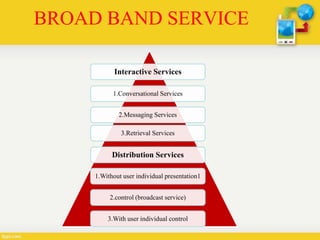
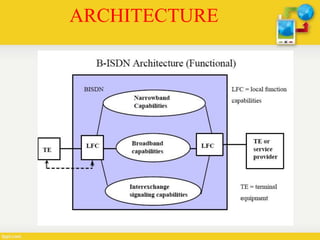
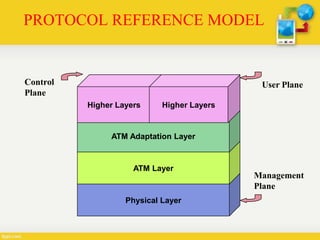
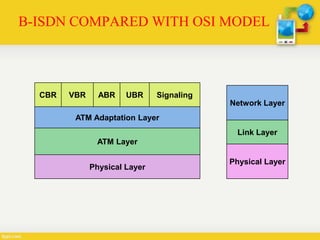
Broadband-ISDN (B-ISDN) is an extension of ISDN that provides broadband capabilities over digital networks. B-ISDN uses asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) and supports transmission speeds greater than 1.544 Mbps. It provides fully integrated services including high-speed data, audio, and full-motion video. The goal of B-ISDN is to achieve complete integration of services from low-bit rate bursty signals to high-bit rate continuous real-time signals.