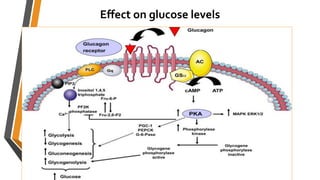
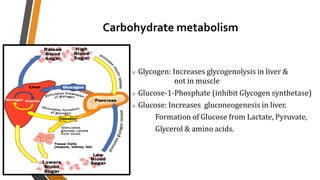
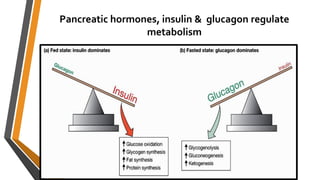
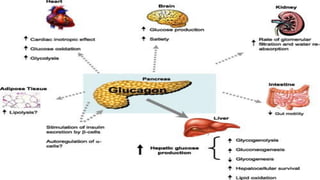
Glucagon is a peptide hormone produced by pancreatic alpha cells that plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism by opposing the action of insulin. It stimulates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver while promoting lipolysis and amino acid transport, helping to maintain blood glucose levels, especially during fasting or stress. Glucagon's secretion is regulated by factors such as low blood glucose, amino acids, and stress hormones, while it serves to prevent hypoglycemia between meals.


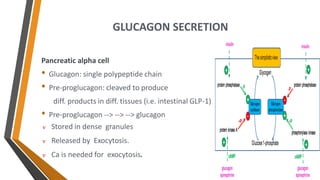


![Inhibitors
Elevated plasma [glucose]
Somatostatin
Secretin
FFA, ketones
Insulin
-Adrnergic stimulation, GABA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glucagon-210120081634/85/Glucagon-6-320.jpg)