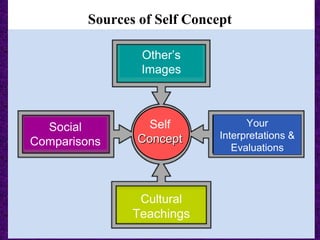
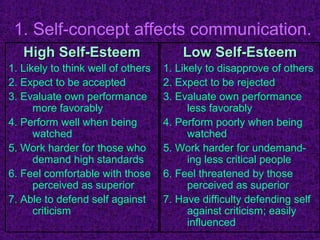
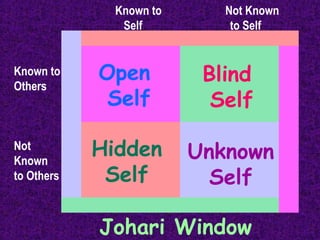
This chapter discusses the concept of self and interpersonal communication. It defines self-concept as how one views themselves and how that develops through others' perceptions, social comparisons, and cultural teachings. The self-concept influences communication and is multidimensional, subjective, resistant to change but flexible if healthy. Cultural influences and communication apprehension also impact one's self-concept. Guidelines are provided for appropriate self-disclosure and responding supportively to others' disclosures in order to have effective interpersonal communication.