1) Service quality is determined by customers' perceptions of consistency between expectations and actual experiences. Meeting 99.9% of expectations still allows for issues like unsafe drinking water or incorrect medical prescriptions.
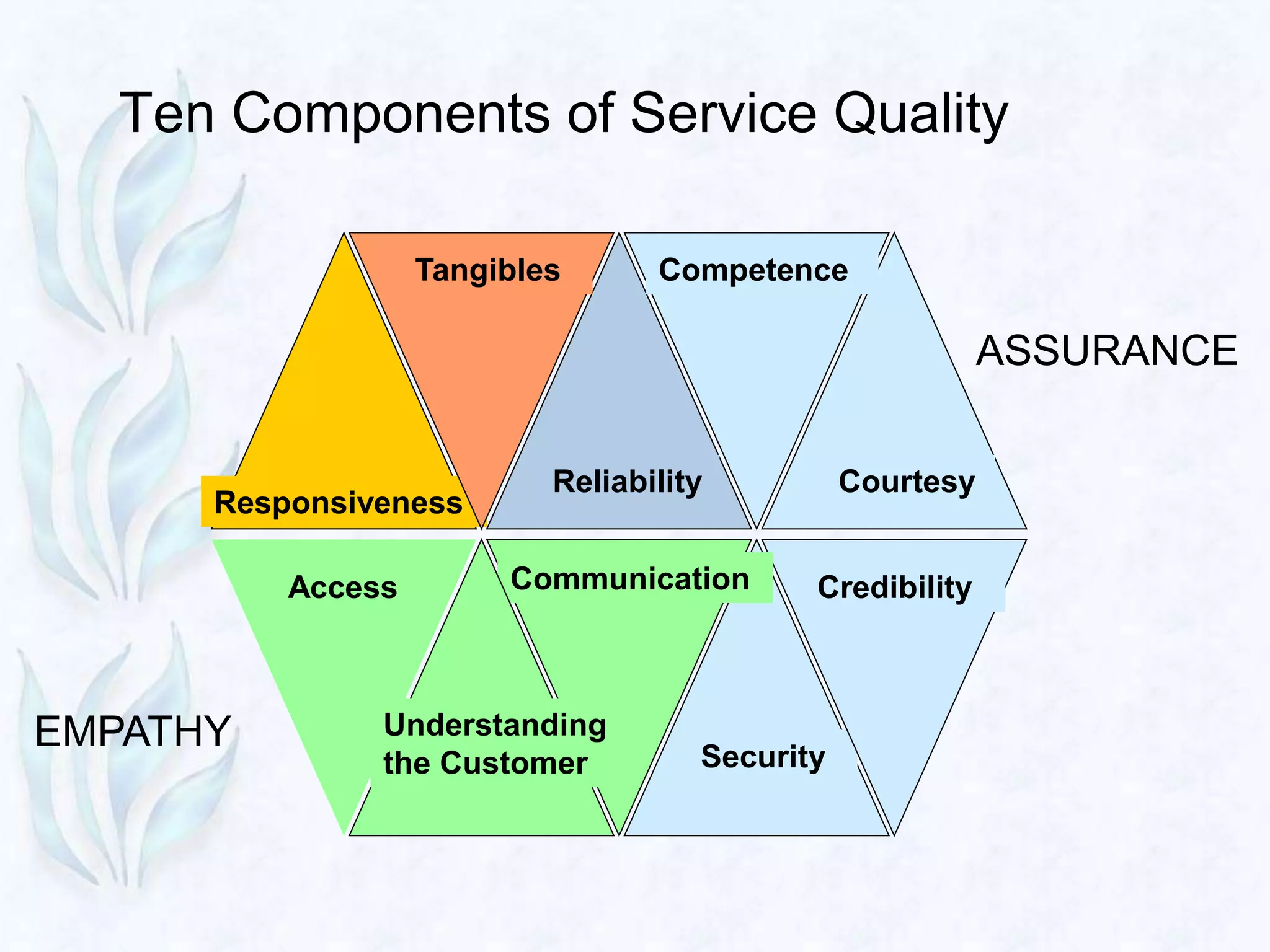
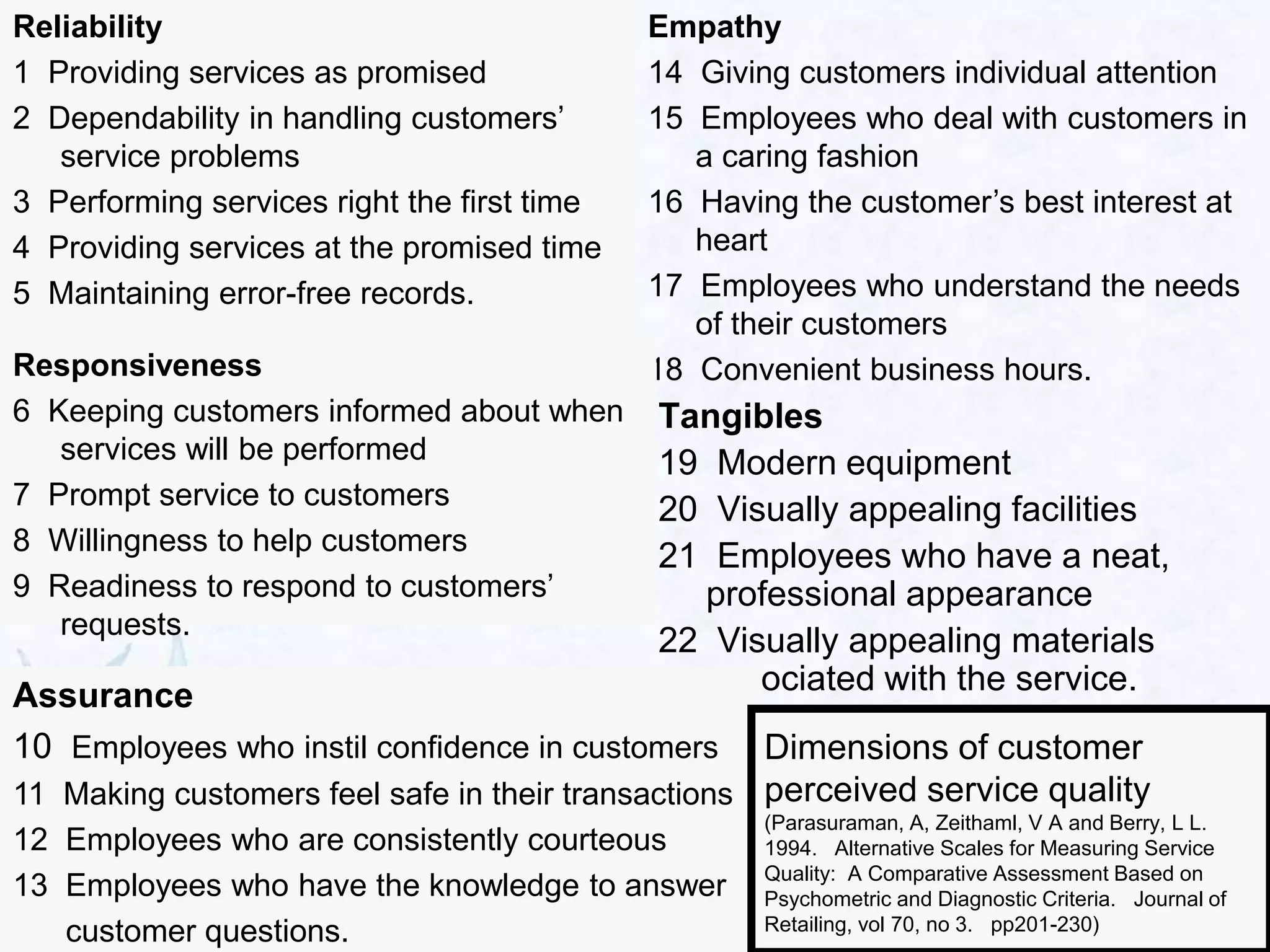
2) There are 10 components of service quality including reliability, responsiveness, empathy, and assurance. Gaps can occur when a company's perceptions do not match customer expectations, in service design/standards, and delivery.
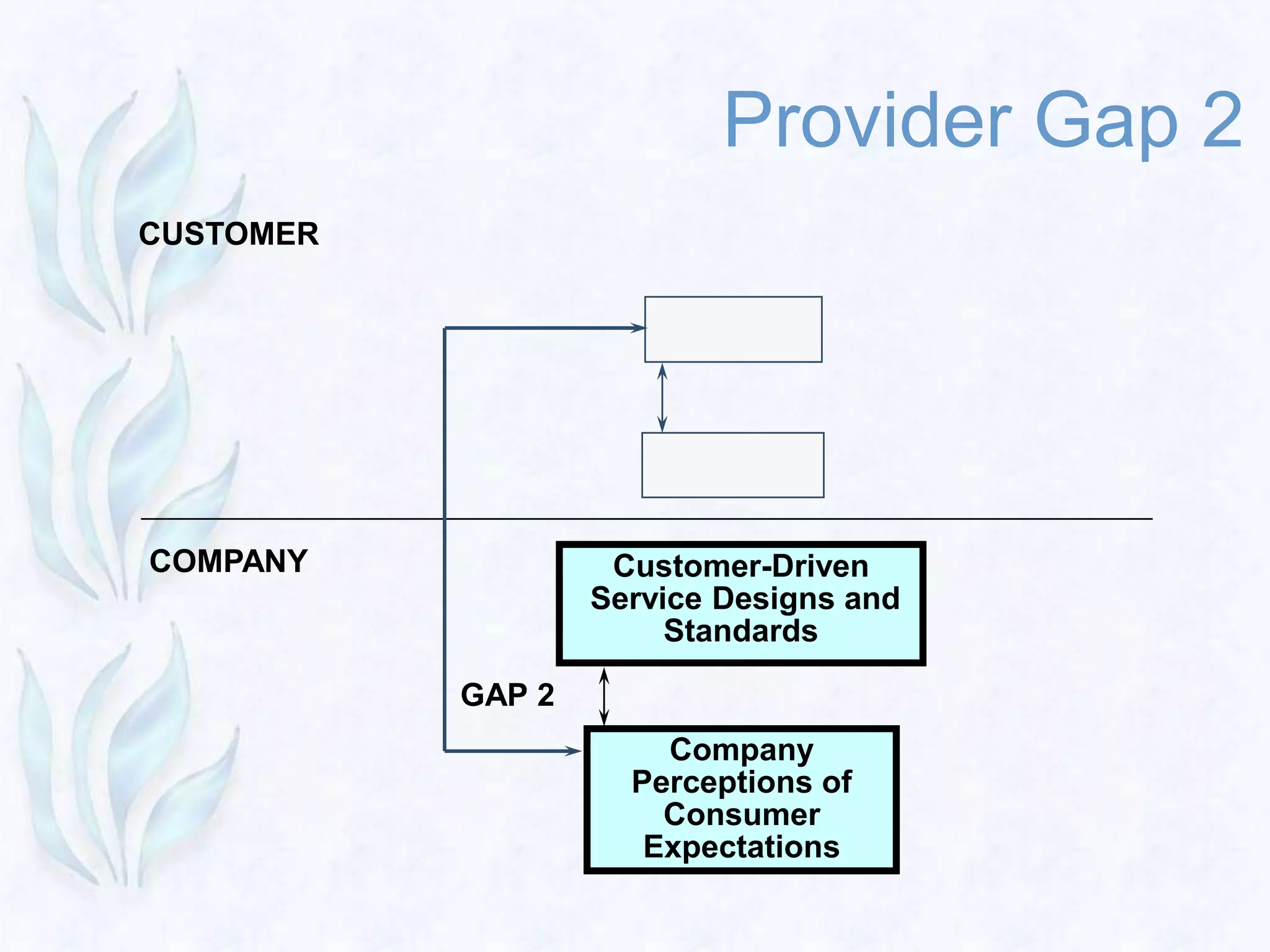
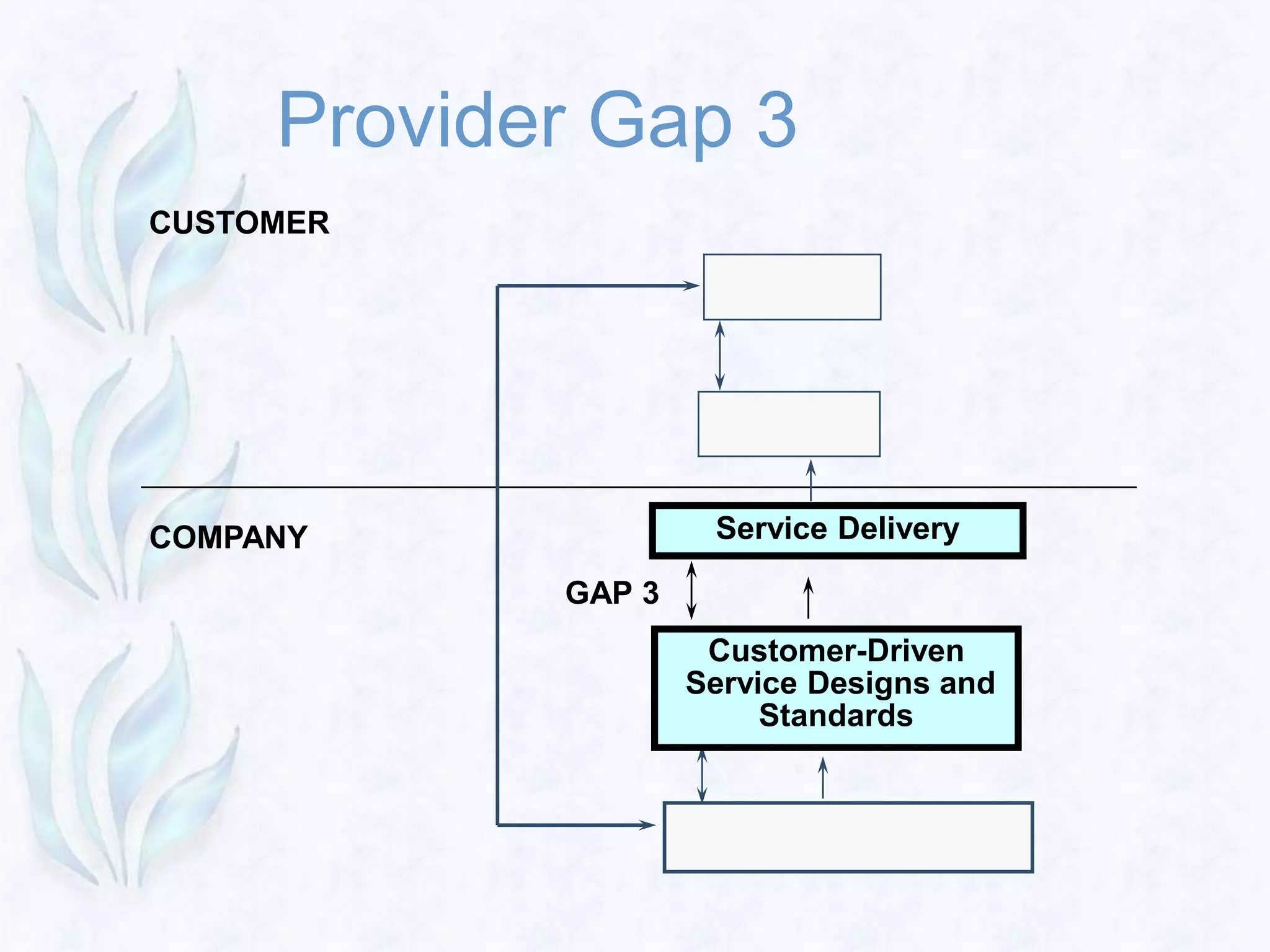
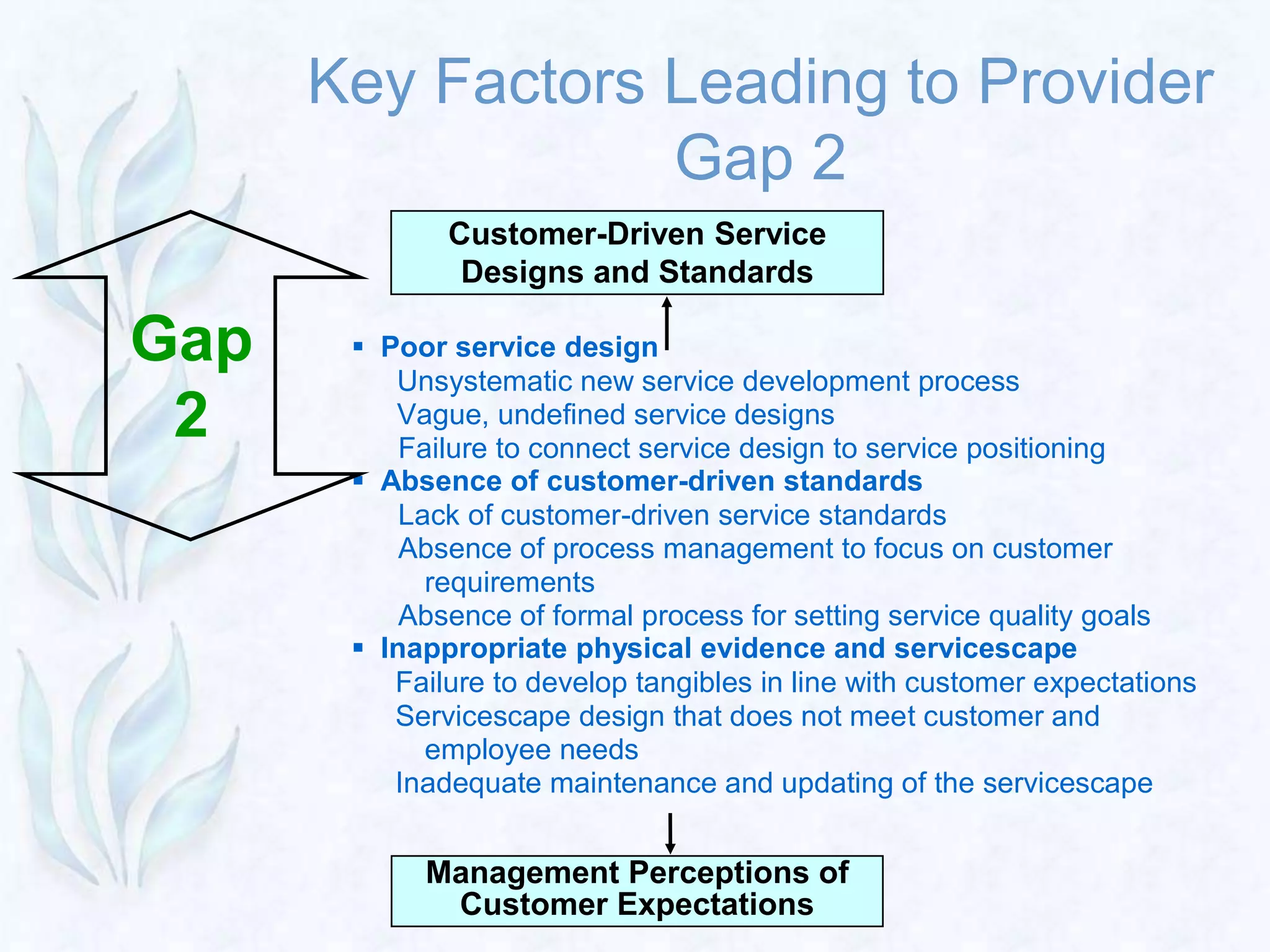
3) The Gaps Model identifies four provider gaps that can lead to the key customer gap between expected and perceived service quality. Addressing these gaps through better marketing research, service design, employee training, and communication can improve a company's service quality.