This document provides an overview of managing customer expectations. It discusses:
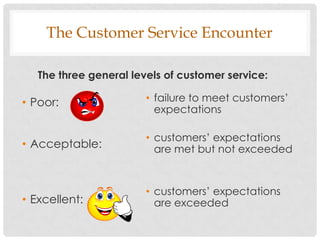
1) Identifying customer expectations, which are their vision of future service and can change over time based on experiences. Customers generally expect competent, efficient service; anticipation of their needs; and explanations in terms they understand.
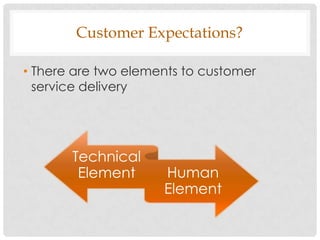
2) There are two key elements to meeting expectations - the technical element of the product/service working properly, and the human element of how customers feel they are treated during the process.
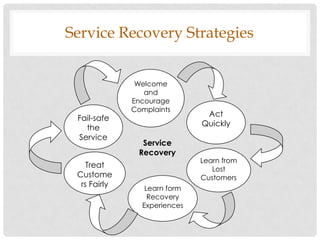
3) Managing expectations at different stages - learn expectations prior to purchase, communicate expectations during service, and follow-up after to ensure expectations were met. Influencing expectations involves establishing trust and communicating the benefits of realistic expectations.