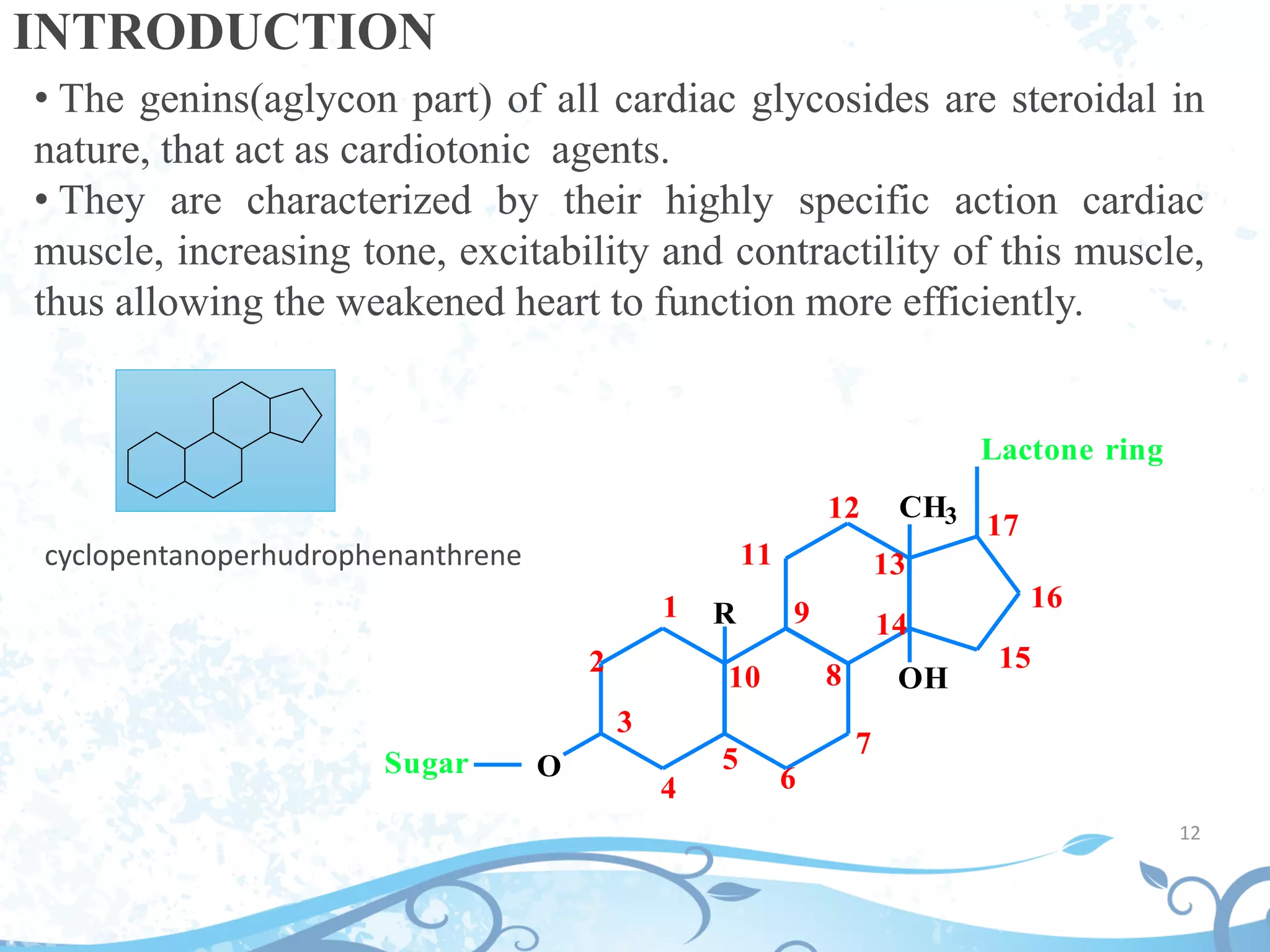
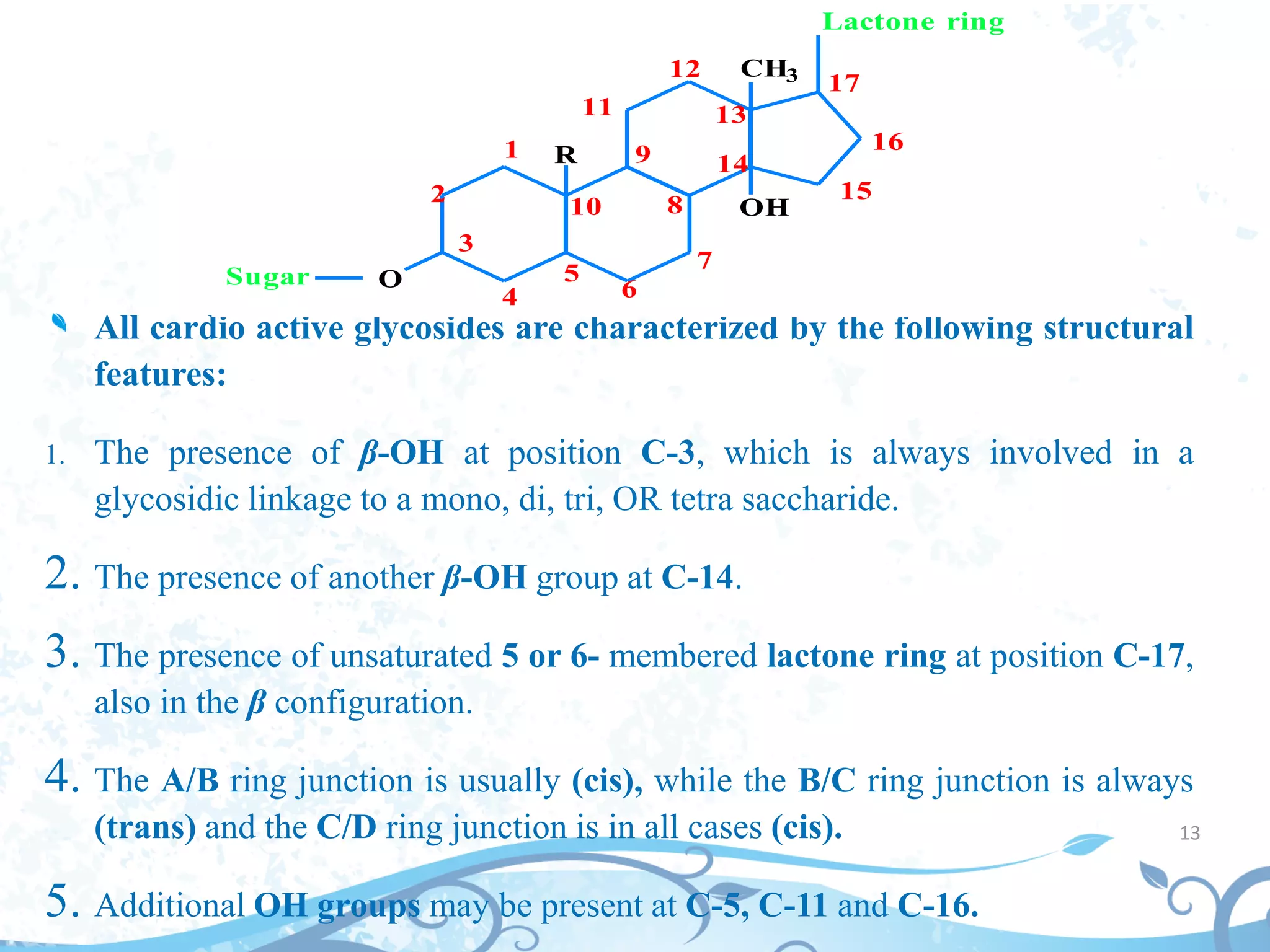
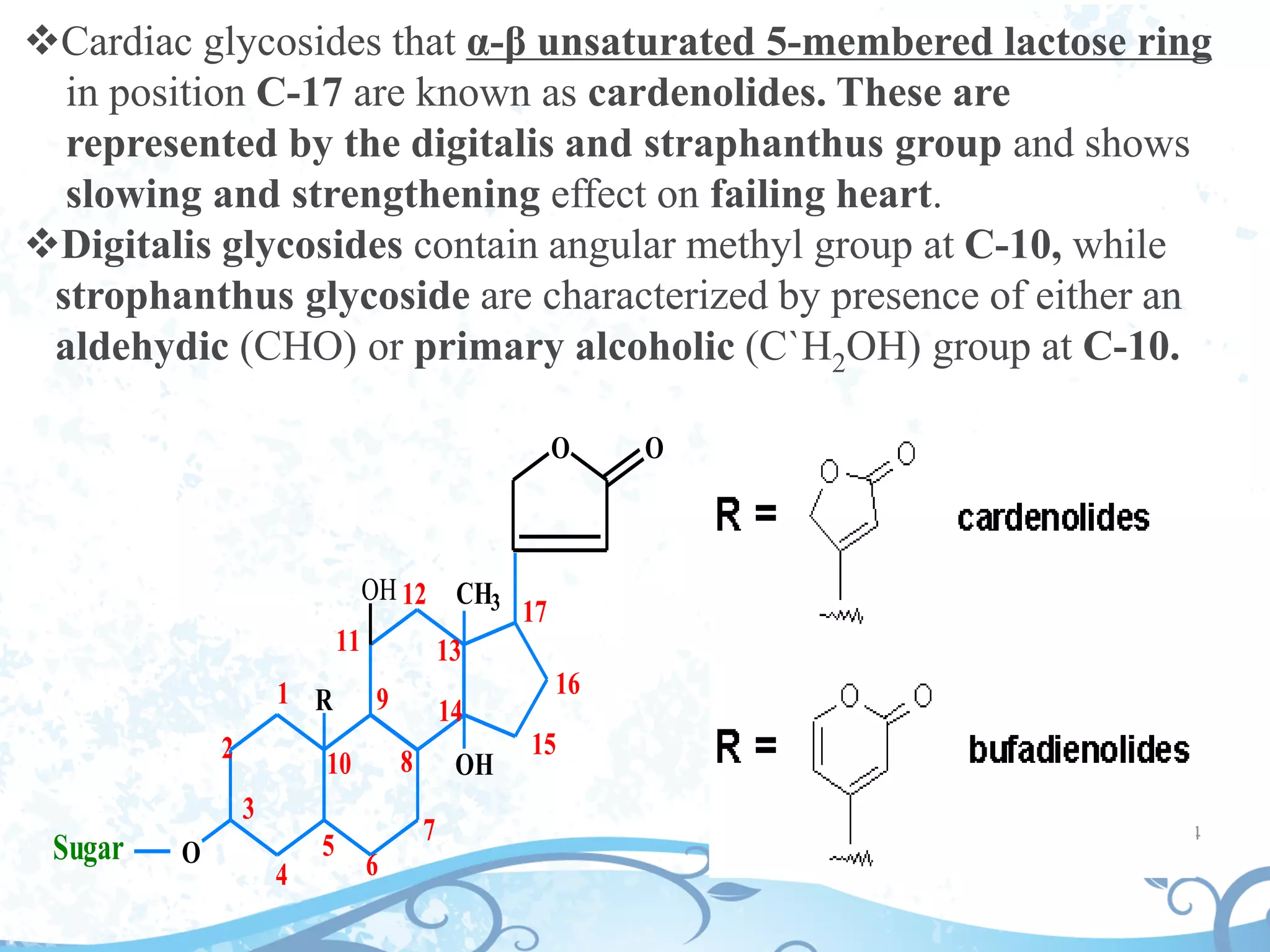
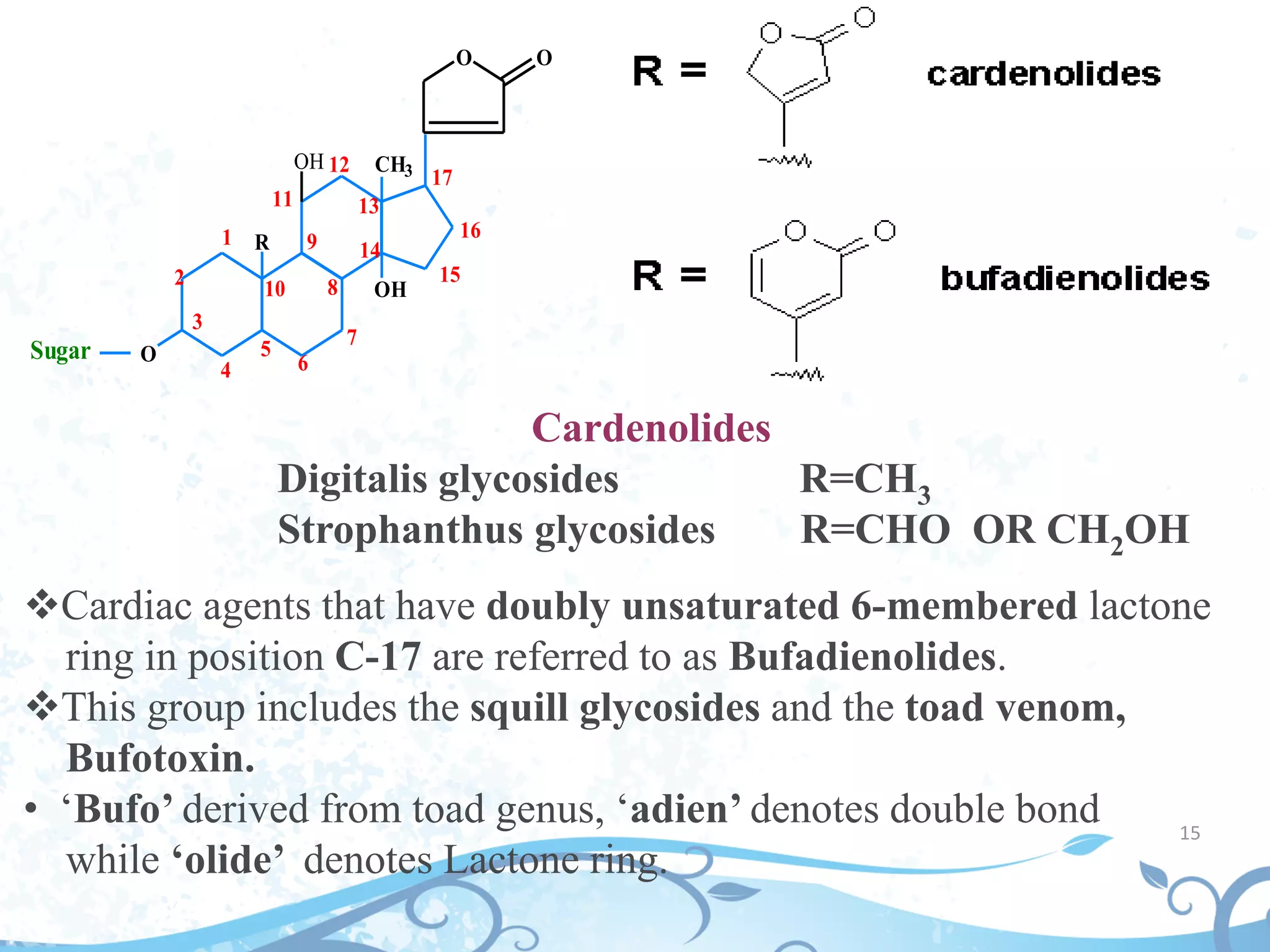
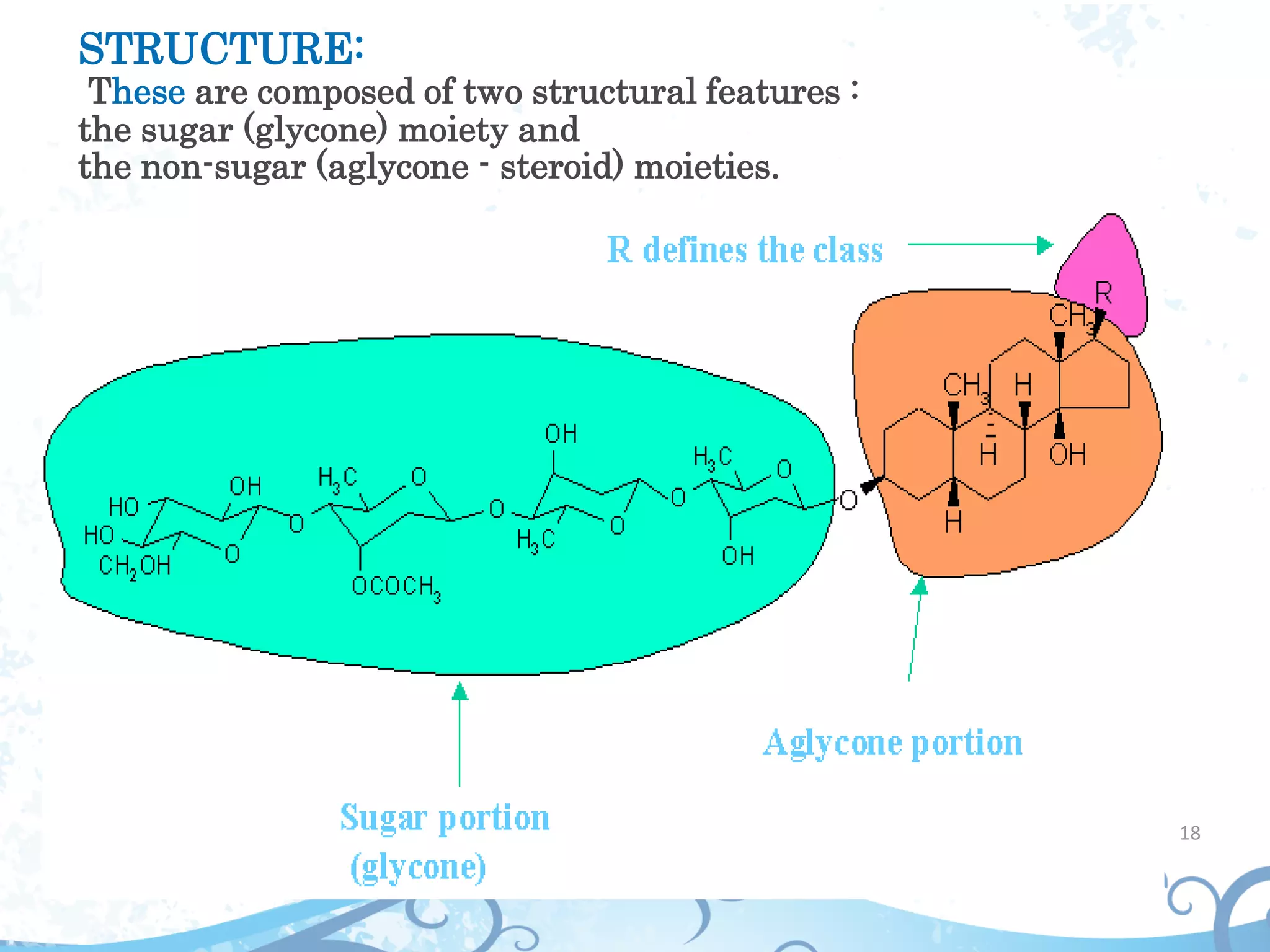
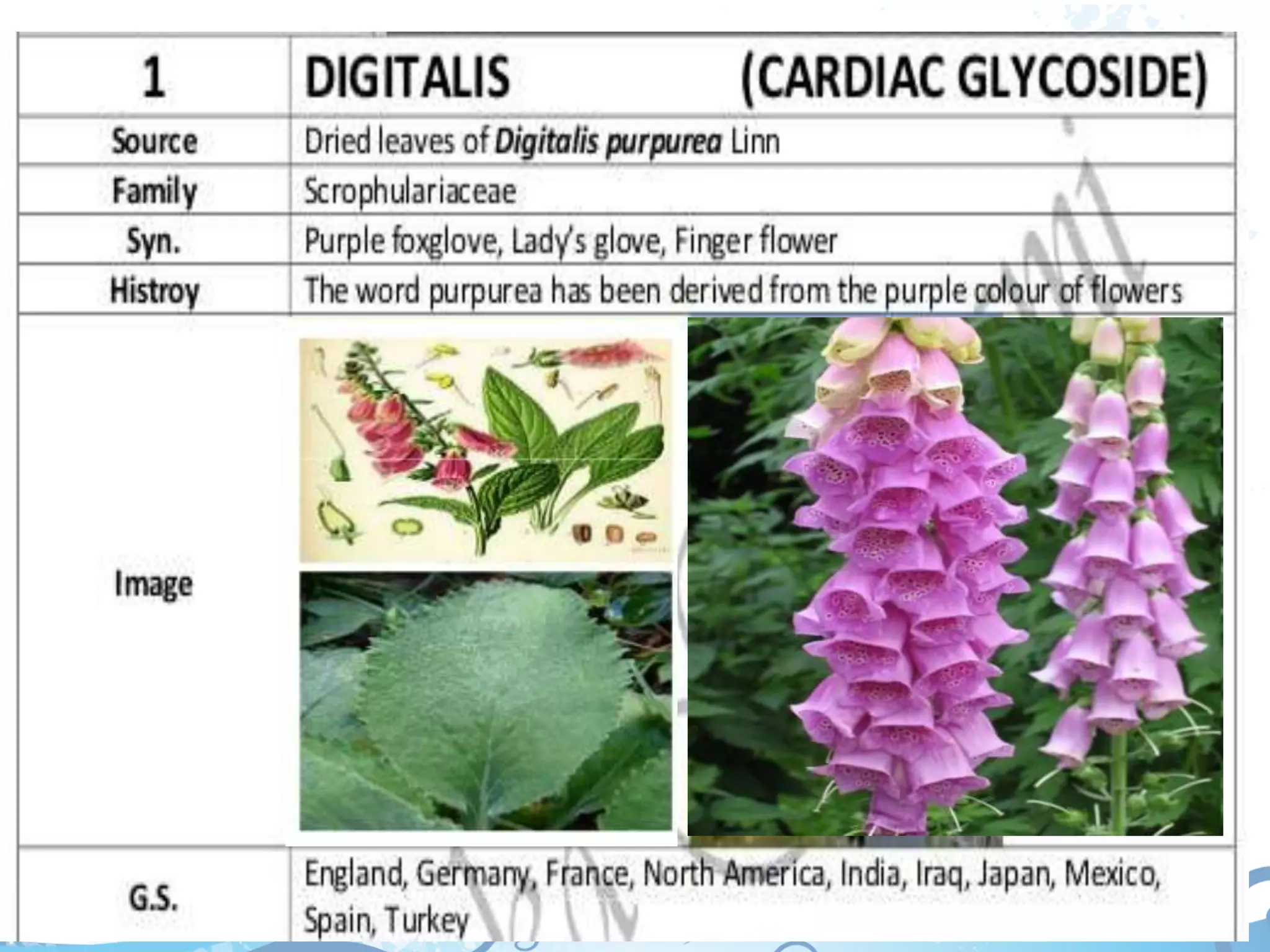
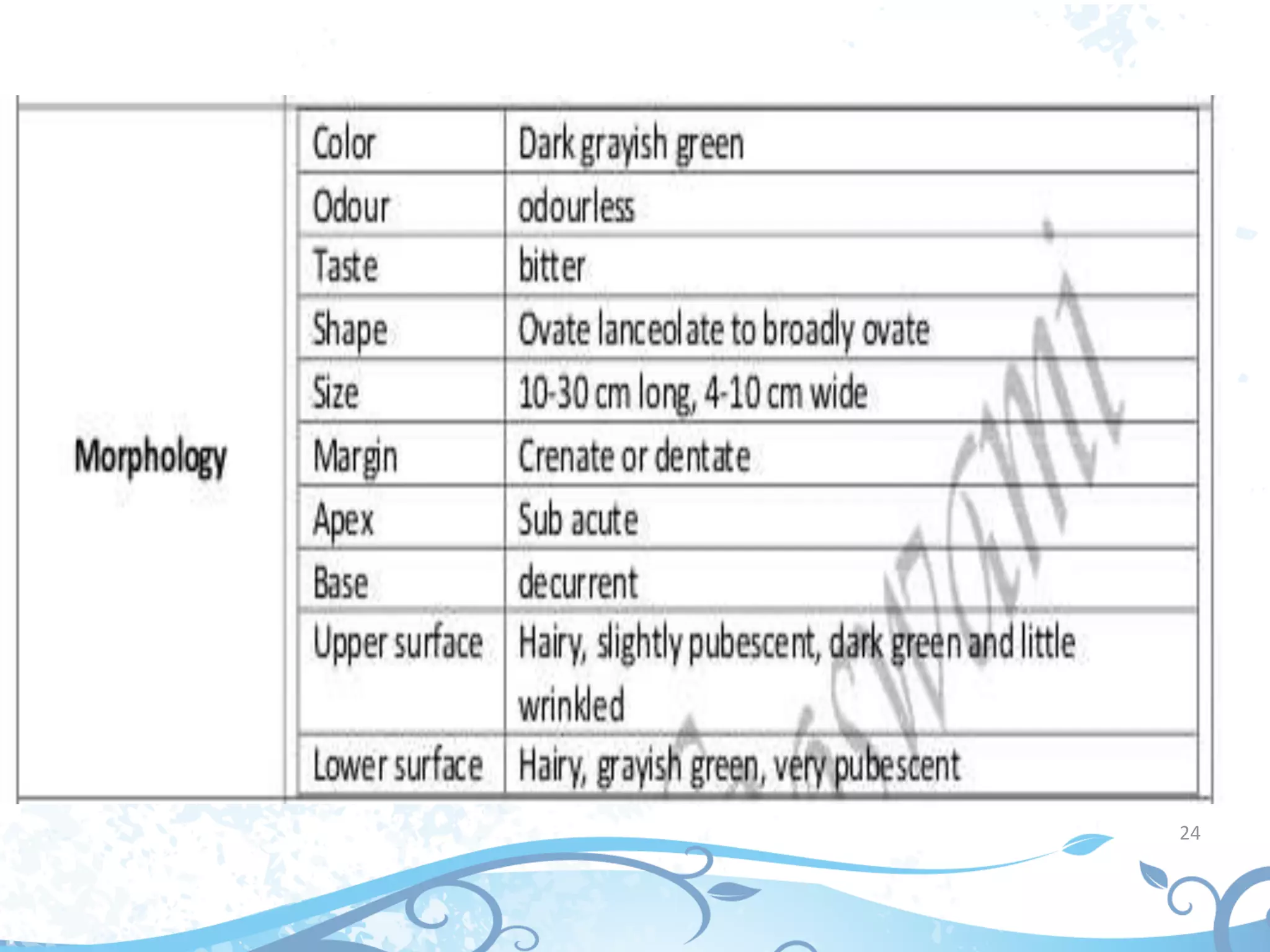
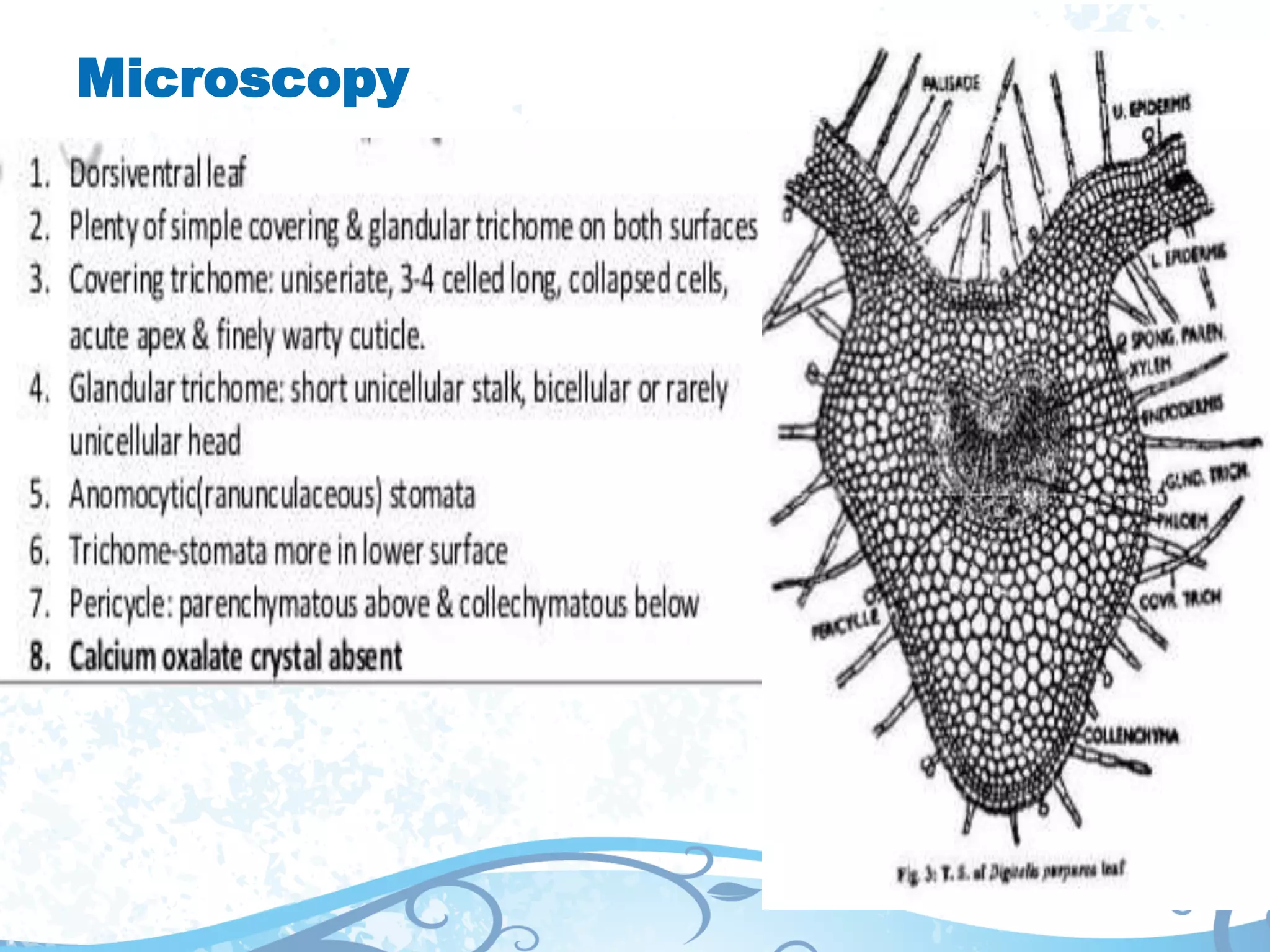
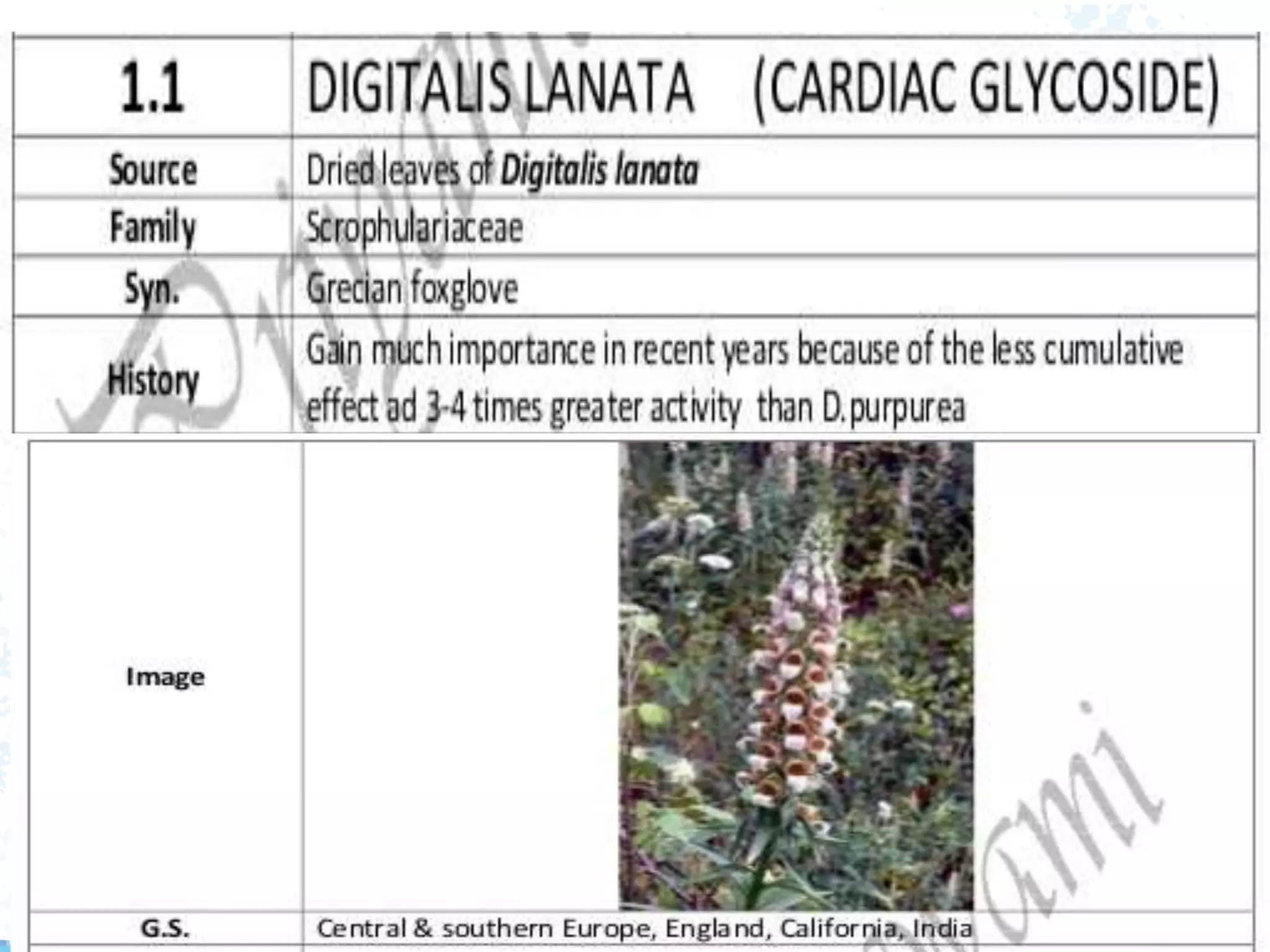
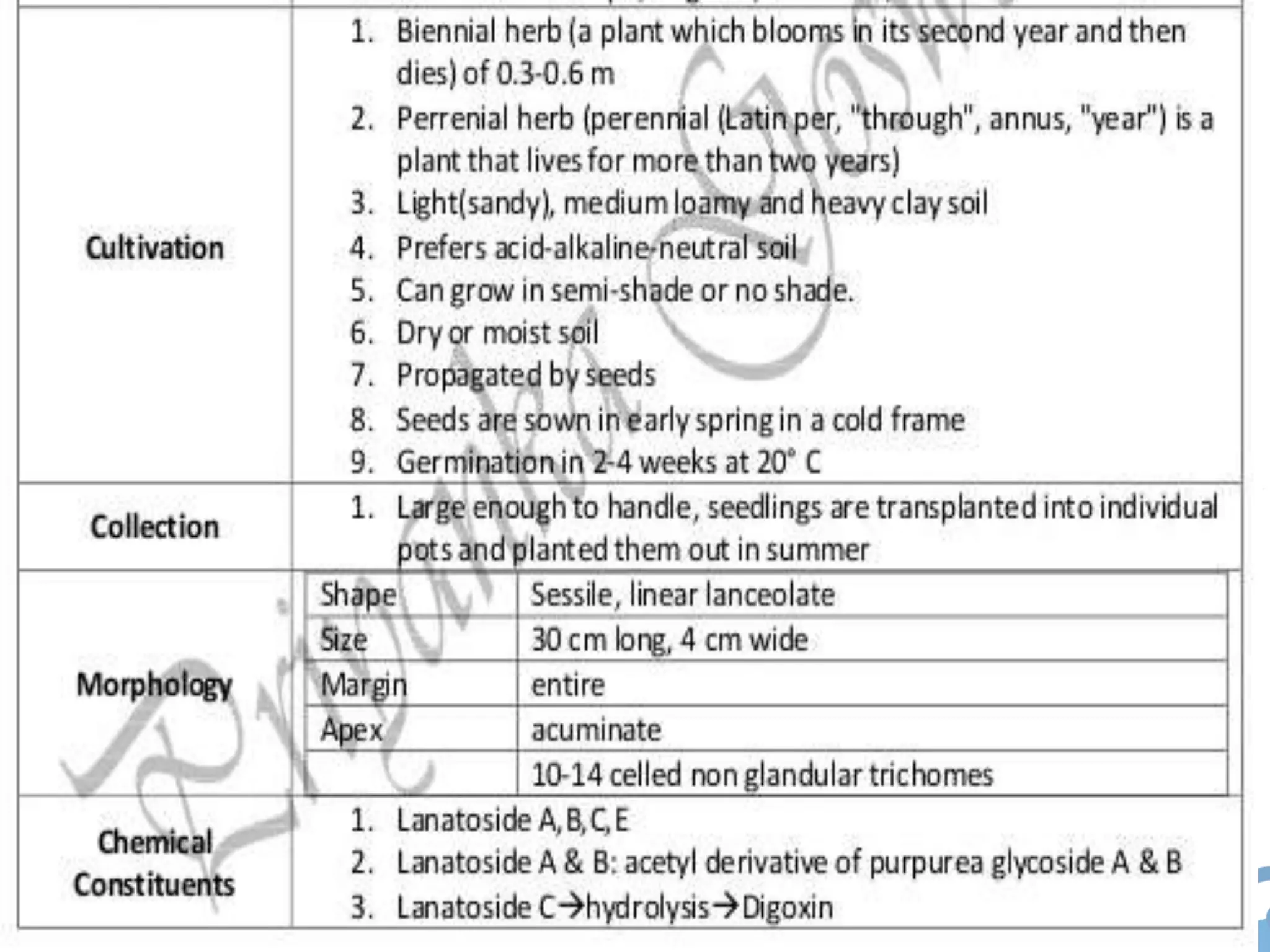
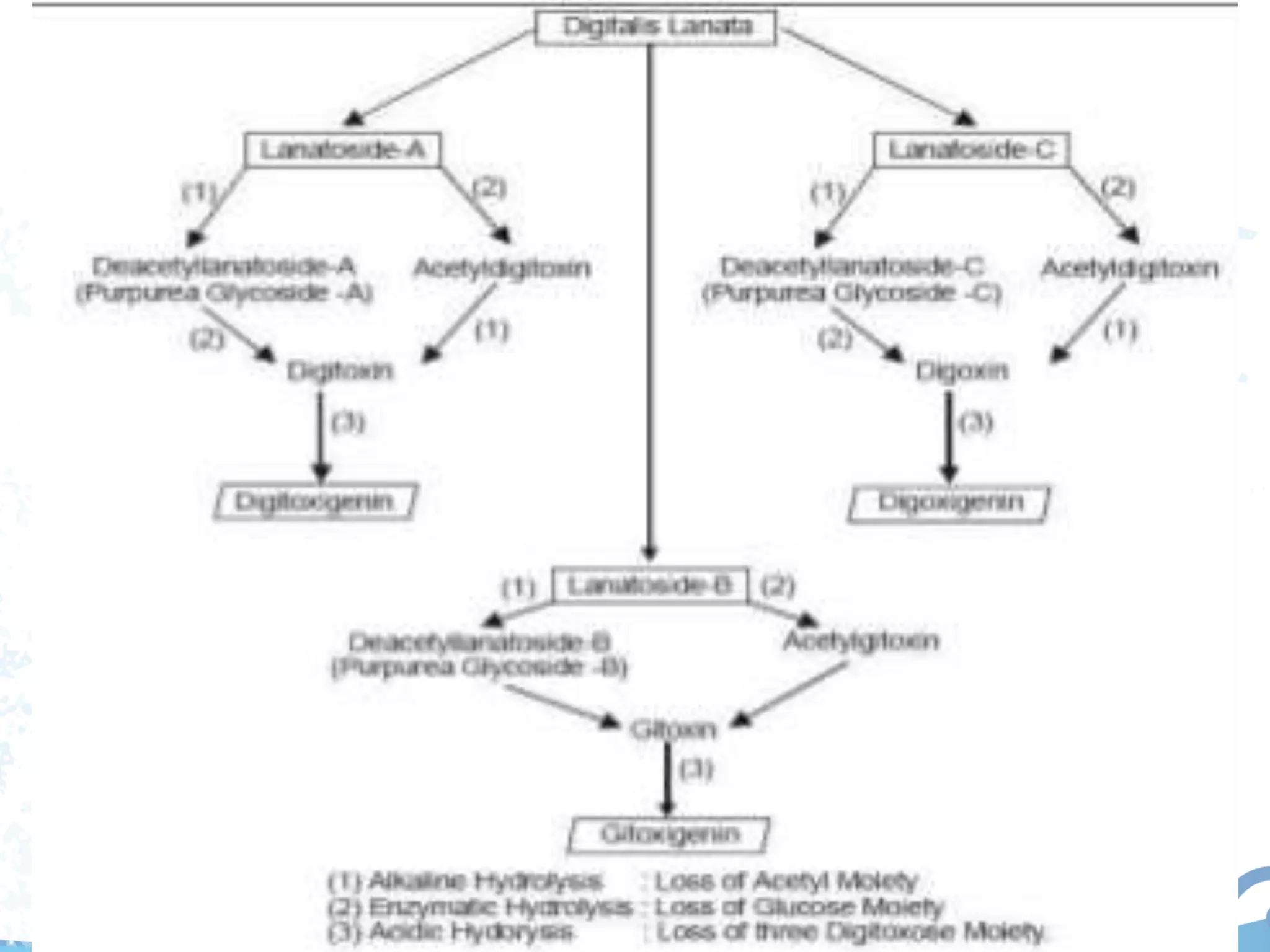
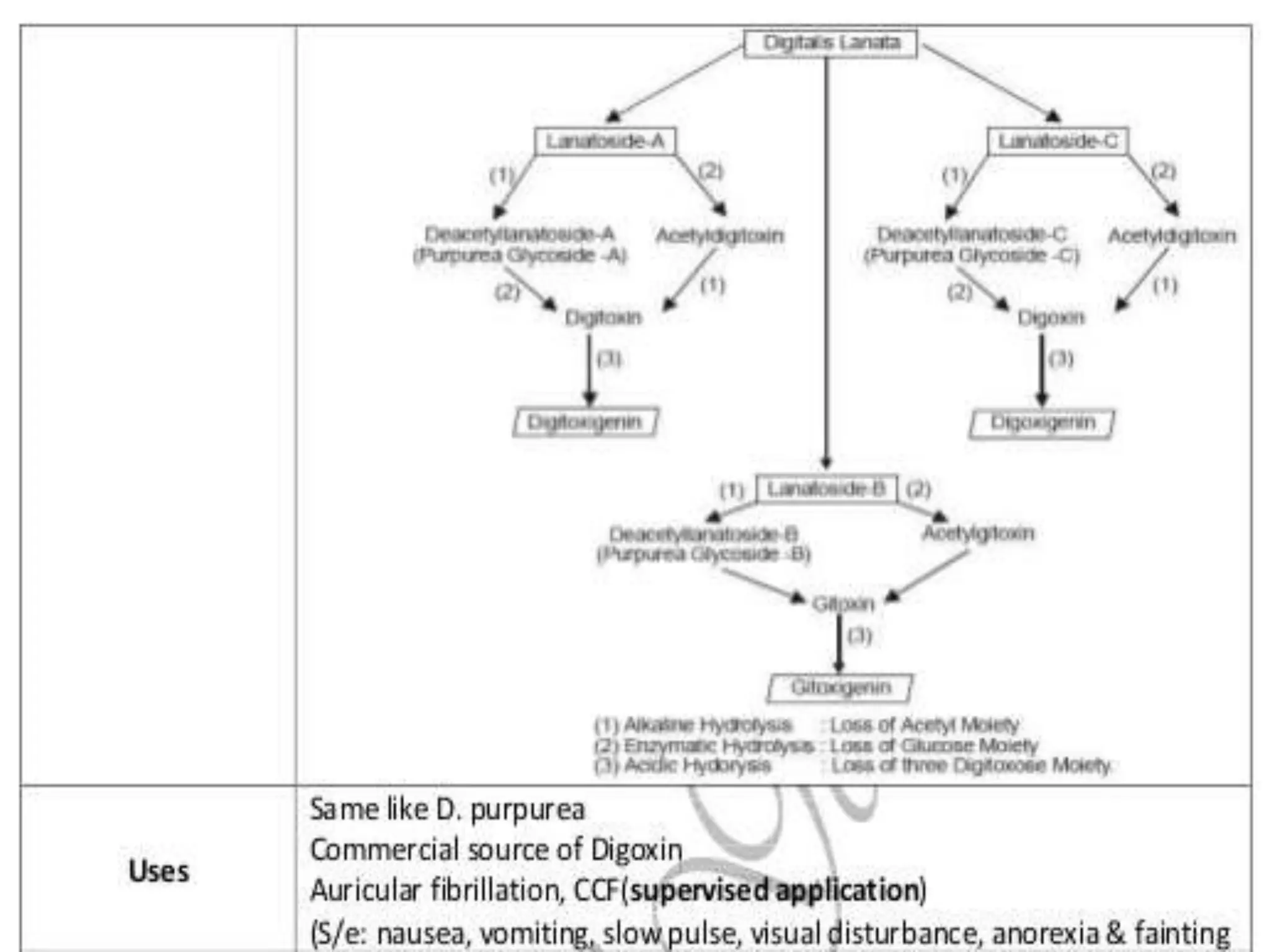
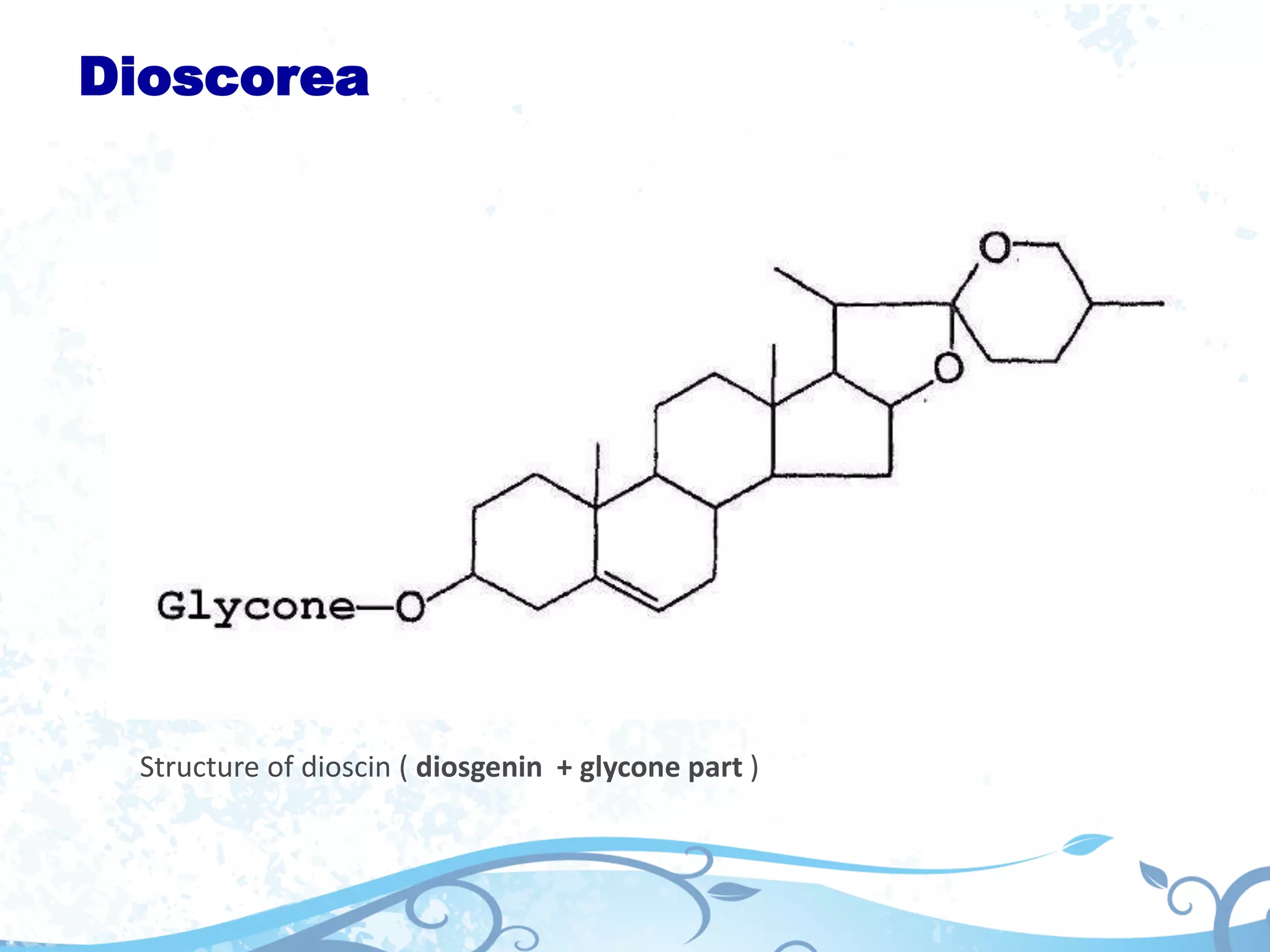
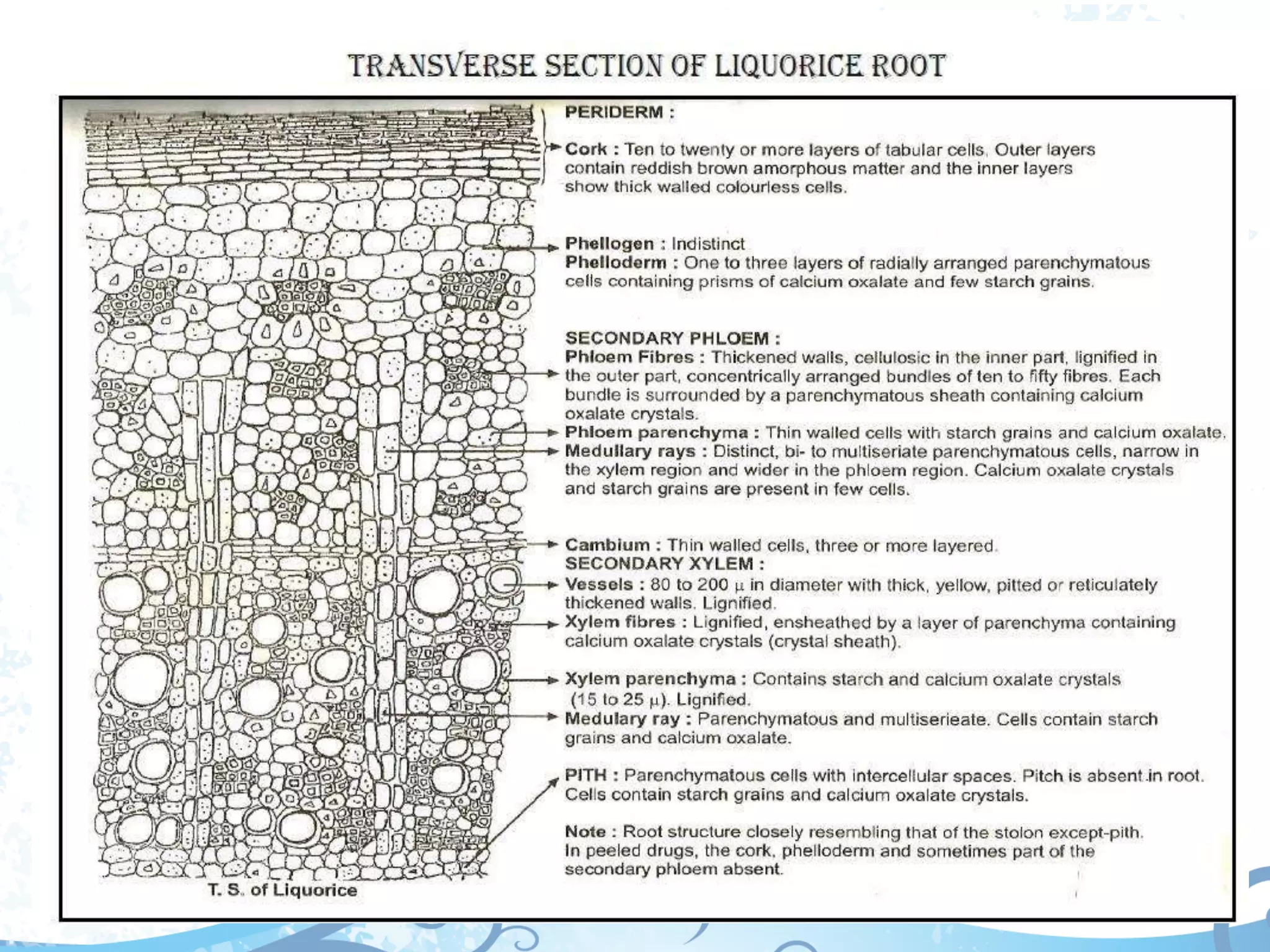
This document provides information about secondary metabolites found in plants, with a focus on cardiac glycosides. It discusses the structural features and chemical properties of cardiac glycosides like digitalis and bufadienolides. Methods for identifying these compounds include Legal's test, Baljet test, and xanthydrol test. Specific cardiac glycoside-containing plants are also summarized, such as Digitalis lanata and Dioscorea deltoidea. The document concludes with details about the morphology, cultivation, and chemical constituents of liquorice root.