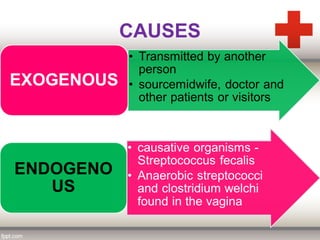
This document discusses puerperal pyrexia, which is a temperature of 100.4°F or higher within the first 10 days following delivery. It defines puerperal pyrexia and notes its historical prevalence. The causes are listed for different time periods postpartum, including atelectasis, urinary tract infections, endometritis, wound infections, and mastitis. Puerperal sepsis is also defined as an infection of the genital tract occurring after delivery. Risk factors and causes are provided. Signs and symptoms, investigations, prophylaxis, treatment including isolation, antibiotics, and potential surgical interventions are summarized.