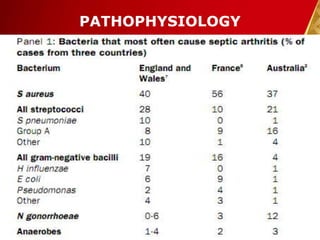
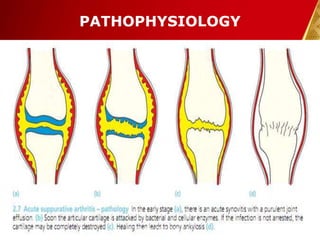
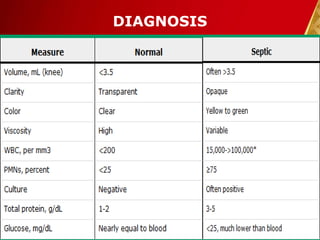
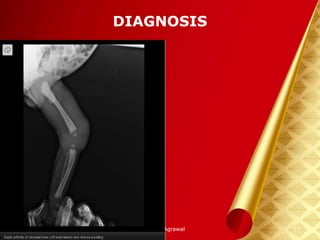
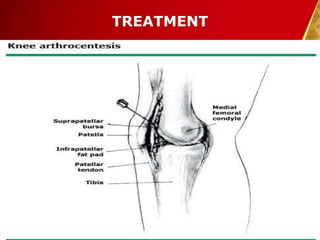
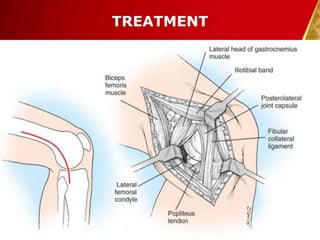
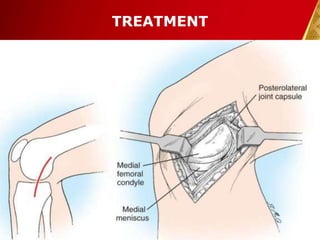
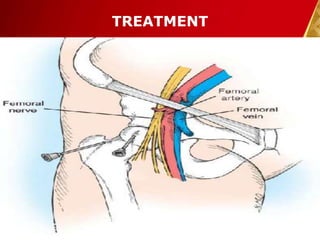
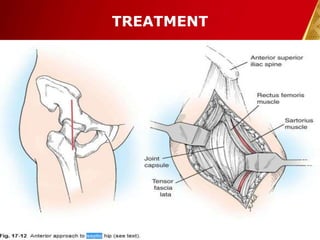
This document discusses septic arthritis, which is an infection of the joint space that is often bacterial but can also be fungal or viral. It is a rheumatologic emergency as it can cause rapid joint destruction and significant morbidity. The document covers the pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and complications of septic arthritis. Joint drainage, antibiotics, and rest are the mainstays of treatment, while complications can include joint destruction and ankylosis if not treated promptly. Prognosis depends on factors like age, joint involved, and treatment delay.