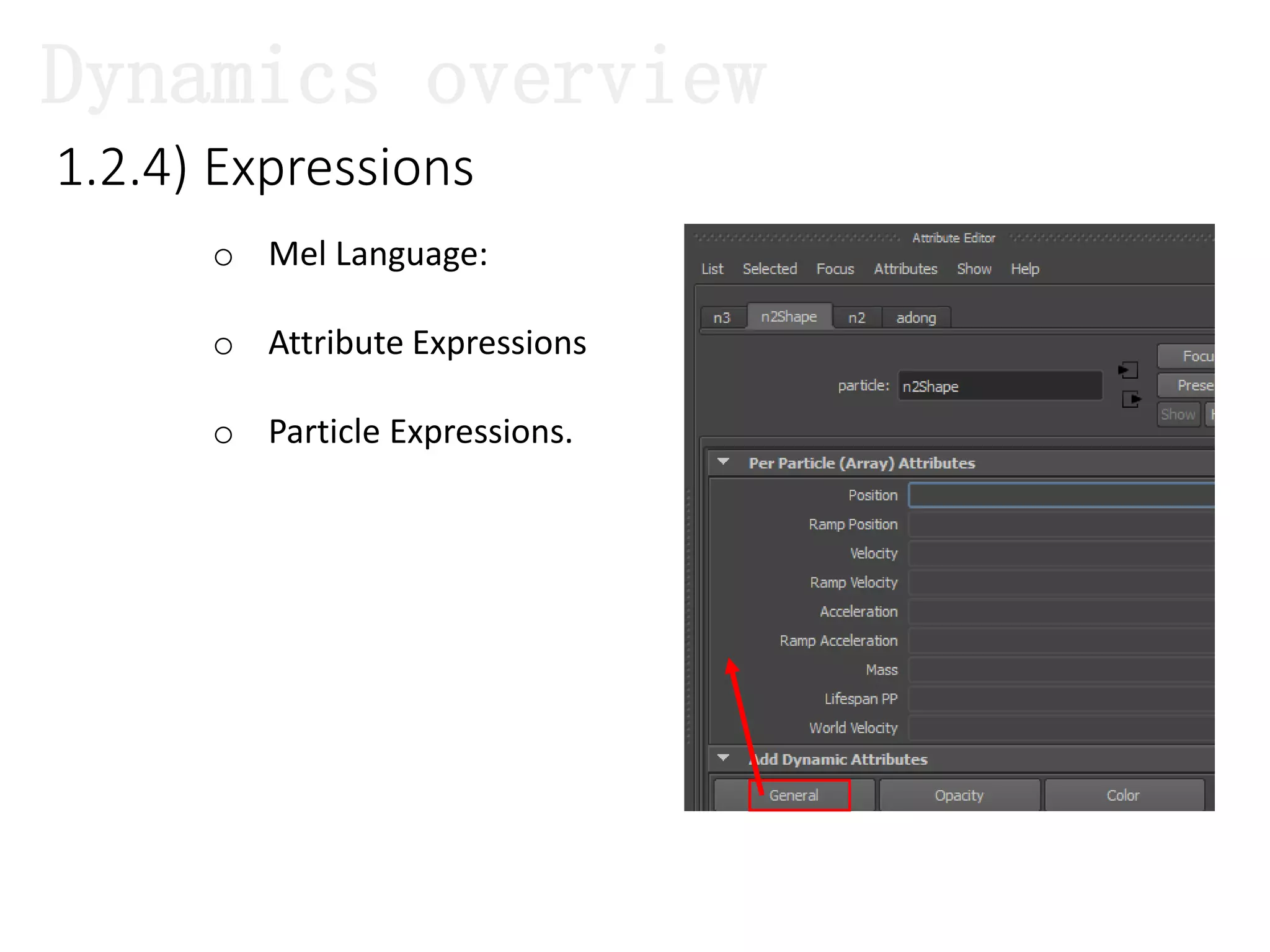
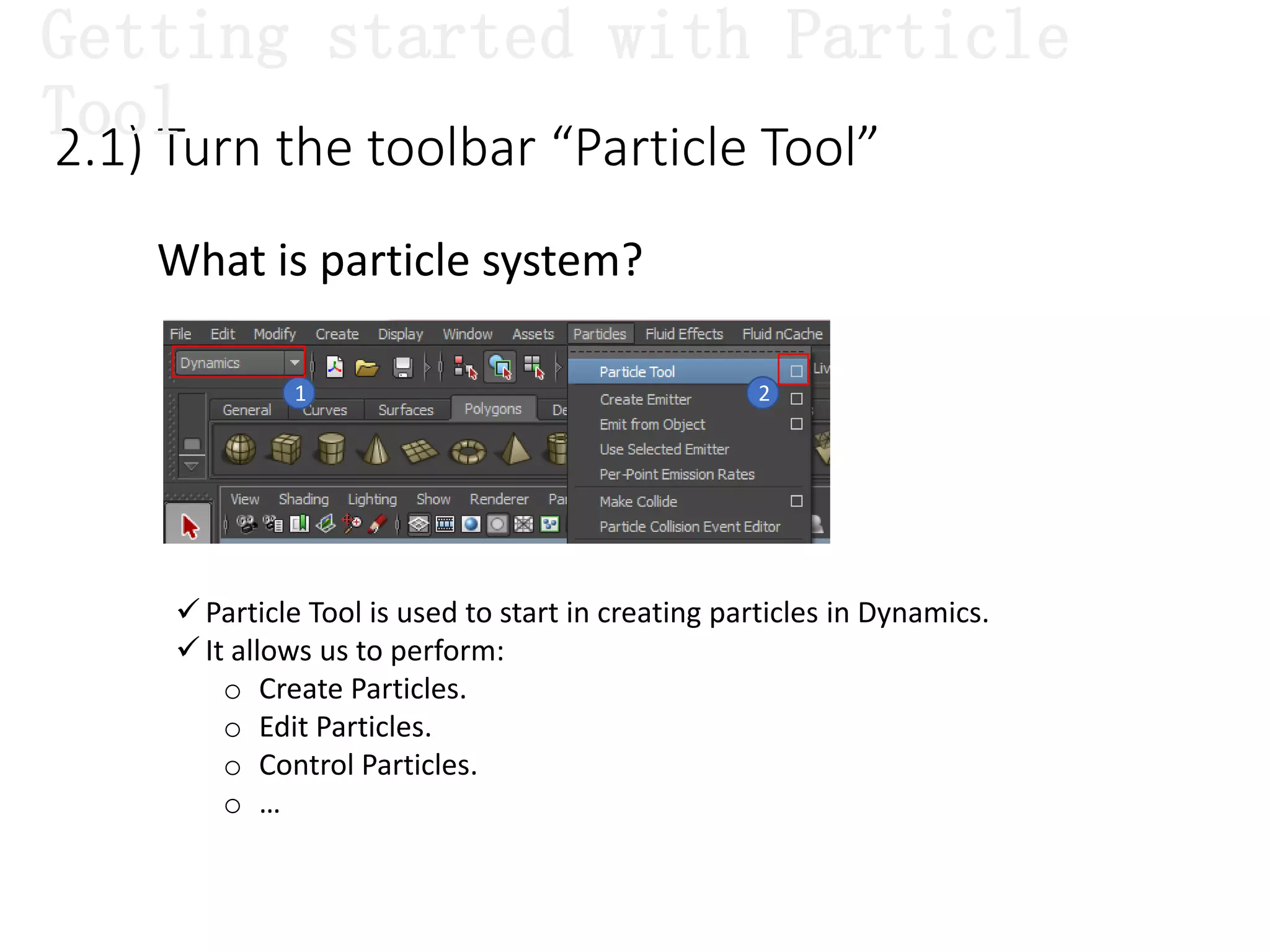
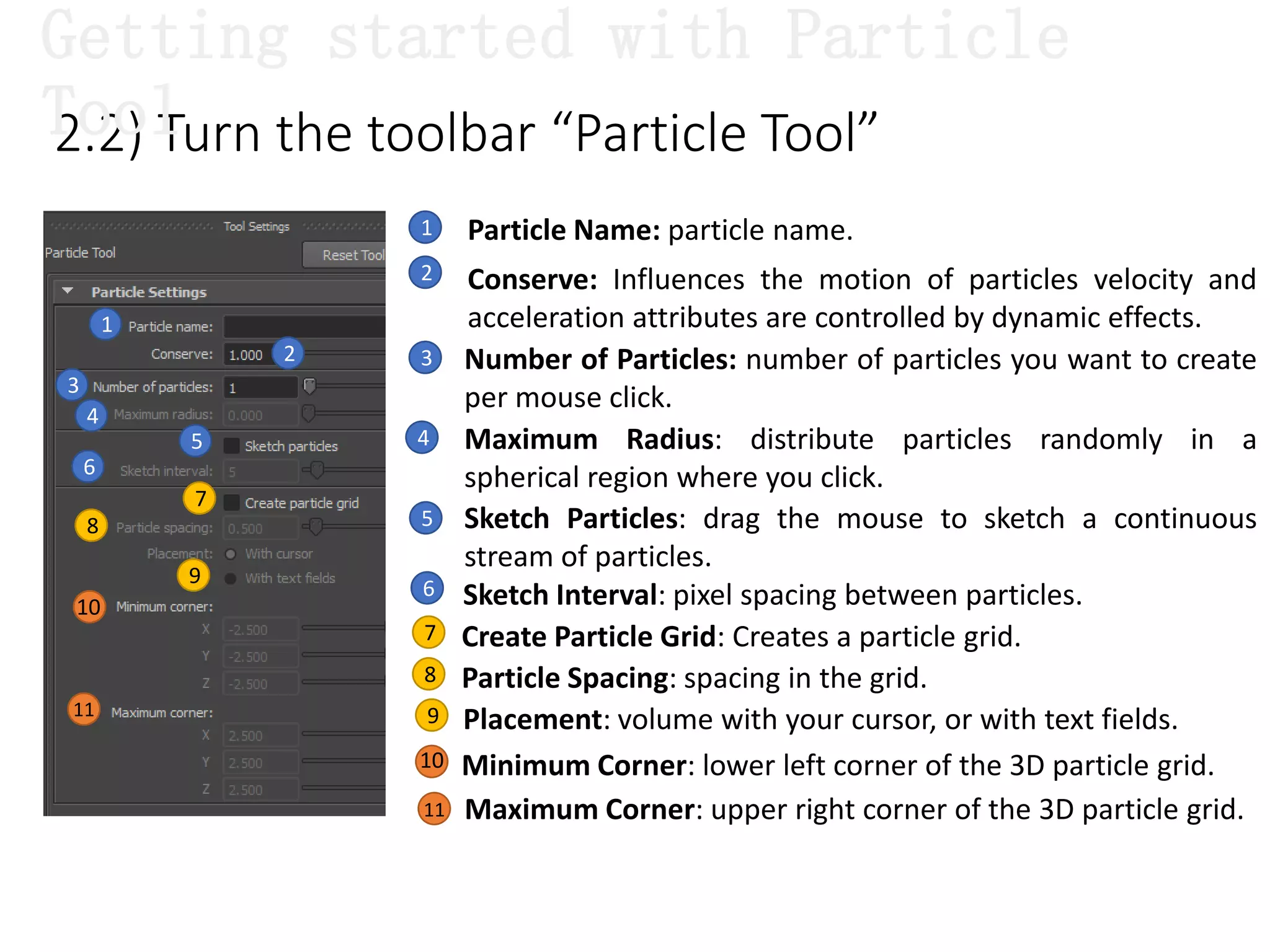
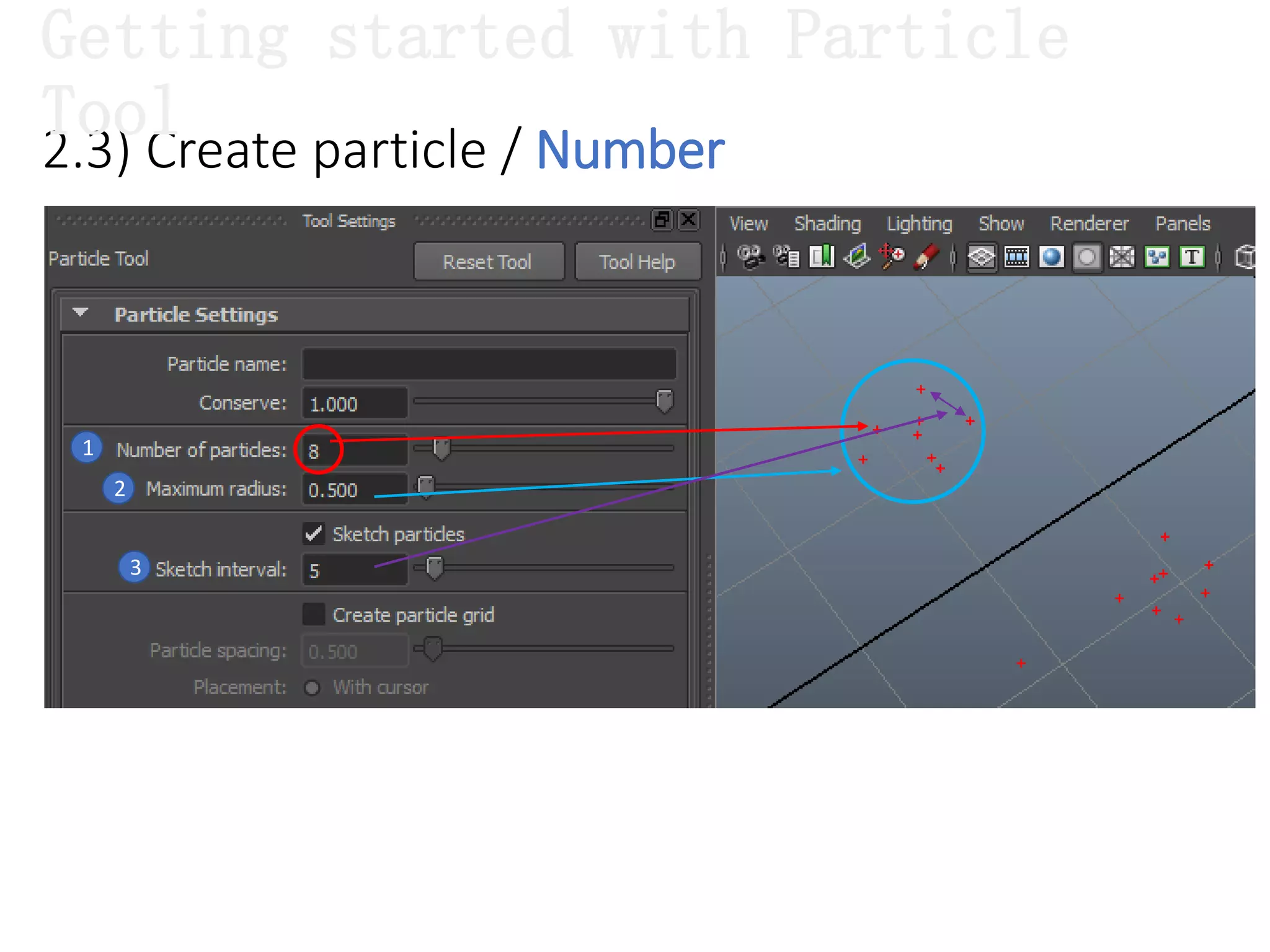
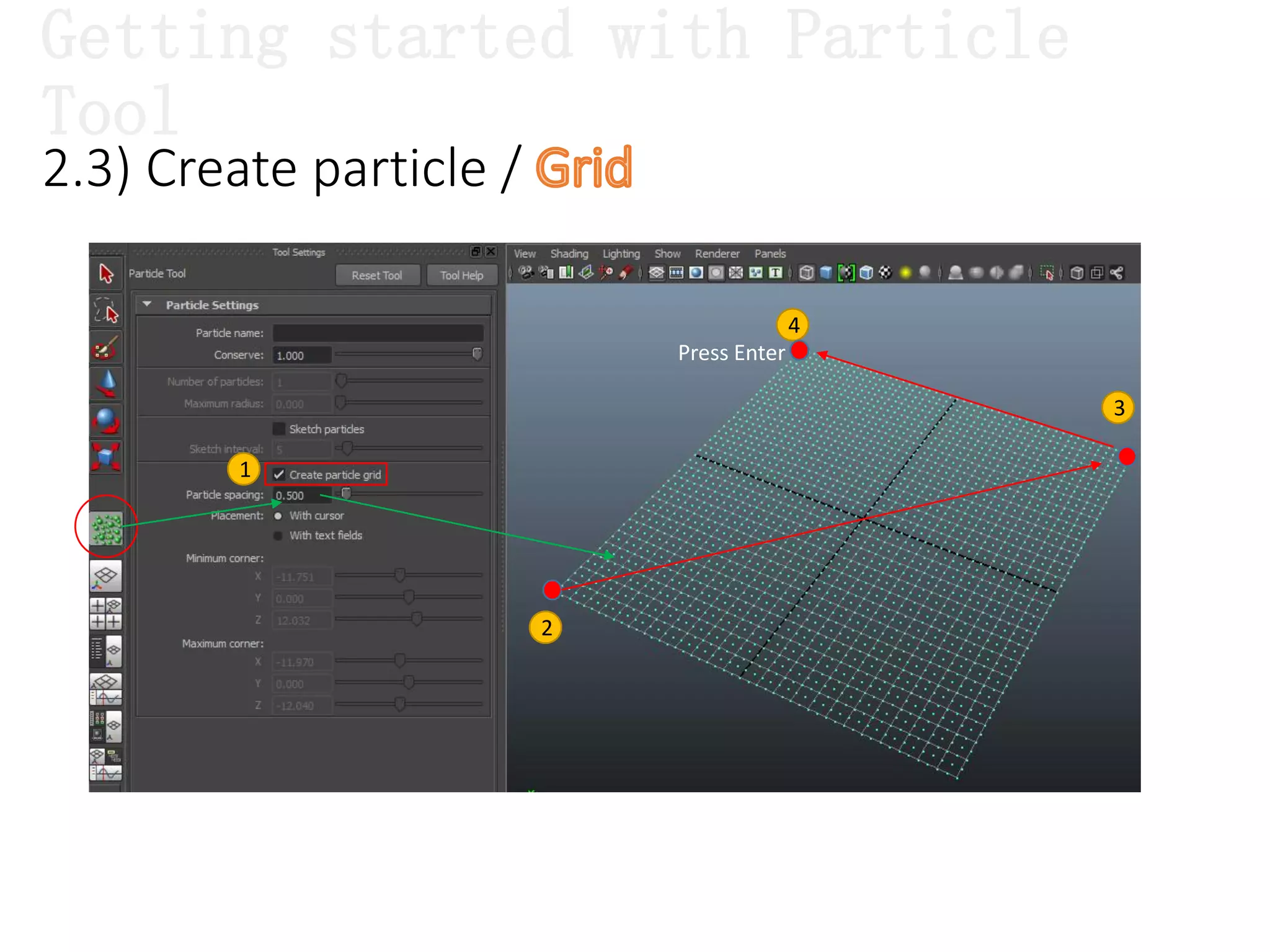
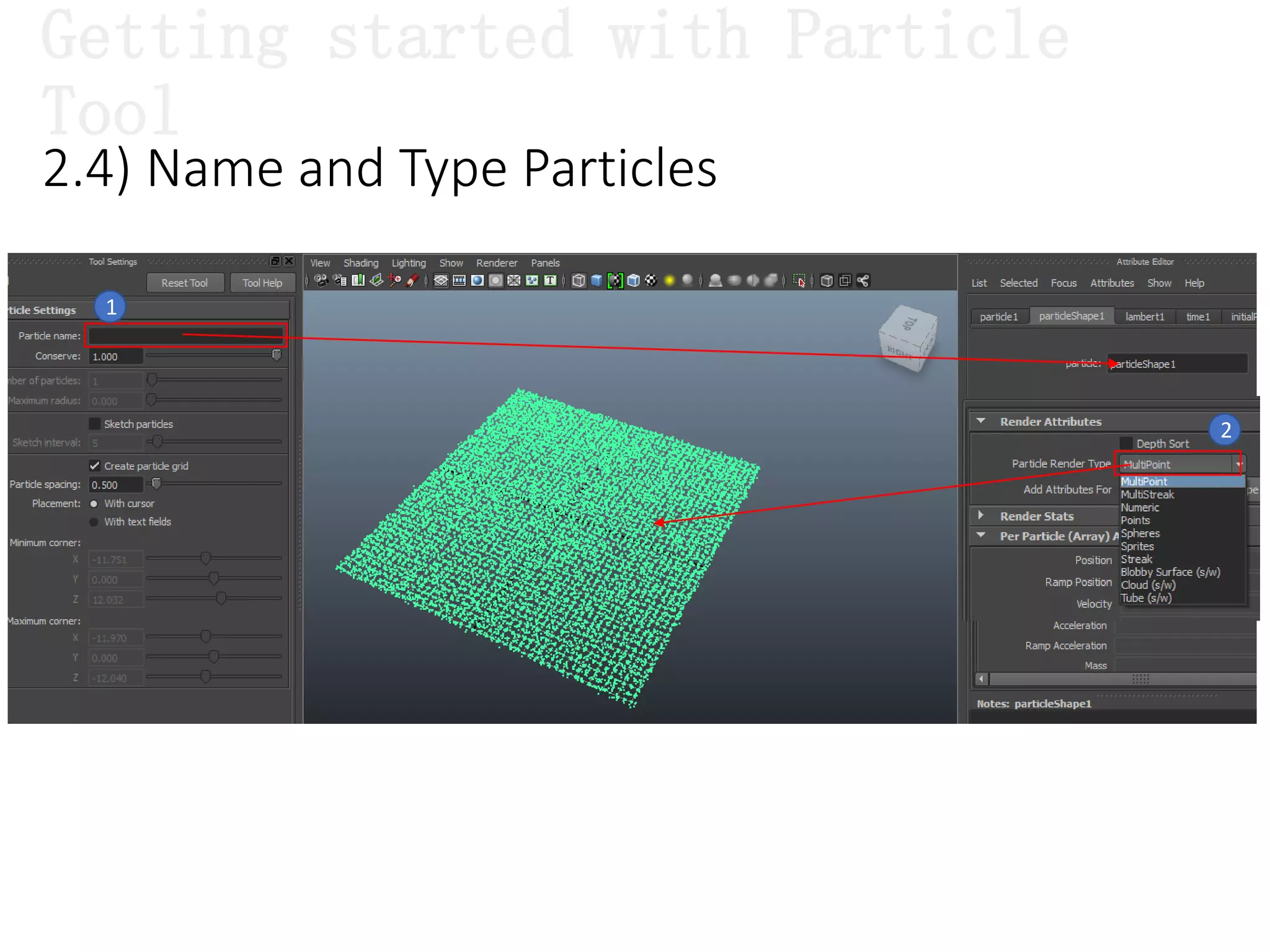
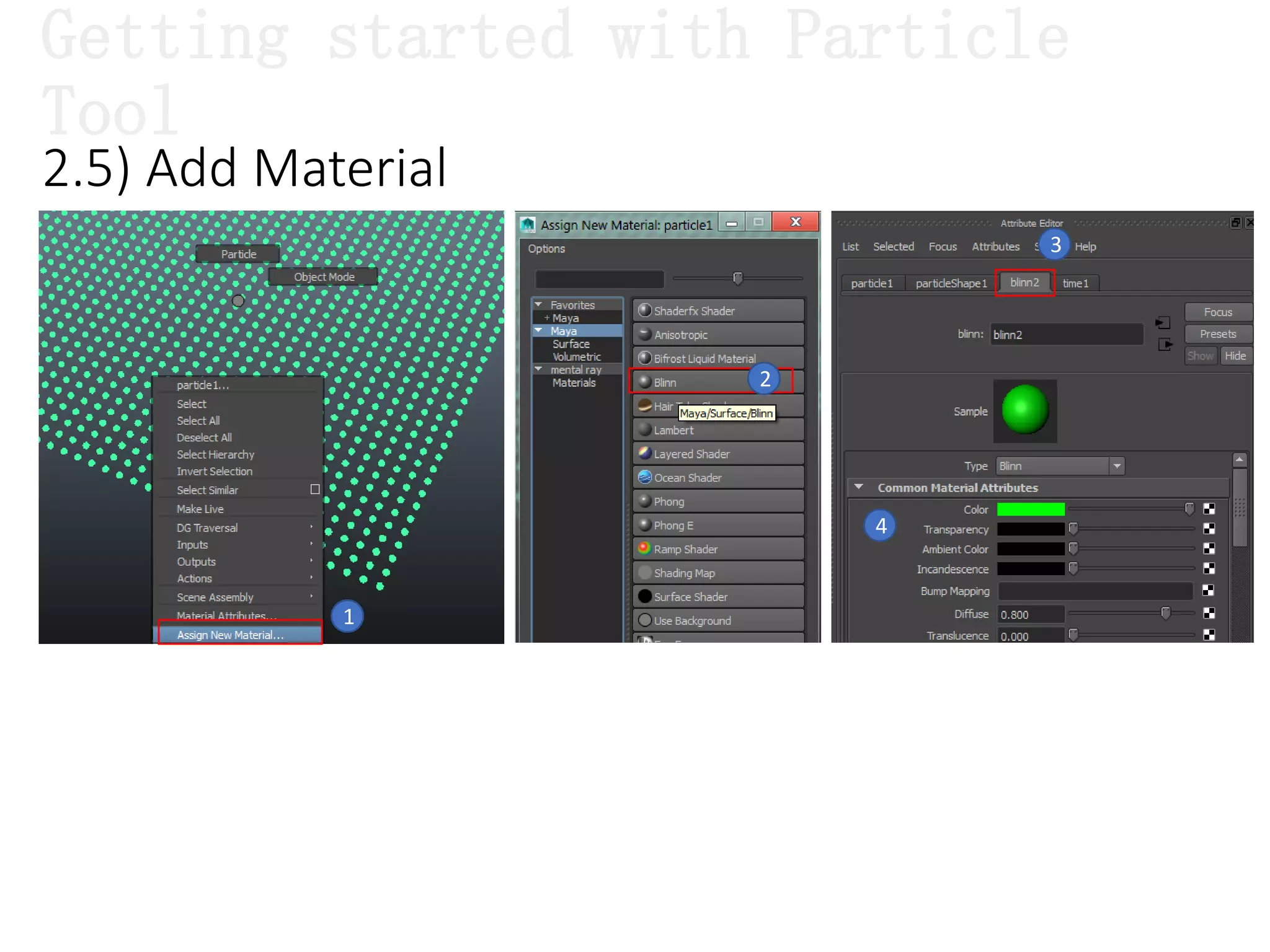
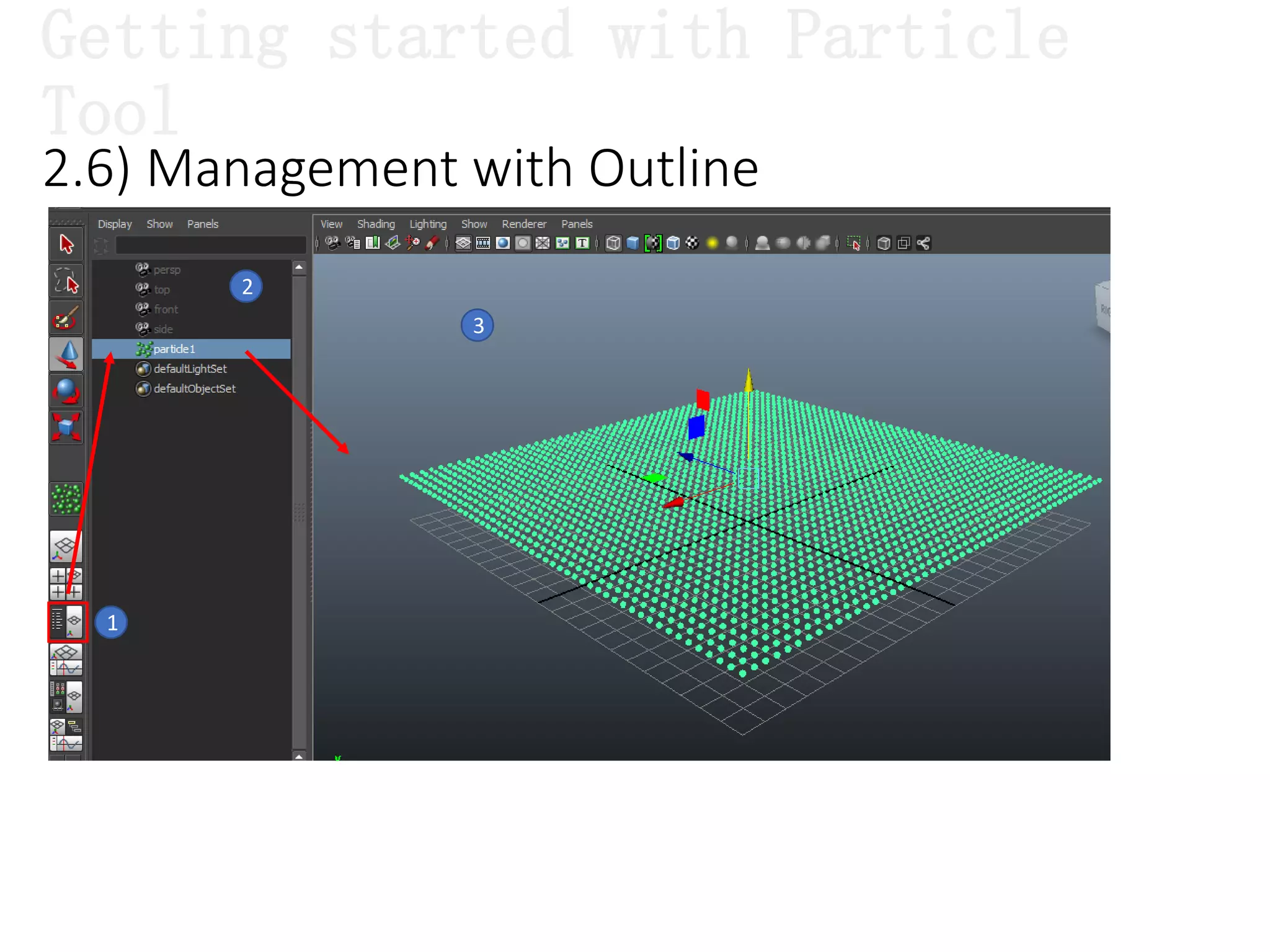
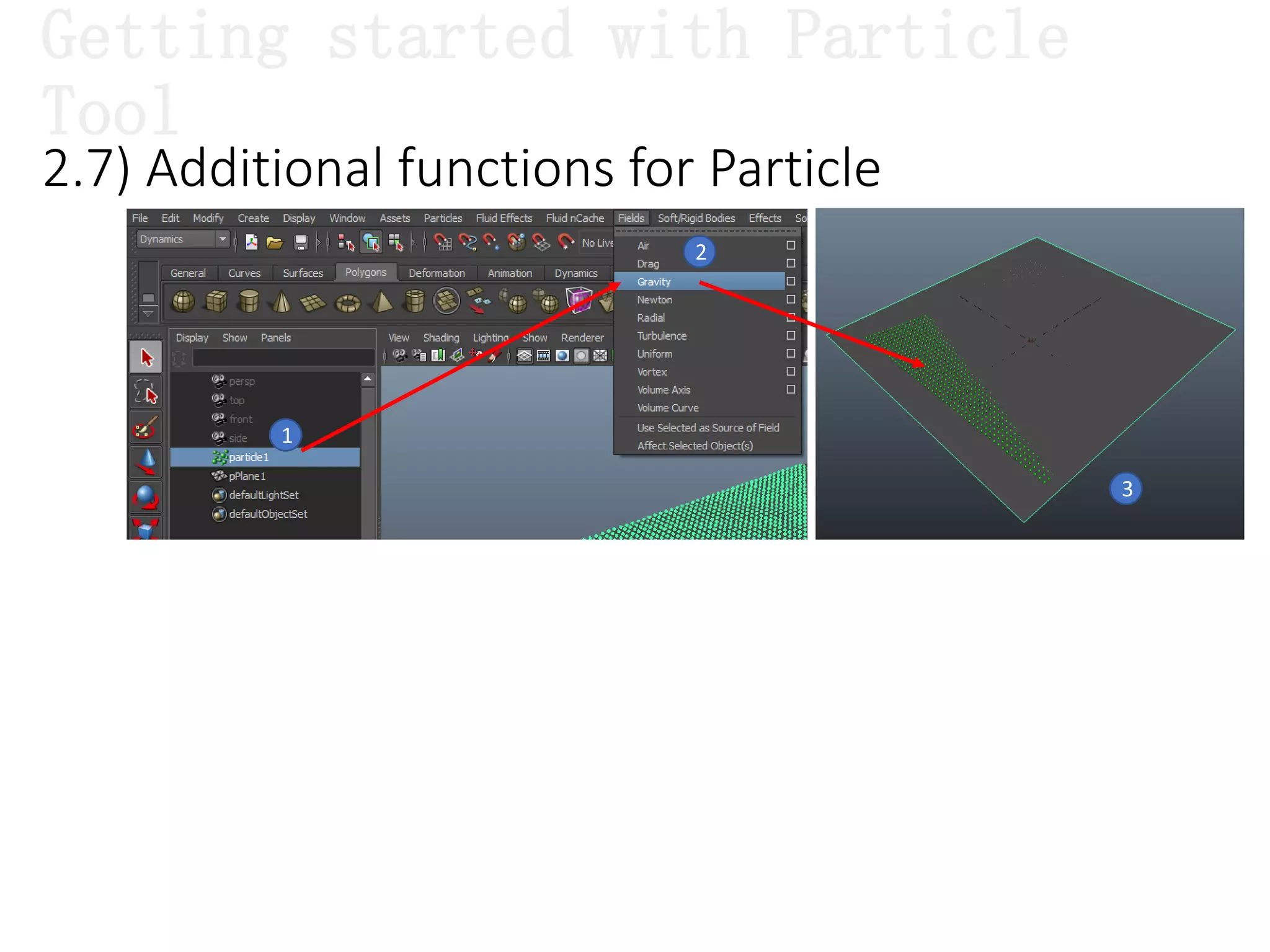
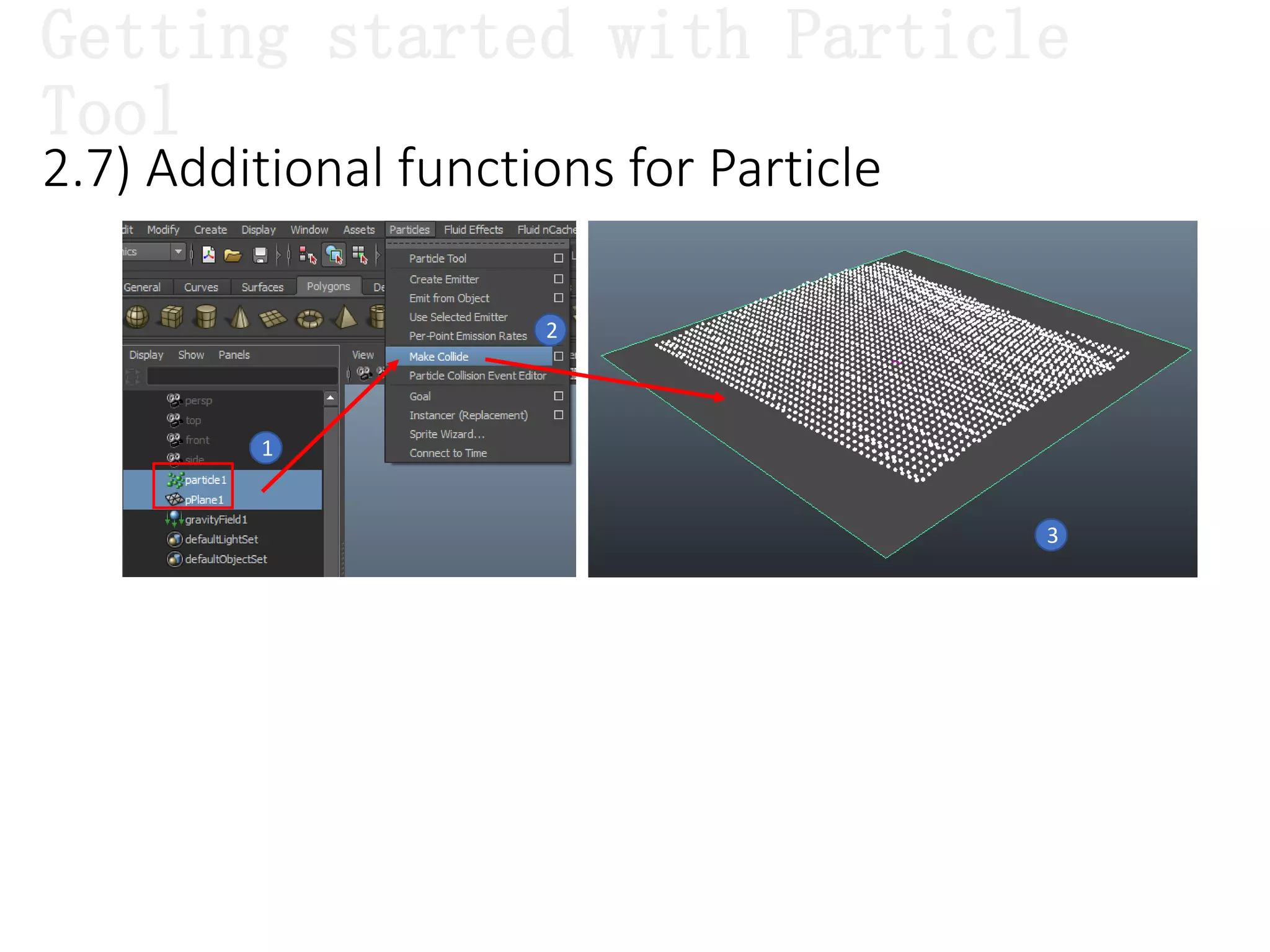
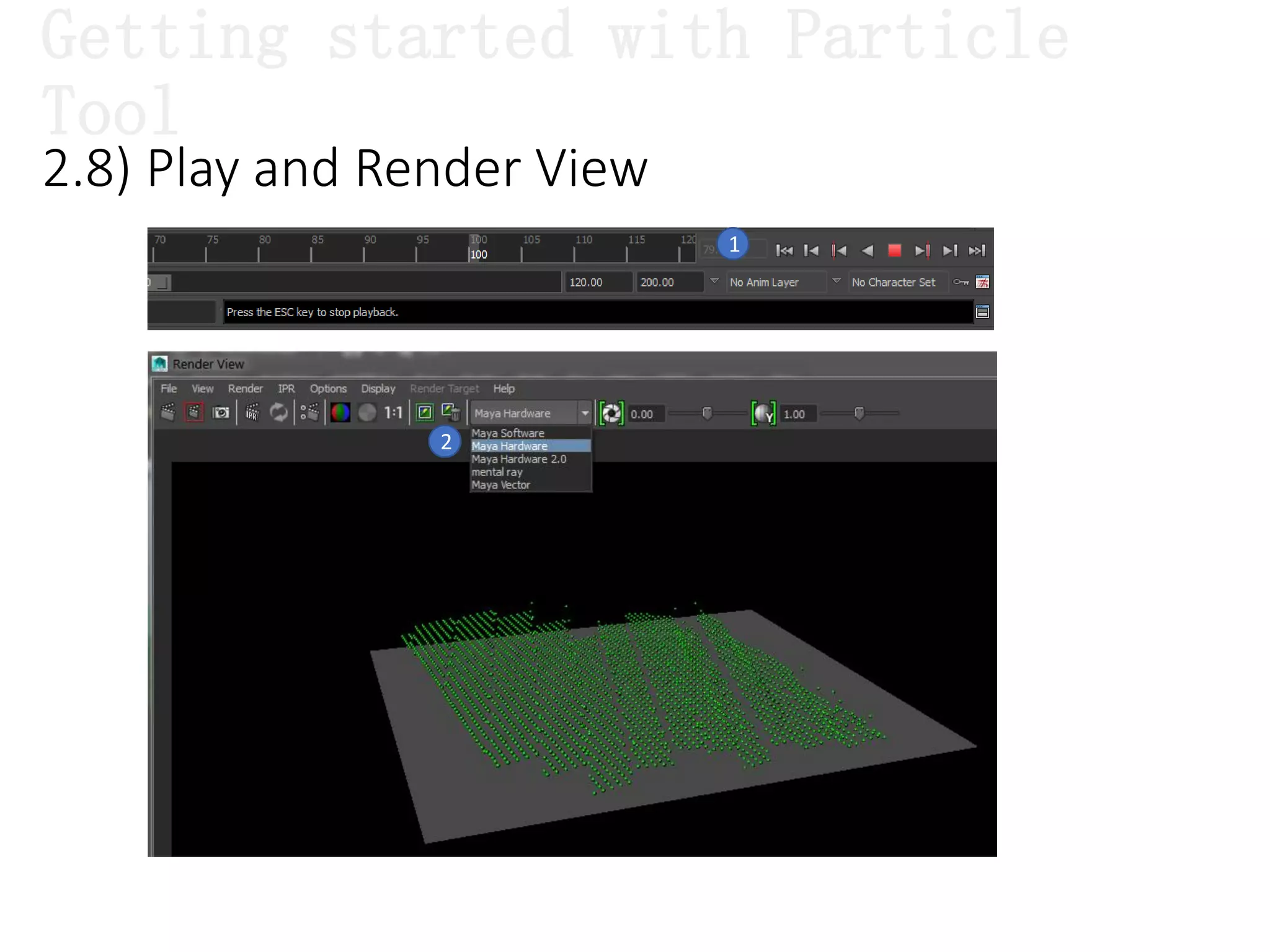
The document introduces Maya Dynamics, focusing on its architecture, features, and applications in creating dynamic animations using particles, soft bodies, and rigid bodies. It outlines how to utilize the particle tool for creating, managing, and rendering particles, as well as the principles of dynamics, including collisions and forces. Key sessions are highlighted, detailing what will be covered in the learning process, from basic particle mechanics to advanced fluid effects.