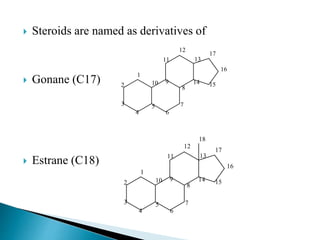
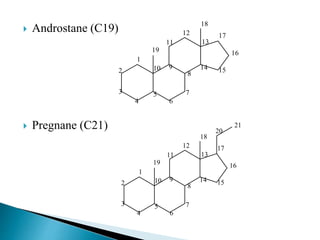
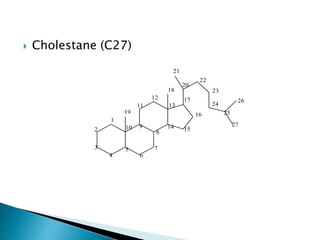
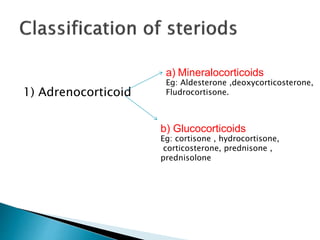
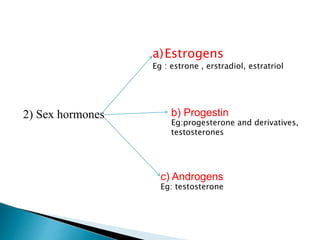
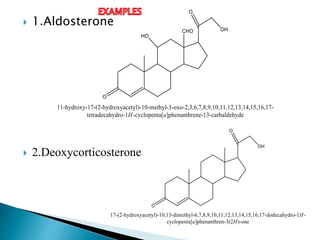
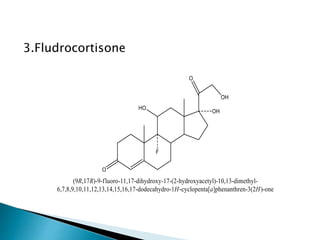
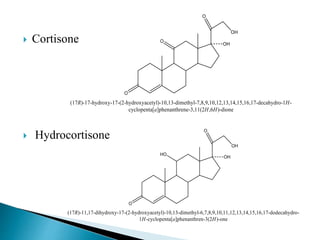
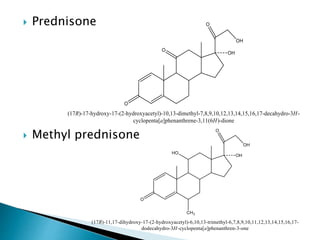
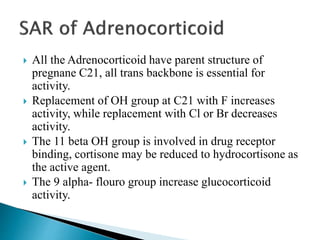
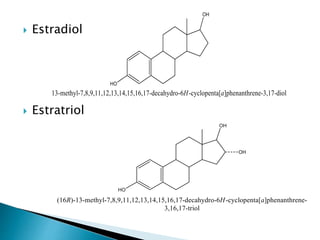
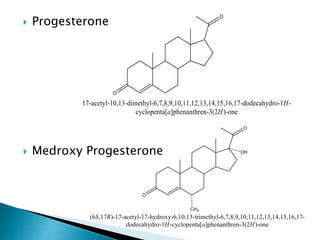
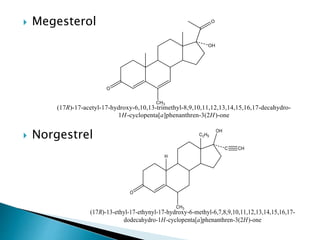
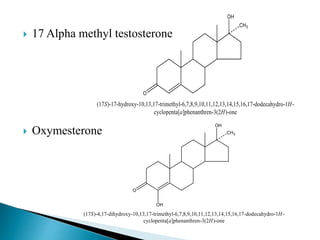
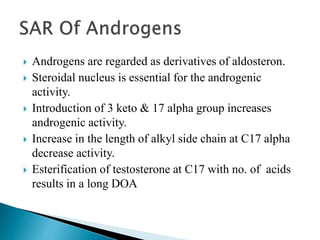
Steroids have a wide distribution in nature and serve important physiological functions. They act as sex hormones, anti-inflammatory agents, cardiac steroids, and diuretics. Steroids contain four fused rings and have a cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene structure. They are classified based on this core structure and include gonane, estrane, androstane, pregnane, and cholestane derivatives. Steroids bind to receptors in target cells and trigger protein synthesis that mediates their physiological effects. Major classes of steroids include glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, estrogens, progestogens, and androgens.