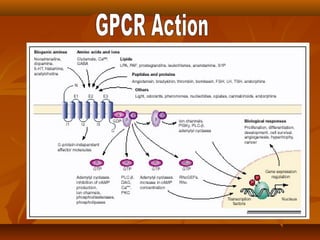
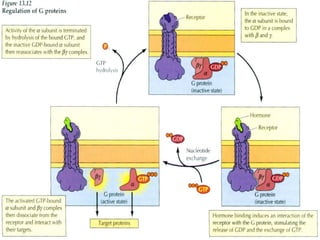
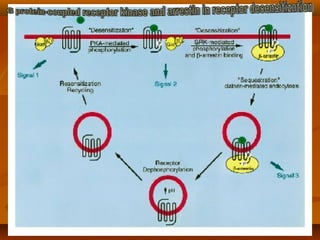
G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large family of cell membrane receptors that are linked to intracellular effector proteins. All GPCRs have seven transmembrane alpha helical segments. The receptors activate intracellular signaling pathways upon binding of an agonist ligand. This leads to the exchange of GDP for GTP on associated G proteins, which then activate downstream effectors to induce cellular responses. The major effector pathways activated by GPCRs are adenylyl cyclase/cAMP, phospholipase C/IP3-DAG, and ion channel regulation.