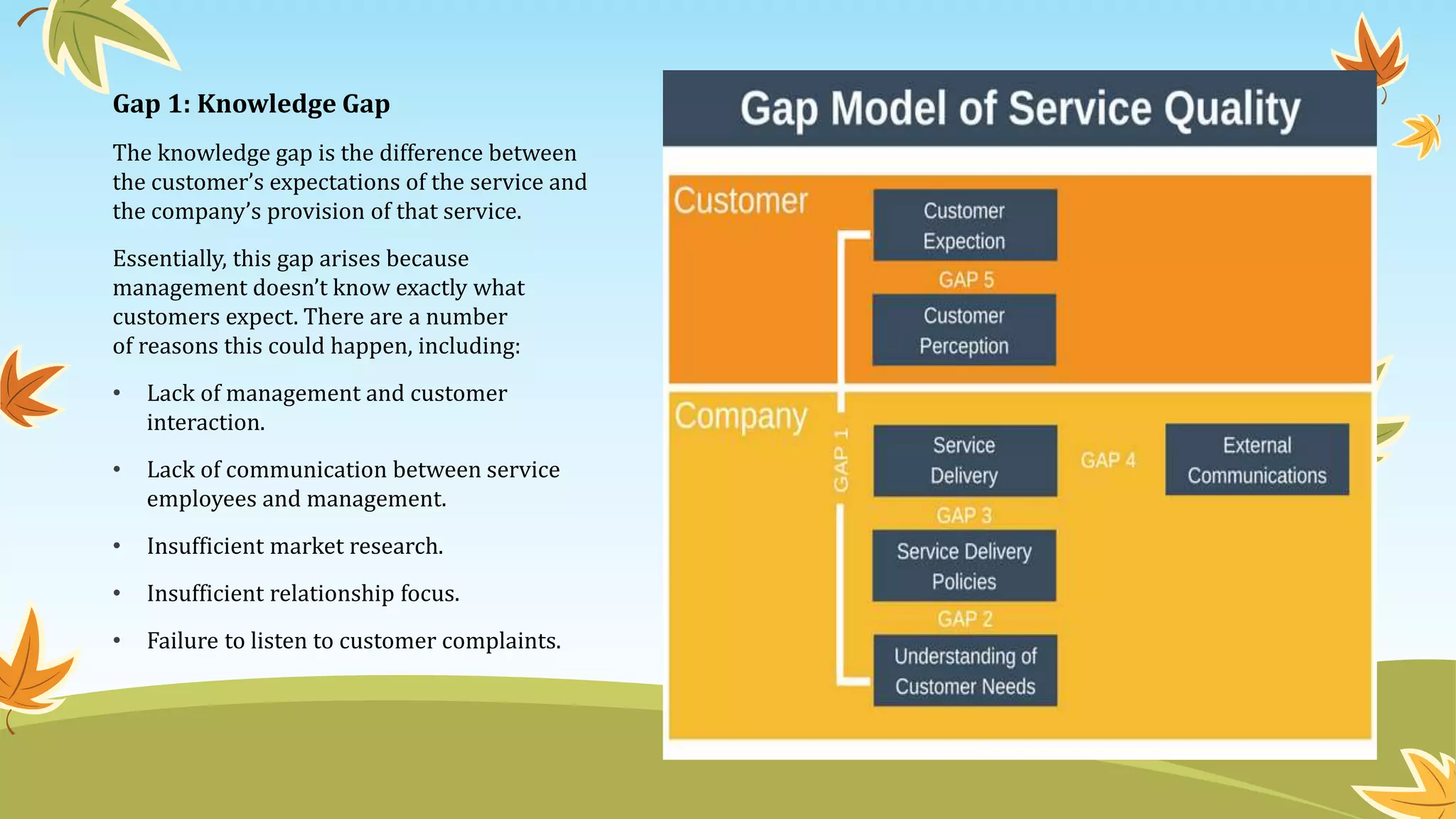
The document discusses service quality management. It defines service quality management as encompassing processes to assess quality according to customer expectations and monitor services. It also discusses measuring the gap between expectations and reality to identify areas for improvement. The benefits of service quality management include implementing systems to monitor quality across touchpoints and receive performance reports to view business from different perspectives. It also discusses the five dimensions of service quality - tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. Finally, it presents the gap model of service quality, which identifies five gaps between customer expectations and perceptions: the knowledge gap, policy gap, delivery gap, communication gap, and customer gap.