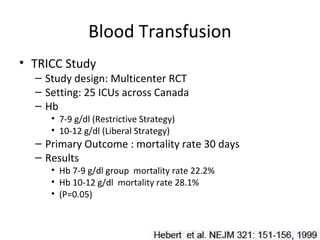
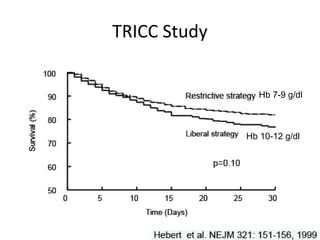
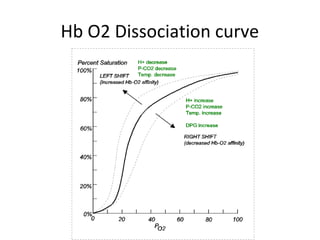
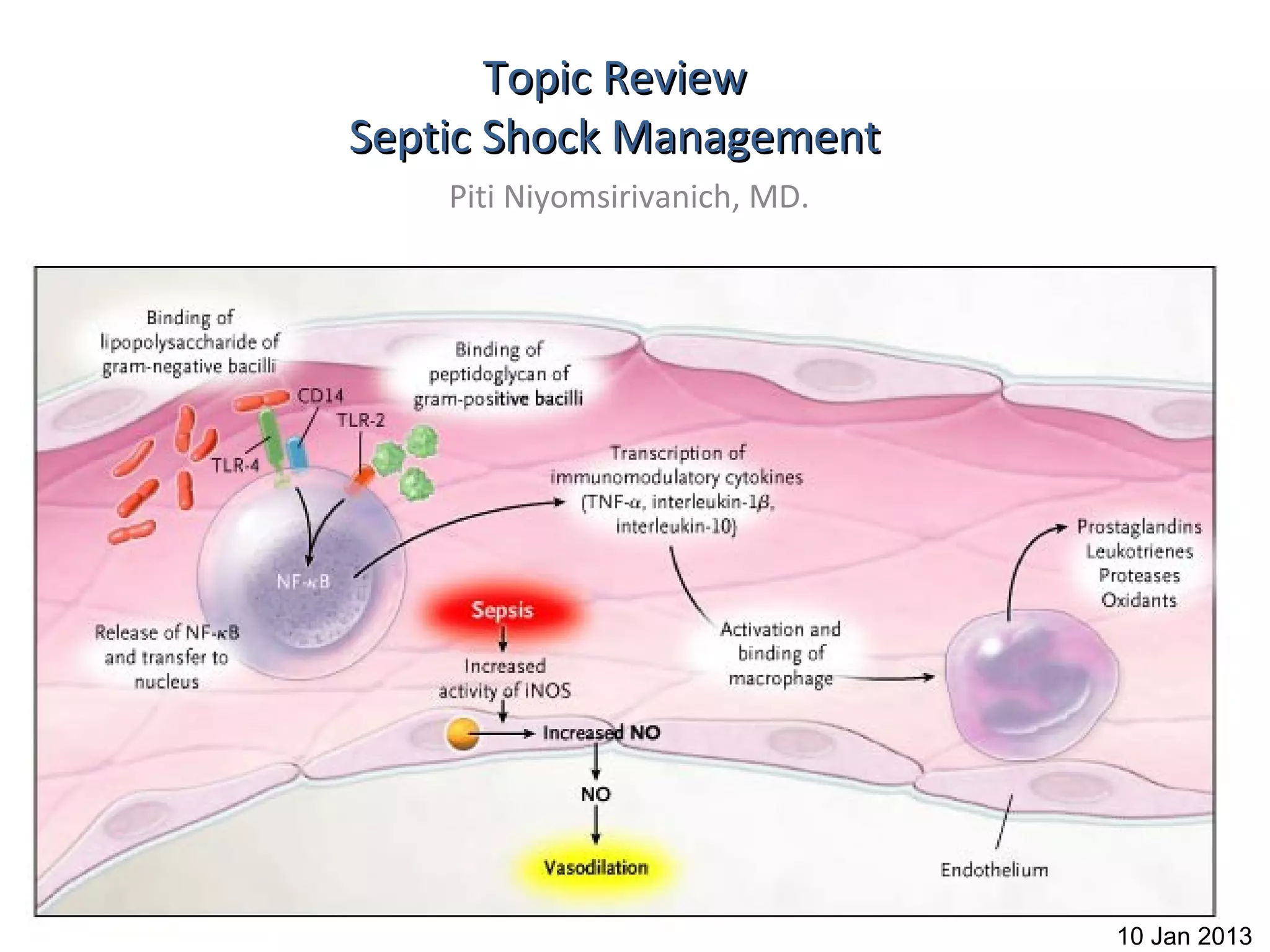
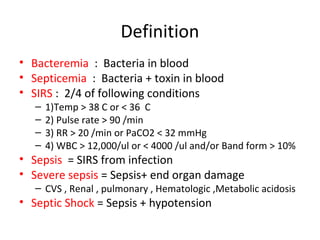
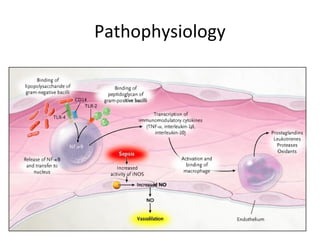
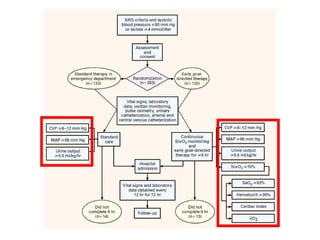
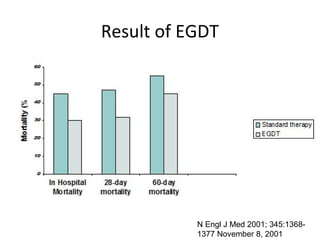
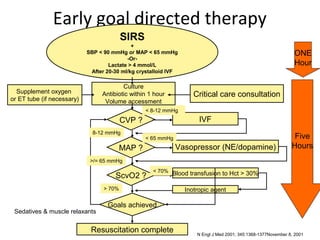
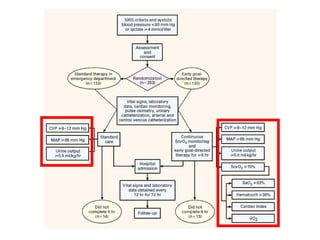
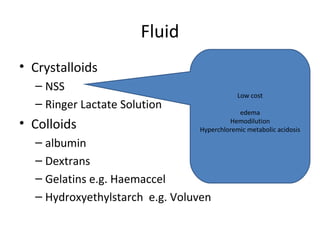
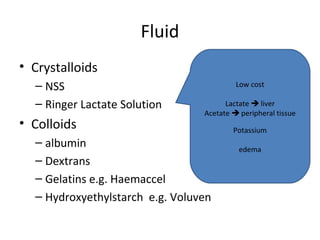
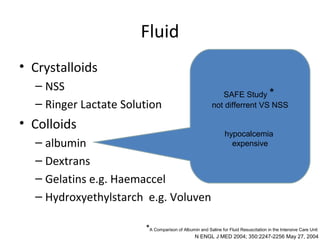
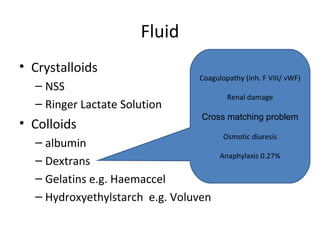
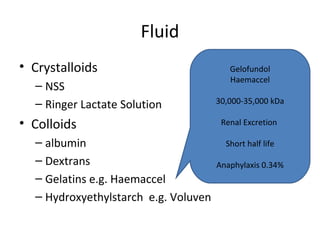
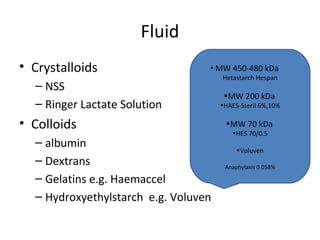
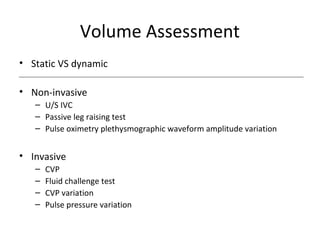
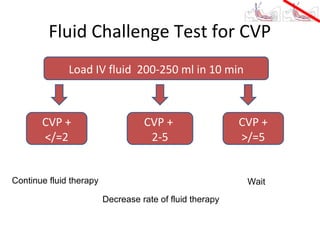
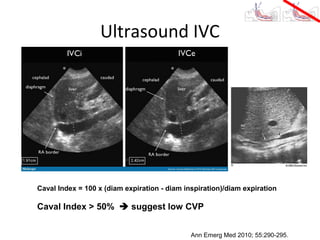
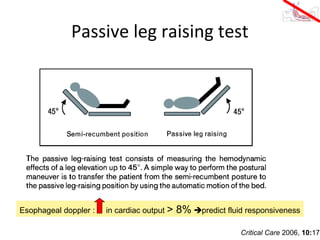
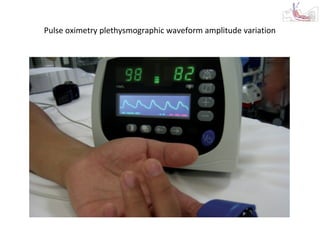
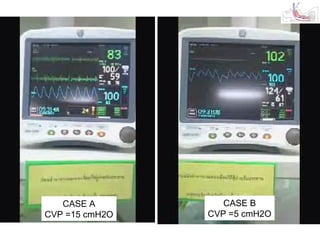
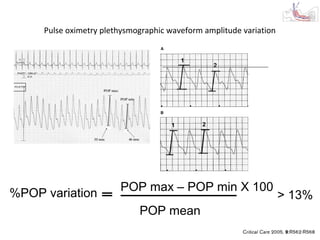
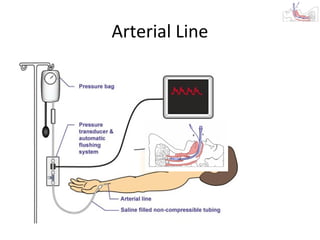
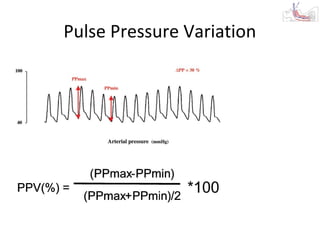
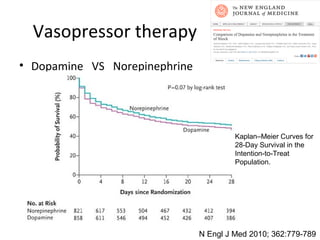
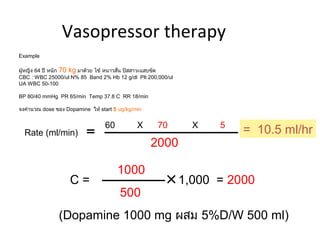
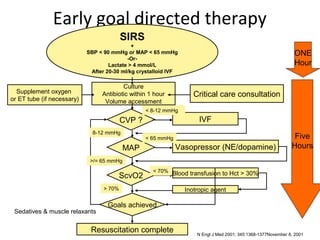
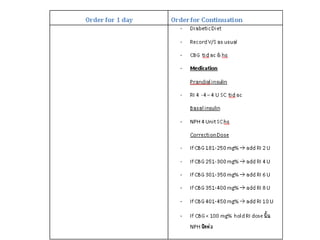
This document provides an overview and outline of topics related to septic shock management. It discusses key points including administering antibiotics within 1 hour, maintaining adequate preload with fluid resuscitation, and using appropriate vasopressors. The outline covers definitions, pathophysiology, early goal directed therapy involving fluid resuscitation, vasopressors, and achieving specific ScvO2 targets. Assessment of volume status and choices for fluid resuscitation are also reviewed.






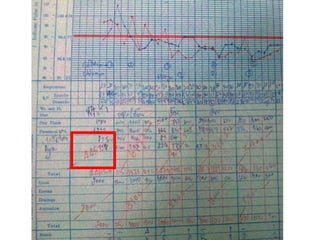




![O2 delivery
• DO2 = [1.39 x Hb x SaO2 + (0.003 x PaO2)] x CO
• Depend on < 70%
Blood transfusion to Hct > 30
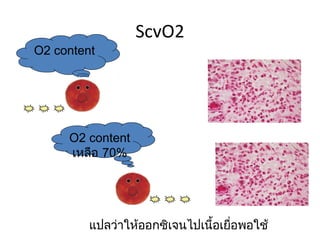
ScvO2
– Hemoglobin > 70% Inotropic agent
– O2 saturation Goals achieved
– Cardiac output
– ScvO2 < 70%
• target Hct > 30
• Inotropic drug increase cardiac output
Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain (2004) 4 (4) 123-126](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/septicshock-130107062047-phpapp01/85/Septic-shock-46-320.jpg)














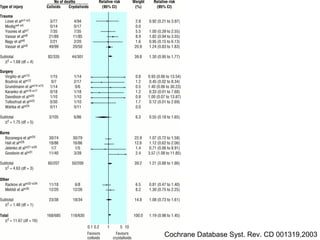
![Blood Transfusion
● Give red blood cells when hemoglobin decreases to 7.0 g/dL (70 g/L) to
target a hemoglobin of 7.0–9.0 g/dL in adults (1B). A higher hemoglobin lev
el may be required in special circumstances (e.g., myocardial ischaemia, se
vere hypoxemia, acute hemorrhage, cyanotic heart disease, or lactic acidosi
s)
● Do not use erythropoietin to treat sepsis-related anemia. Erythropoietin may
be used for other accepted reasons (1B) Do not use fresh frozen plasma to
correct laboratory clotting abnormalities unless there is bleeding or planned i
nvasive procedures (2D)
● Do not use antithrombin therapy (1B)
Administer platelets when (2D) Counts are 5000/mm3 (5 109/L) regardless
of bleeding
Counts are 5000–30,000/mm3 (5–30 109/L) and there is significant
bleeding risk
Higher platelet counts (50,000/mm3 [50 109/L]) are required for surgery or
invasive procedures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/septicshock-130107062047-phpapp01/85/Septic-shock-69-320.jpg)