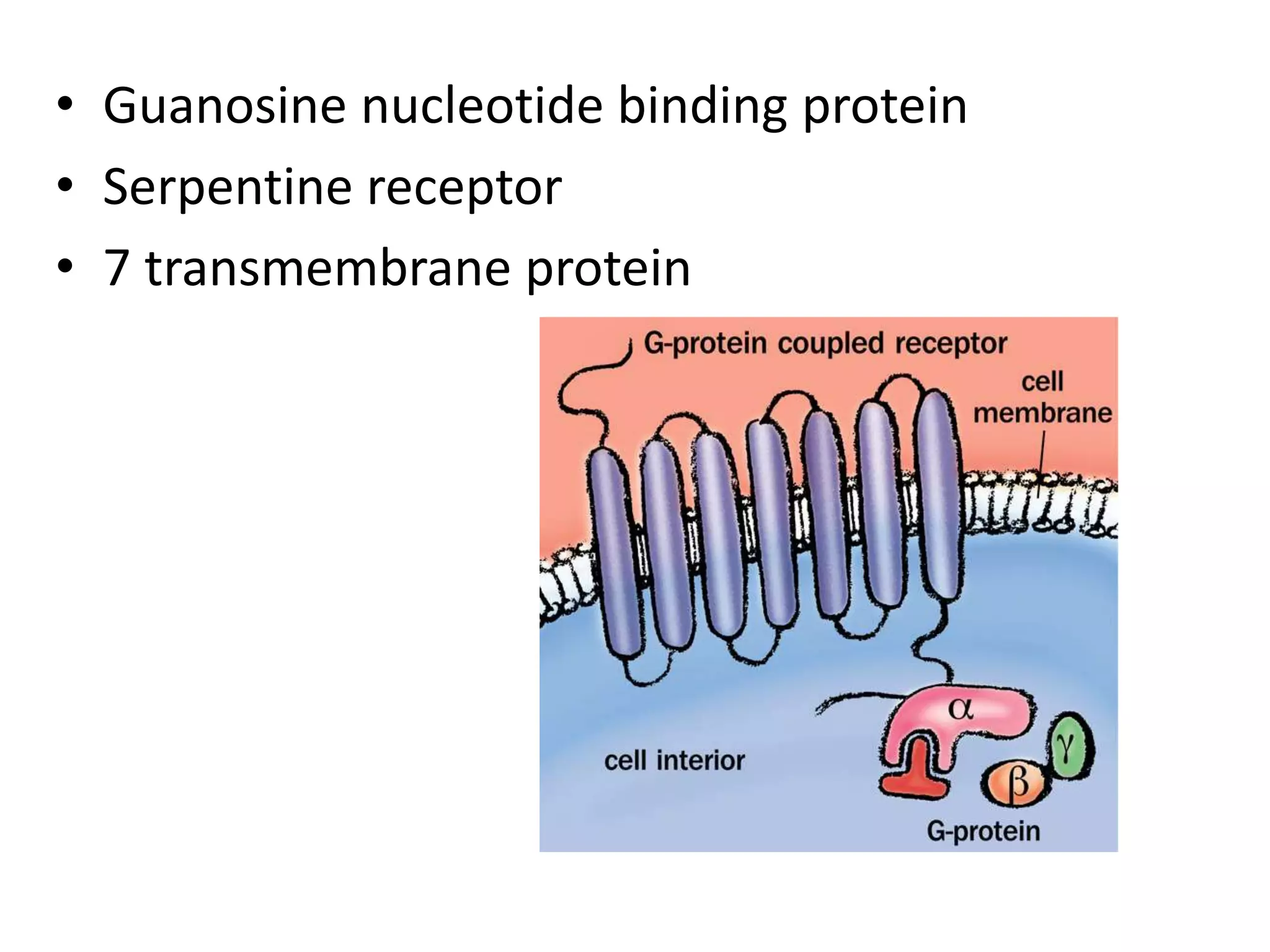
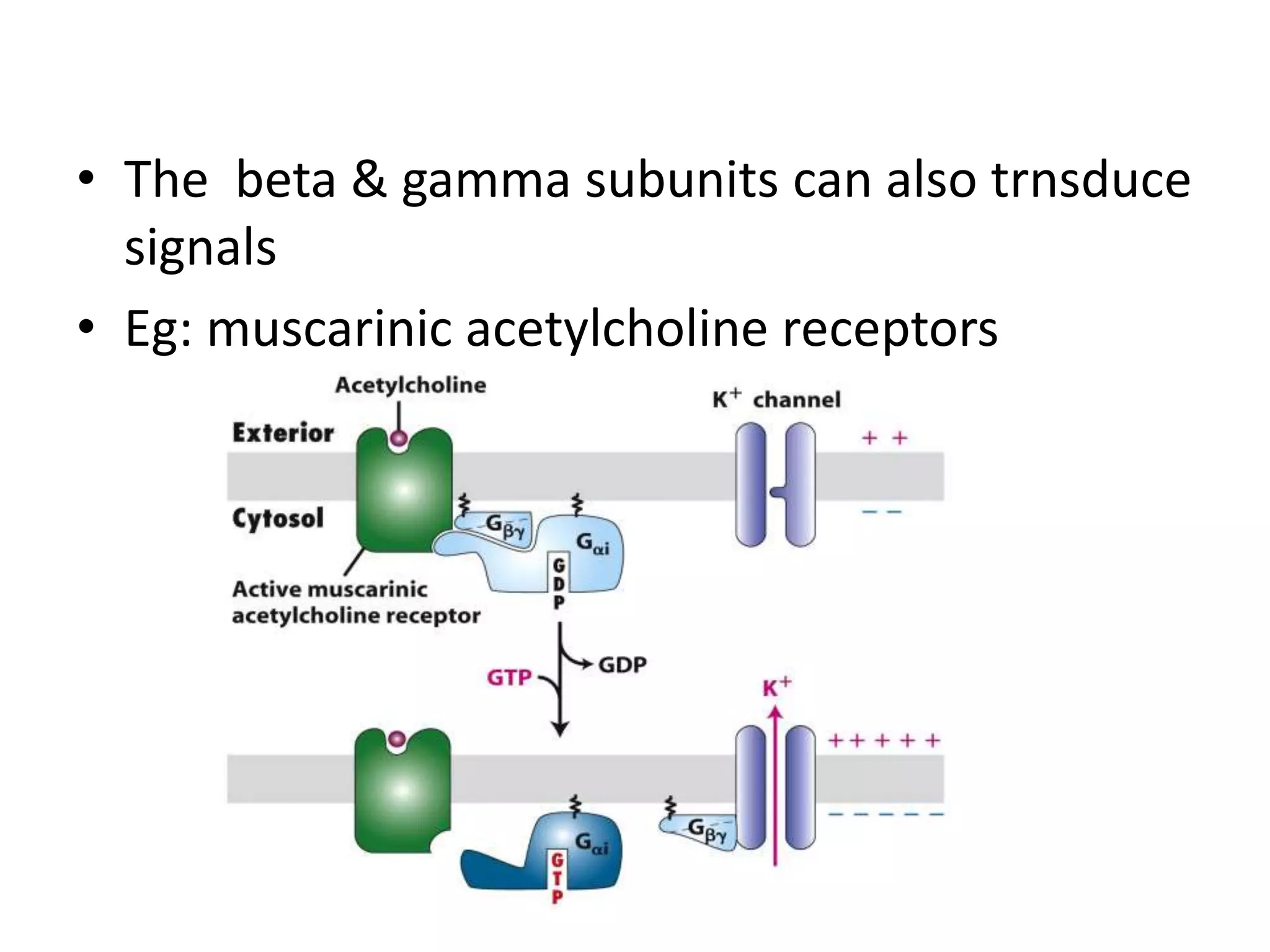
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are 7 transmembrane proteins that bind extracellular ligands and activate intracellular G proteins. When a ligand binds to a GPCR, it undergoes a conformational change that causes the bound G protein's alpha subunit to exchange GDP for GTP. The activated G protein alpha subunit then detaches from the beta and gamma subunits to initiate downstream signaling, such as by increasing cyclic AMP production. GPCRs function as molecular switches and their signaling persists as long as the G protein alpha subunit remains GTP-bound. Examples of GPCRs include olfactory, adrenergic, and hormone receptors.