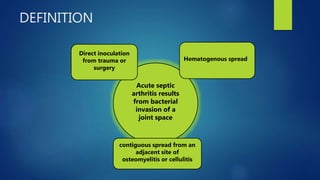
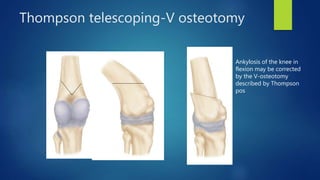
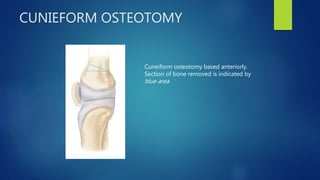
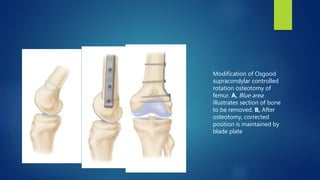
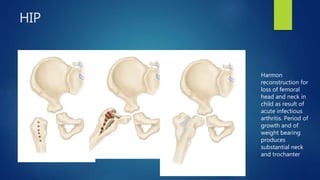
1. Septic arthritis results from bacterial invasion of a joint space and can occur through hematogenous spread, direct inoculation from trauma or surgery, or contiguous spread from an adjacent infection.
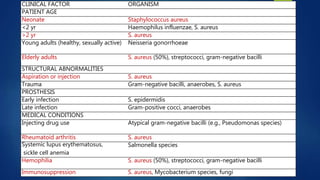
2. Risk factors include rheumatoid arthritis, prosthetic joints, IV drug use, diabetes, and previous joint injections. Clinical presentation varies from pain and swelling to no symptoms in neonates.
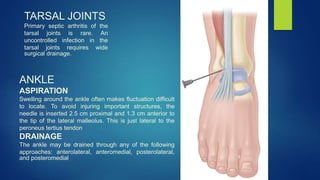
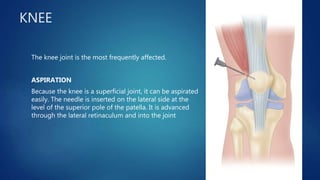
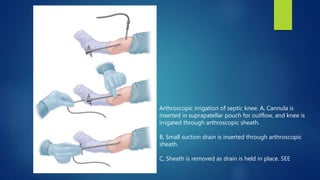
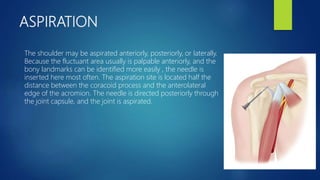
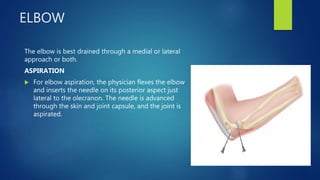
3. Treatment involves joint aspiration, antibiotics based on patient factors, and sometimes surgical drainage. Duration of treatment depends on the infecting organism but usually lasts 4-6 weeks.