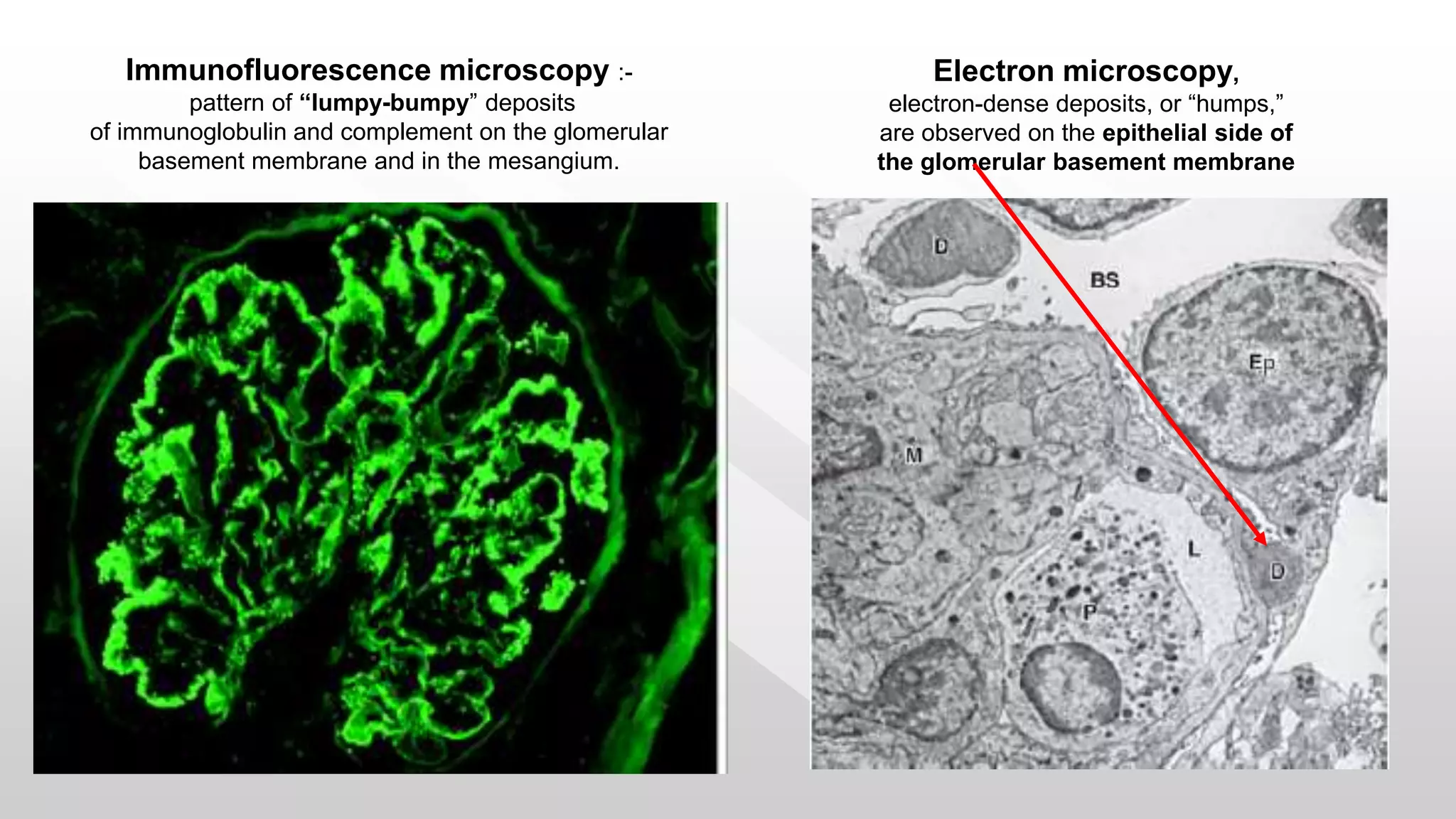
Acute glomerulonephritis is an acute inflammation of the renal glomeruli characterized by sudden onset of oliguria, hematuria, hypertension and edema. It is commonly caused by a streptococcal infection and results in the deposition of immune complexes in the glomeruli. On pathology, glomeruli appear enlarged and infiltrated by polymorphs with epithelial crescents. Immunofluorescence shows "lumpy-bumpy" deposits of immunoglobulin and complement. Management involves controlling hypertension and edema with diuretics, treating any underlying infection, and managing complications such as acute renal failure. The prognosis is generally good with complete recovery in most cases.





























![Management of Hypertensive Crisis / Encephalopathy
1. Intravenous Sodium Nitroprusside [Arterial & venous vasodilator]
Dose : 0.3 µg / kg / min (max 10 µg / kg / min)
2. Propranalol: [b 1 selective blocker]
Dose: 1-3 mg / kg / dose q 12 h
3. Esmolol: [b 1 selective blocker]
Dose: 130 – 300 µg / kg / min
4. Nifidepine: (Calcium channel blocker)
Dose : 0.5 mg / kg Sublingual repeated after 30 min
5. Amlodepine:(Calcium channel blocker)
Dose : 0.1 to 0.6 mg / kg / d in 2-3 doses – Oral
6. Labetelol: [Combined b -adrenergic (b1 & b2) and a-adrenergic blocker] Dose : 0.2-1.0
mg/kg can be given as an IV bolus every 10 min; Dosages of 0.25 - 3 mg / kg / hr by IV infusion..
7. Hydralazine: [Direct arterial vasodilator with no effect on venous circulation]
Dose : 0.1 - 0.2 mg / kg every 2 hrs (max 10 µg / kg / min)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuteglomerulonephritis-forugs-200611133728/75/Acute-glomerulonephritis-for-UGs-31-2048.jpg)



