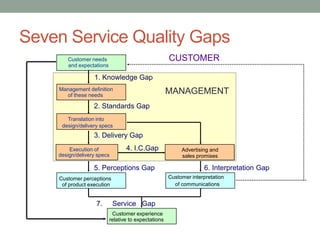
This document discusses models of service quality including five dimensions of service quality: reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, and tangibles. It describes seven service quality gaps that can occur between customer expectations and the services delivered. It provides prescriptions for closing these gaps such as learning customer expectations and ensuring service performance matches quality standards. The document also discusses hard and soft measures of service quality, return on quality, productivity in a service context, and measuring service productivity focusing on outcomes rather than just outputs.