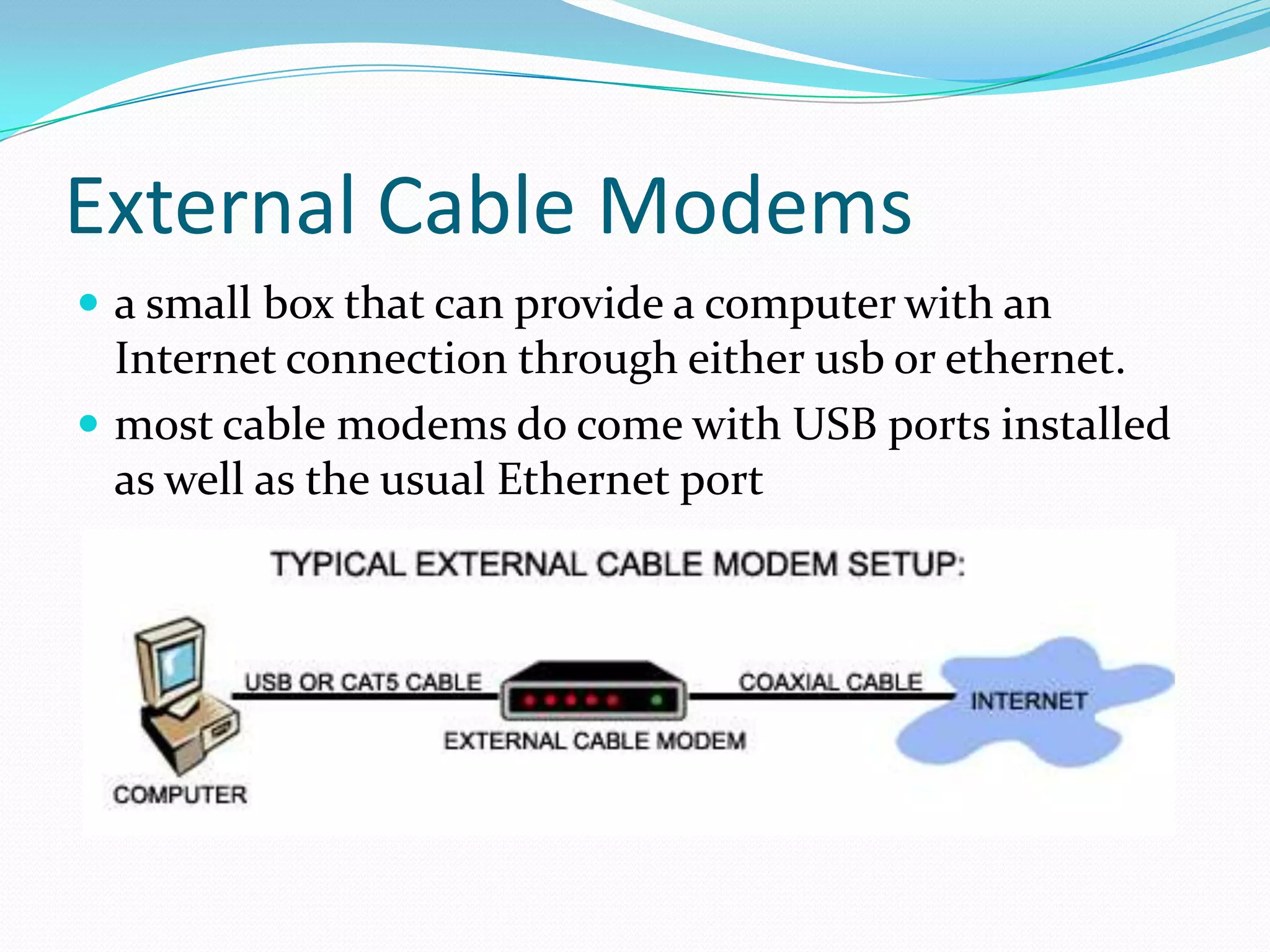
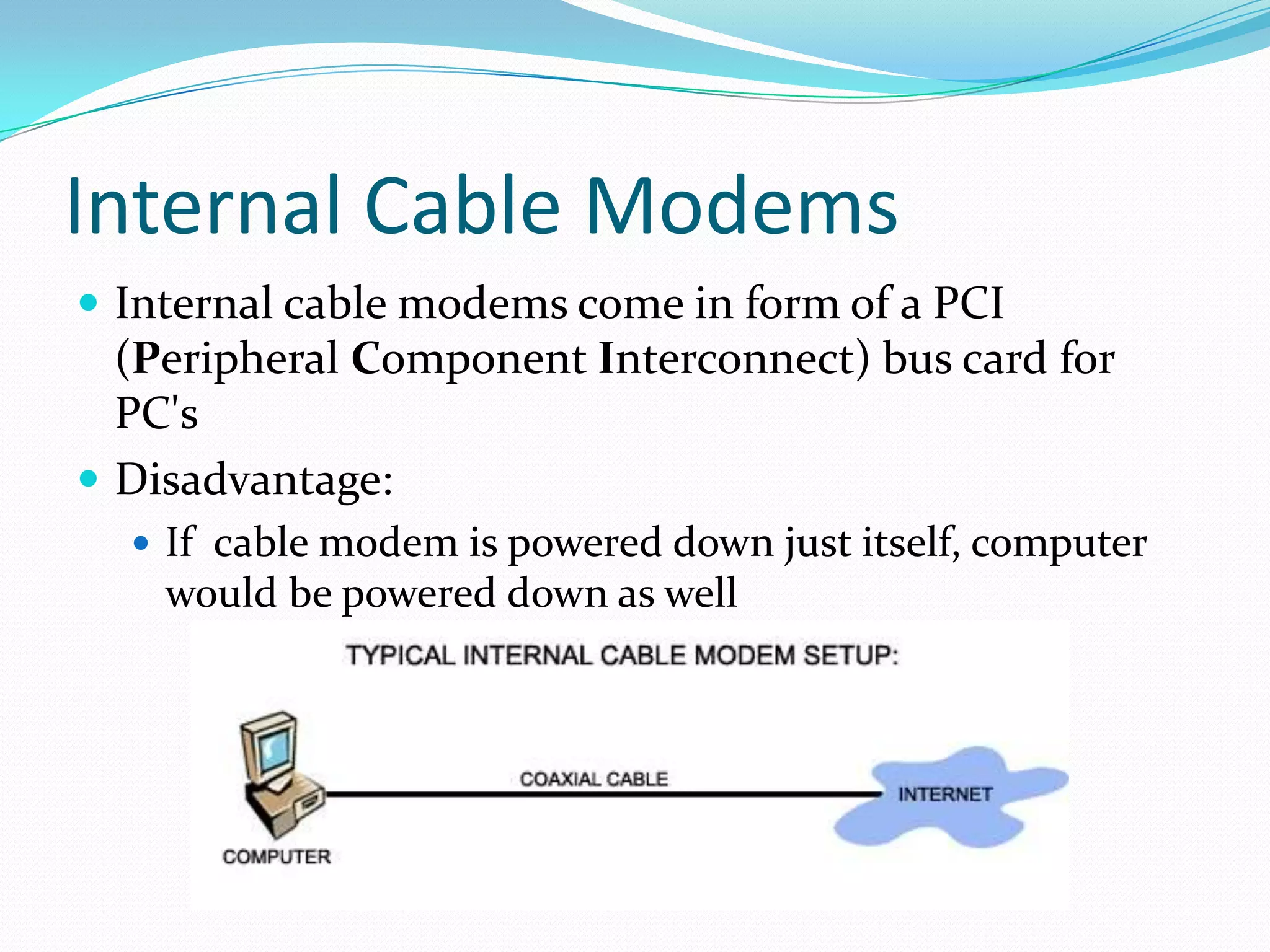
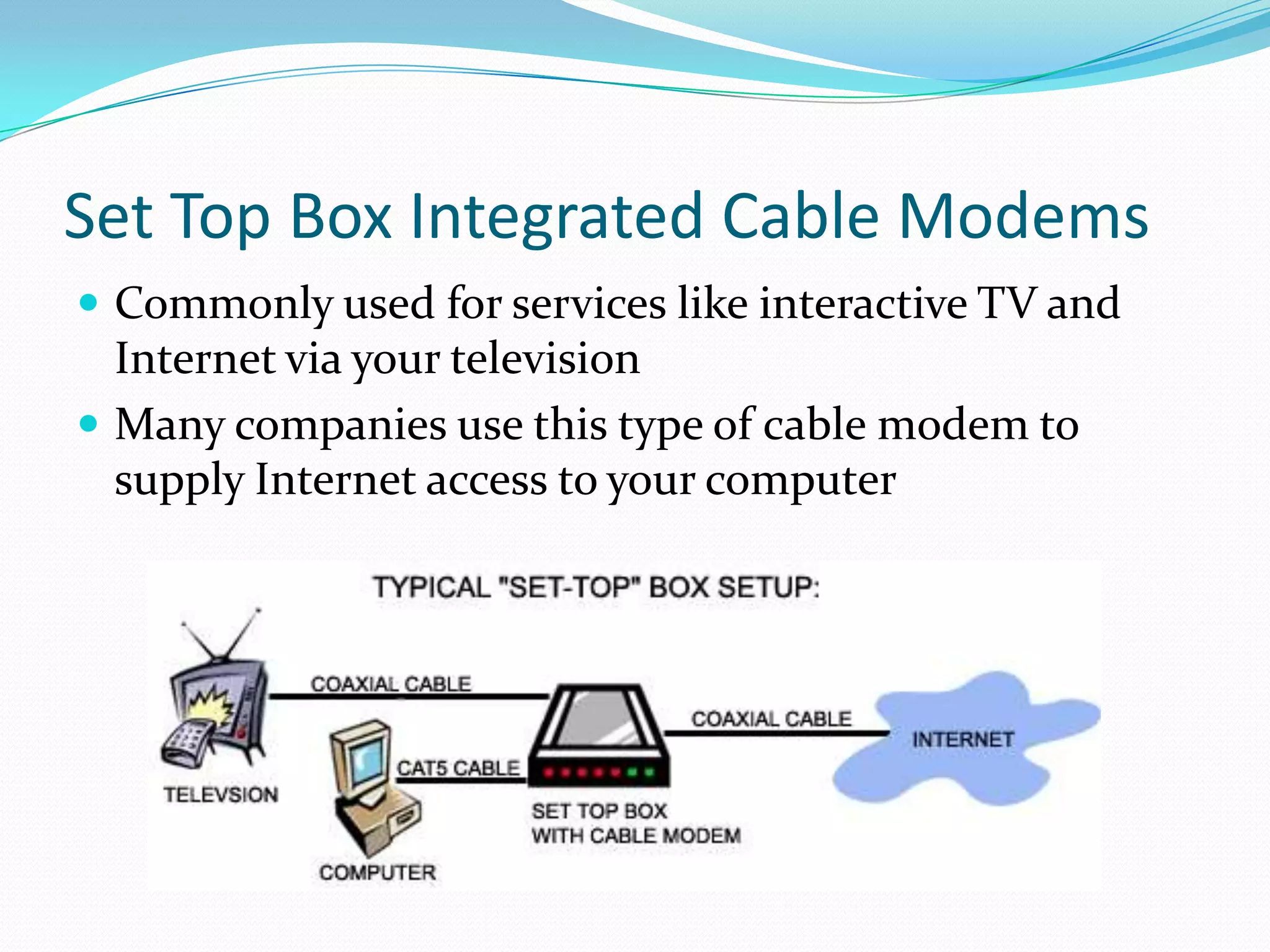
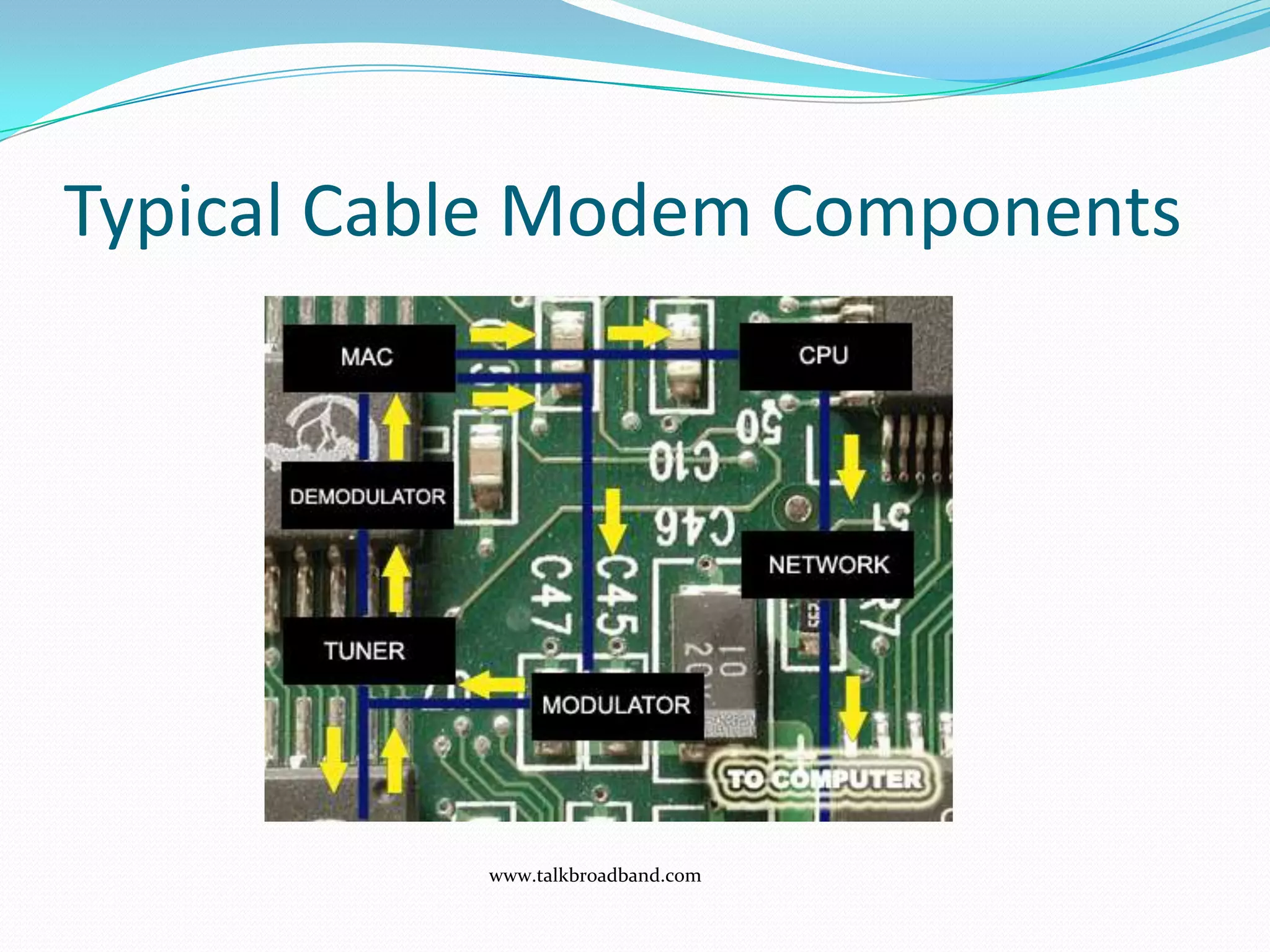
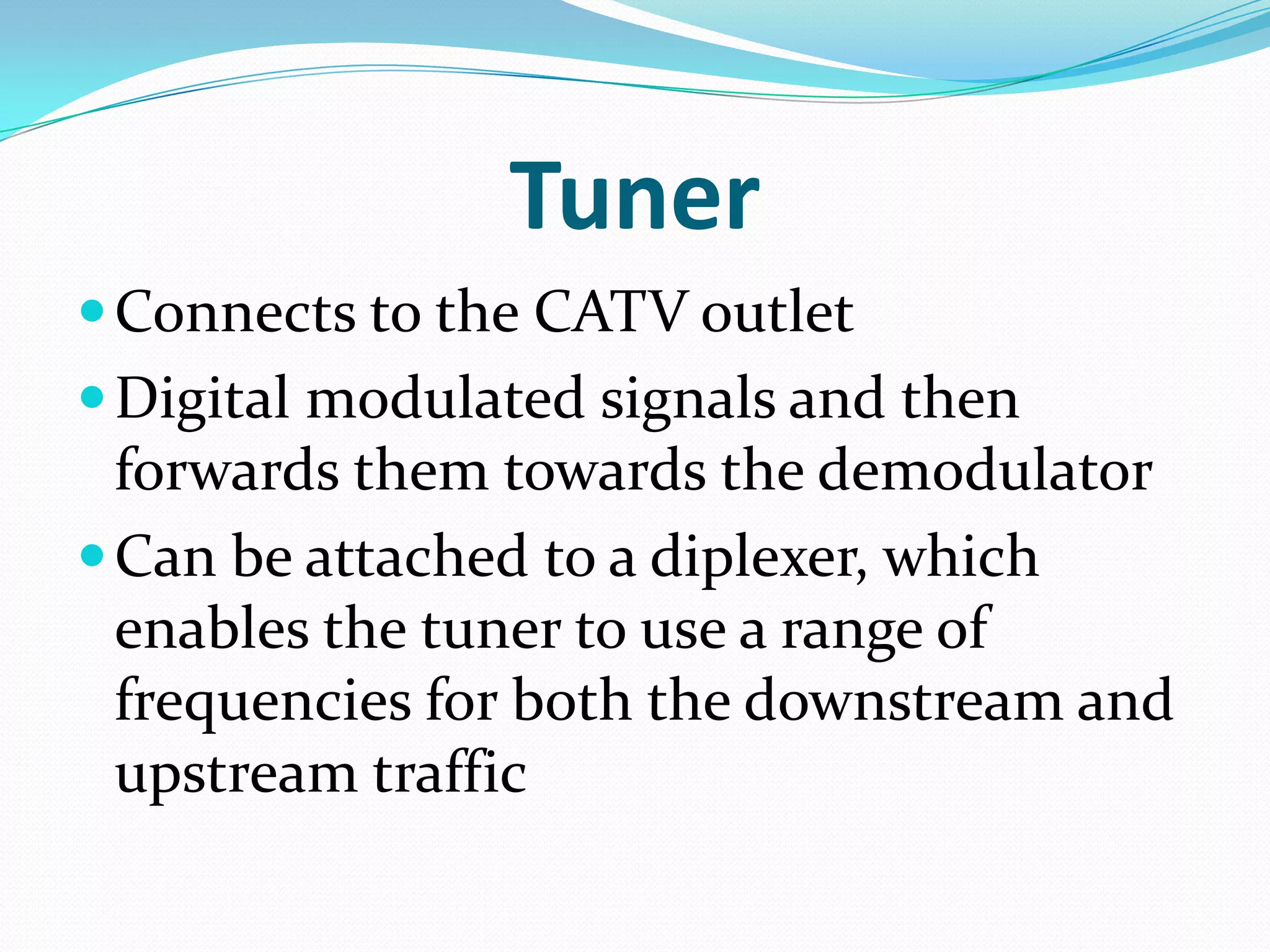
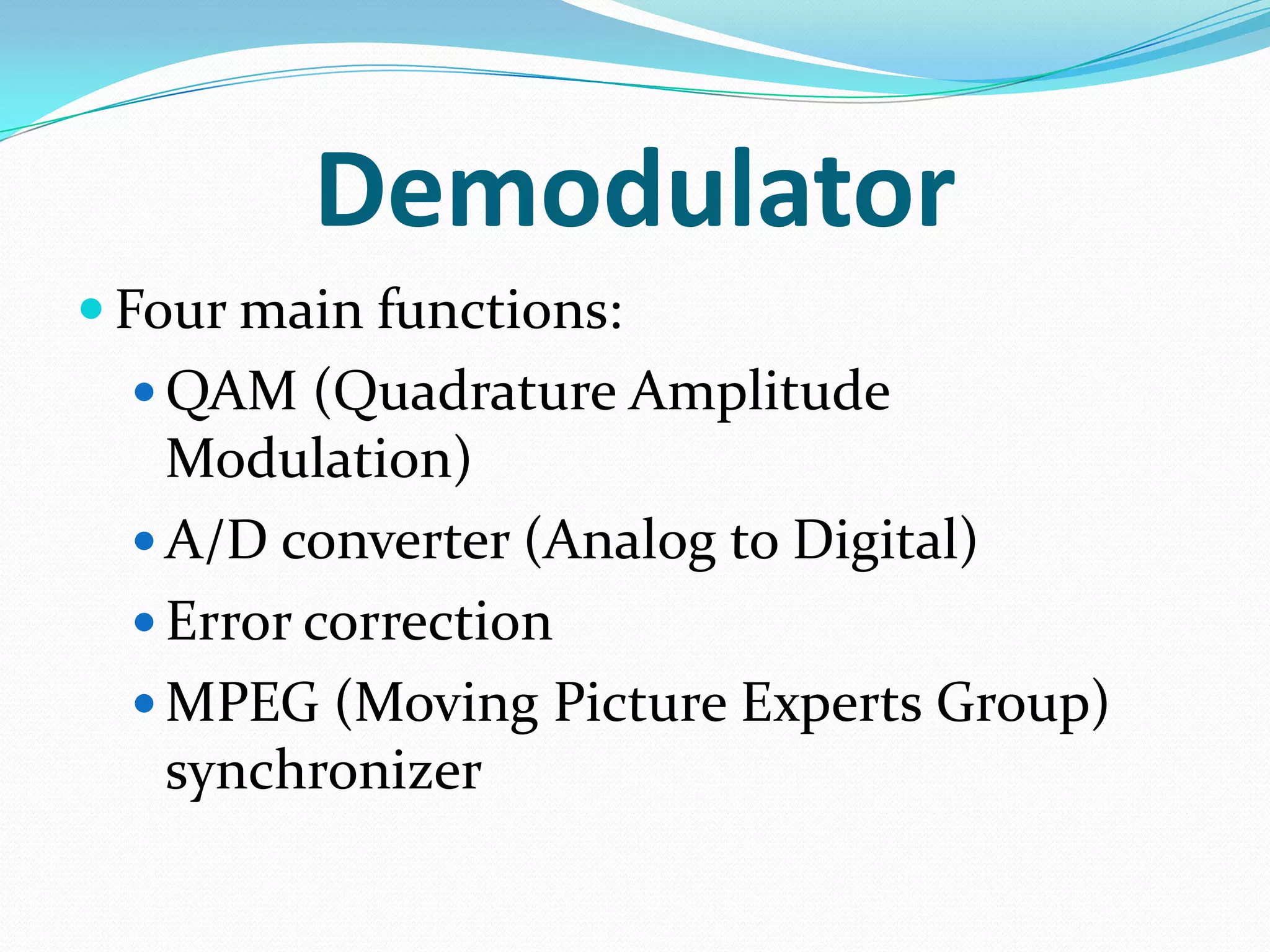
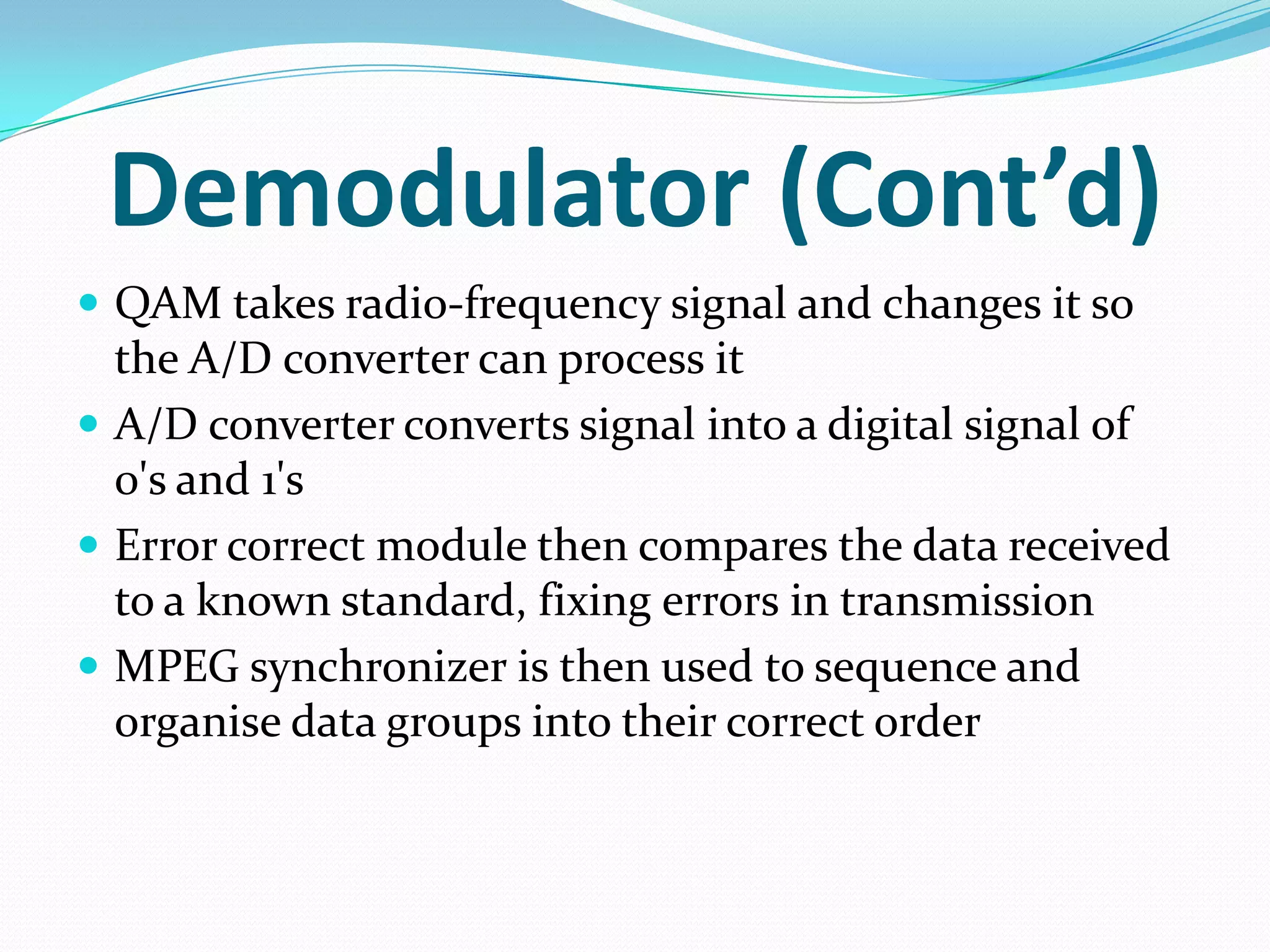
External cable modems connect computers to the internet via USB or Ethernet ports, while internal cable modems are PCI cards installed inside computers. Set top box integrated cable modems provide internet access through televisions. Cable modems use hybrid fibre-coaxial (HFC) infrastructure and consist of a tuner to connect to the cable line, a demodulator to process signals, a modulator to transmit upstream data, and a central processing unit to control operations.