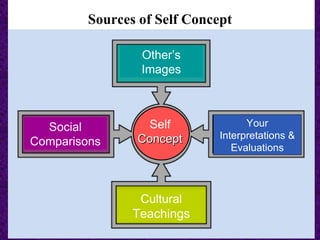
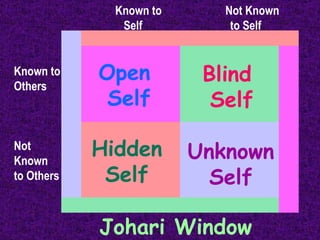
This chapter discusses the concept of self, including how self-concept develops through social interactions and cultural influences. It notes that self-concept is subjective, multi-dimensional, and resistant to change. The chapter also discusses self-awareness, self-esteem, self-disclosure, and communication apprehension. It provides guidelines for appropriate self-disclosure and responding to others' disclosures, as well as theories for managing apprehension.