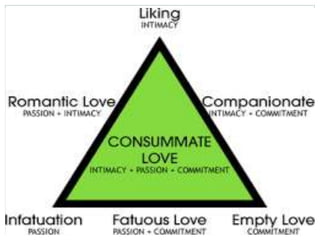
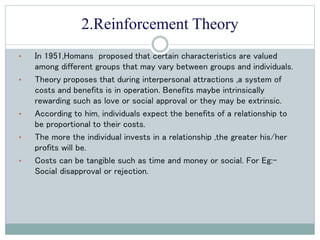
Interpersonal attraction is influenced by physical attractiveness, proximity, familiarity, and similarity. The triangular theory of love proposes that attraction consists of intimacy, passion, and commitment. Reinforcement theory states that individuals expect greater benefits relative to their costs in a relationship. Social exchange theory suggests people evaluate fairness in relationships based on equitable contributions and outcomes. Complementary theory proposes that opposite sex attraction fosters reproductive success. Attachment theory posits that seeking attachment figures in times of stress develops from responsive caregiving as a child.