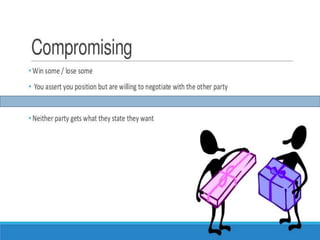
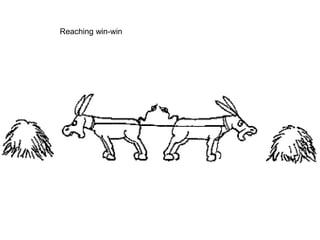
This document discusses conflict and conflict resolution. It defines conflict as occurring when one party perceives another has negatively affected something they care about. Common causes of conflict include scarce resources, differing attitudes and poor communication. There are different levels of conflict including organizational, group and individual. Conflict management strategies include competing, collaborating, compromising, avoiding and accommodating. Resolving intra-group conflict involves recognizing members' roles and realizing unity is stronger than division. Effective conflict resolution requires remaining calm, addressing issues not people, and finding a private space for discussion.