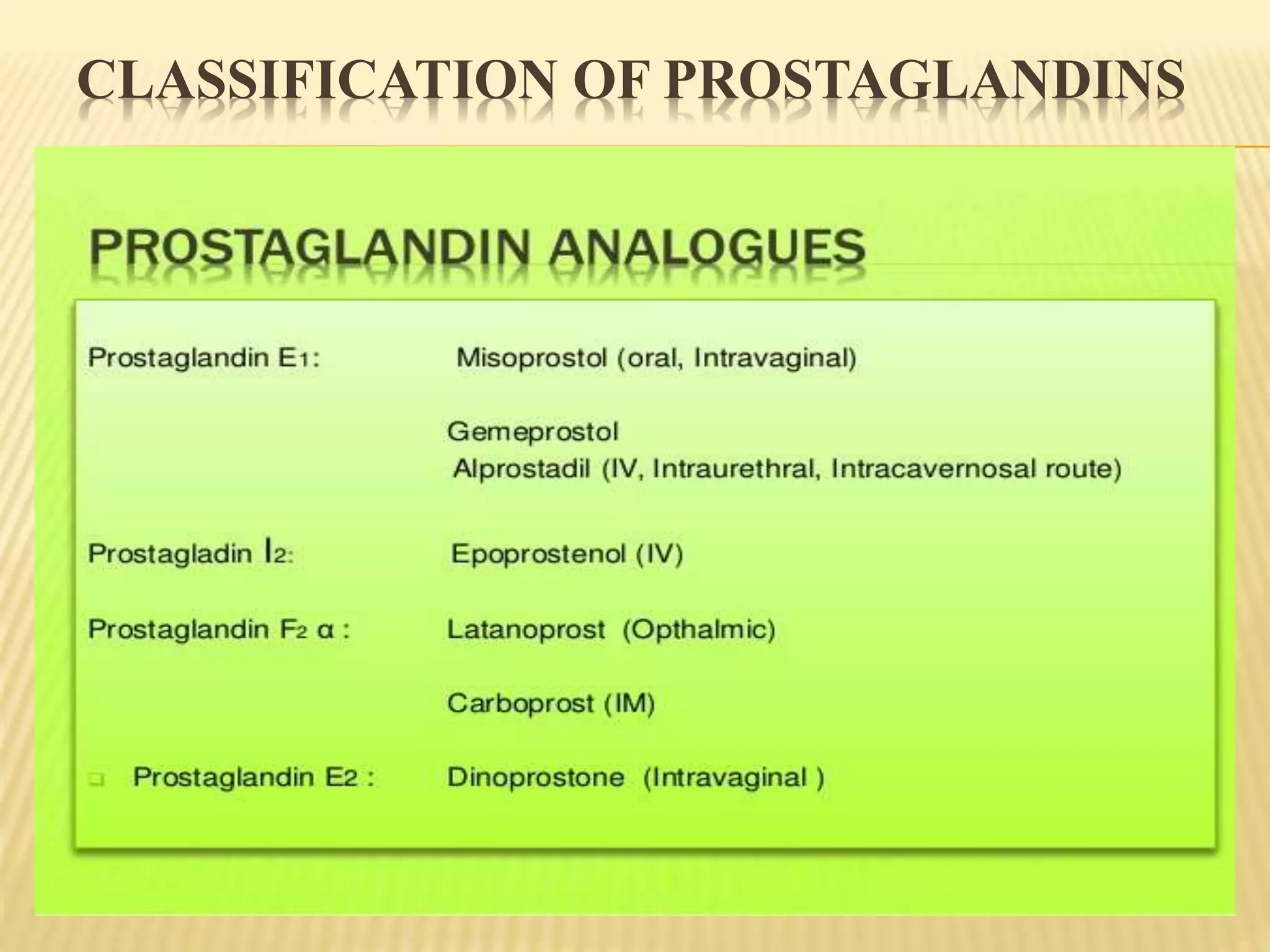
Prostaglandins are biologically active lipid compounds derived from fatty acids. The two main prostaglandins, PGE2 and PGF2α, are released during mechanical, chemical, or infectious insults and play a key role in inflammation. They are synthesized from cell membrane phospholipids and have diverse pharmacological actions in various organ systems. Prostaglandins act as vasodilators or vasoconstrictors depending on the tissue, and are involved in processes like uterine contraction, bronchodilation, renal function, and hormone release. Therapeutic uses of prostaglandins include cervical ripening, labor induction, postpartum hemorrhage control, and abortion induction.