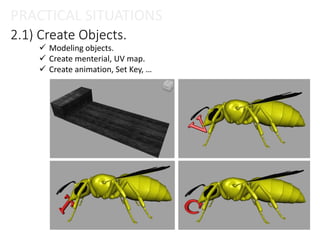
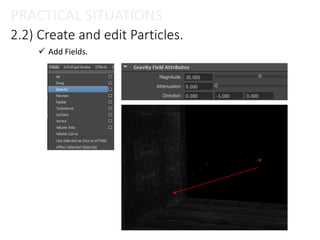
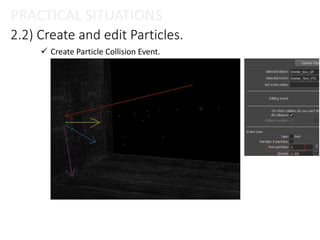
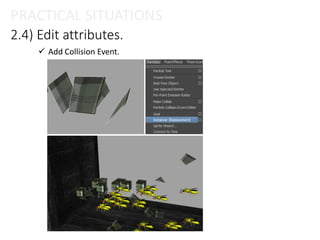
The document provides an overview of the Particle Instancer, a tool in Maya Dynamics for creating instances of geometry controlled by particles. It explains the concepts of instancing and particle instancing, along with practical applications and steps to create a Particle Instancer. Additionally, it includes practical situations and an exercise involving flying lanterns.