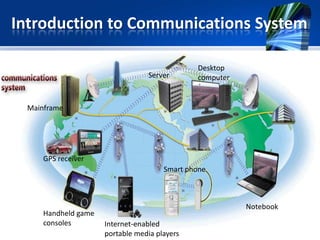
This document provides an overview of telecommunications components and transmission media. It describes the basic components required for communication between sending and receiving devices, including physical transmission media like twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable. It also covers wireless transmission media and different types of communication lines over the telephone network, such as dial-up, DSL, ISDN, and dedicated lines. Common communication devices like modems, network cards, routers and hubs/switches are also described.