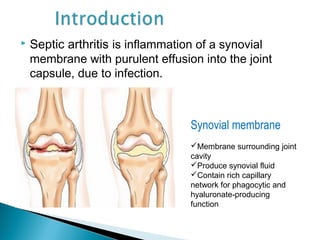
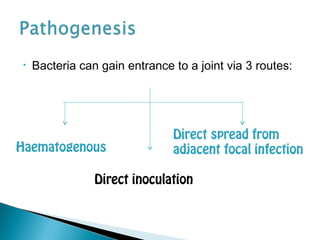
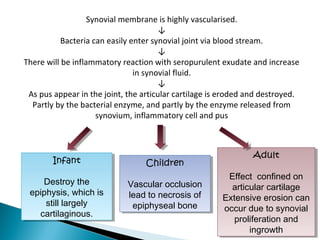
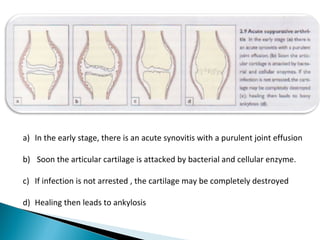
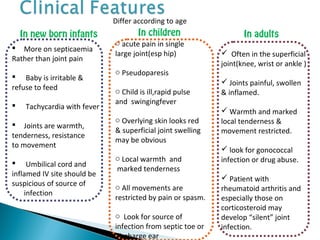
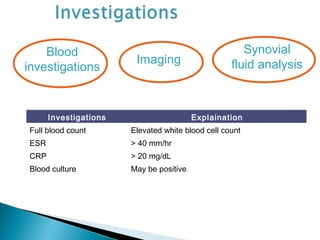
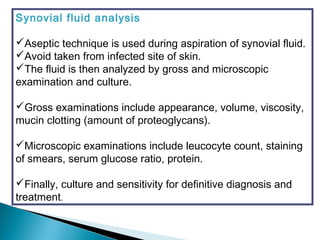
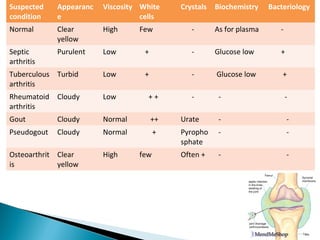
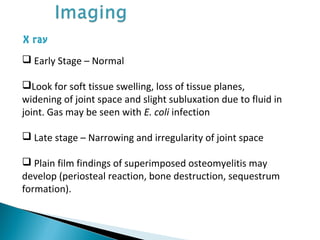
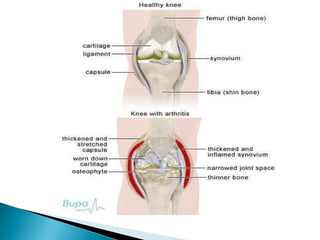
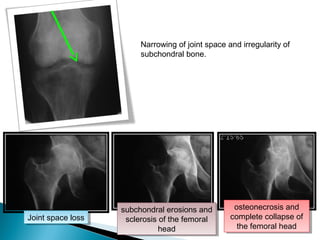
This document discusses septic arthritis of the knee. It begins with an introduction and overview of pathogenesis. Septic arthritis is caused by bacterial infection of the synovial membrane, usually by Staphylococcus aureus. Clinical features include pain, swelling and limited movement of the infected joint. Investigations may include blood tests, synovial fluid analysis, x-rays and ultrasound. Treatment involves antibiotics, surgery drainage and splinting the joint to promote healing. Complications can include bone and cartilage destruction, joint dislocation, growth disturbances or secondary osteoarthritis.