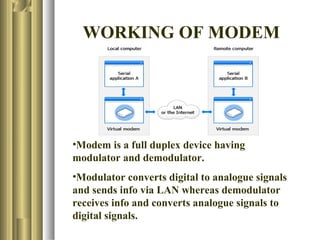
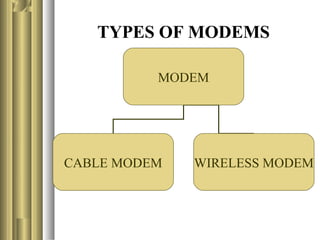
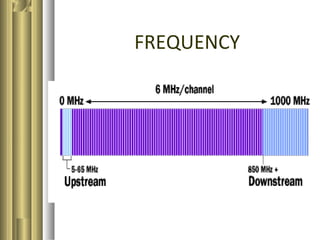
The document discusses the history and development of the internet and modems. It explains that the internet was first developed by the US military in 1979 and later opened to the public in the early 1990s. It then describes how modems allow users to connect to the internet by converting digital signals to analog signals that can be transmitted over phone lines. Finally, it outlines different types of modems including cable modems, wireless modems, and differences between DSL and broadband connections.