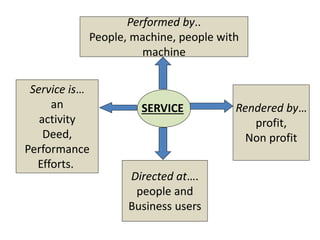
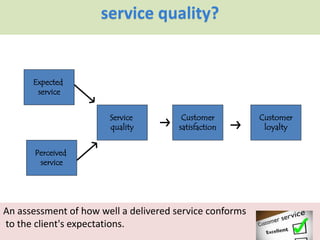
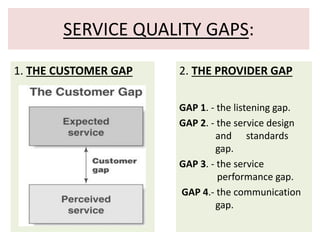
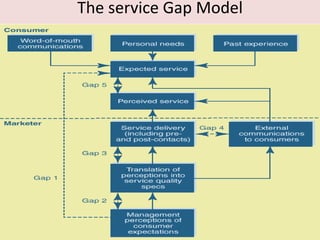
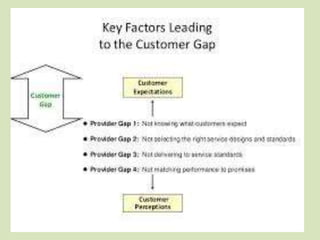
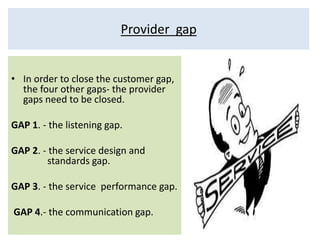
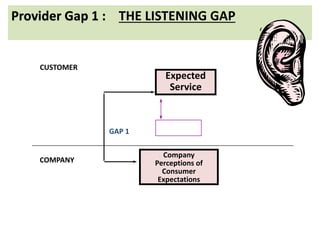
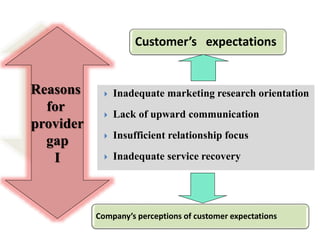
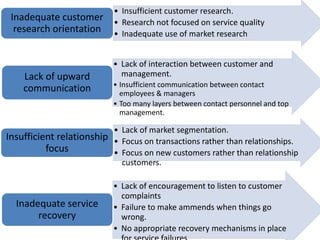
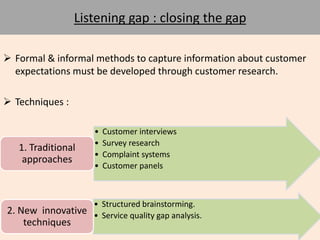
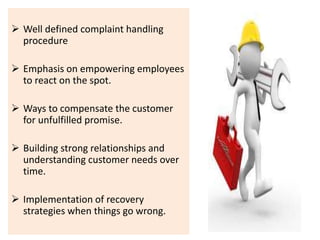
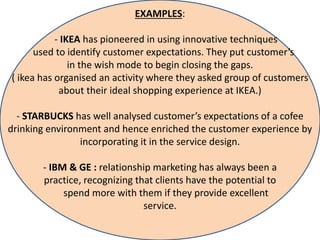
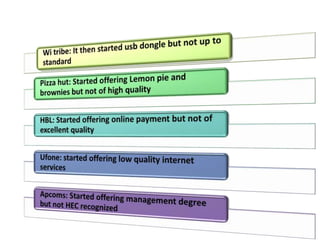
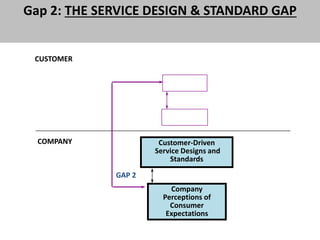
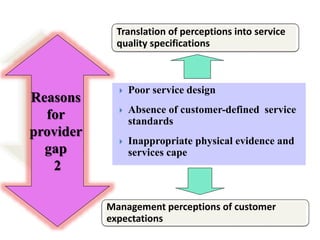
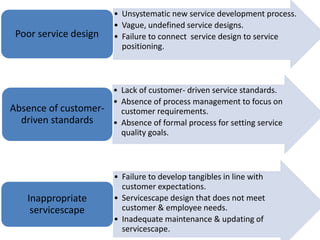
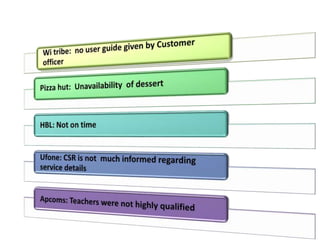
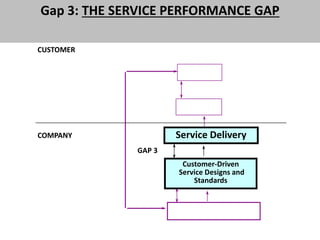
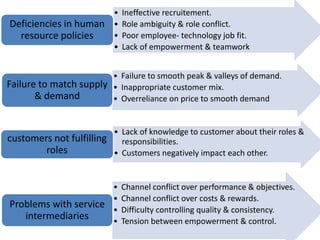
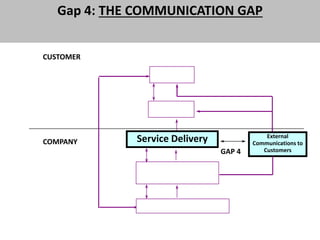
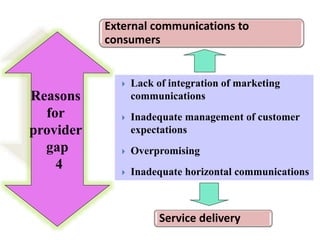
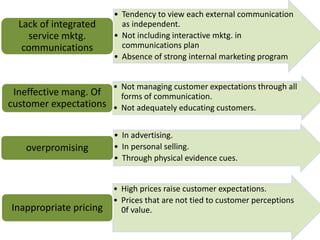
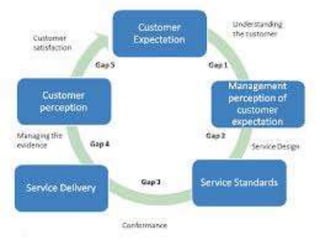
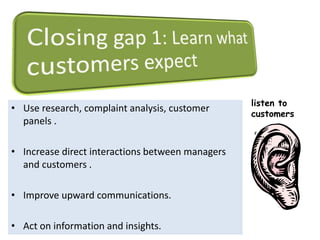
The document discusses the Service Quality Gaps Model, which identifies four key gaps between a customer's expectations of service and a provider's actual service performance. The four gaps are: 1) differences between customer expectations and management perceptions, 2) differences between management perceptions and service quality specifications, 3) differences between specifications and actual service delivery, and 4) differences between service delivery and external communications to customers. The document also provides examples of how companies like IKEA, Starbucks, IBM and GE work to close these gaps to improve customer satisfaction.