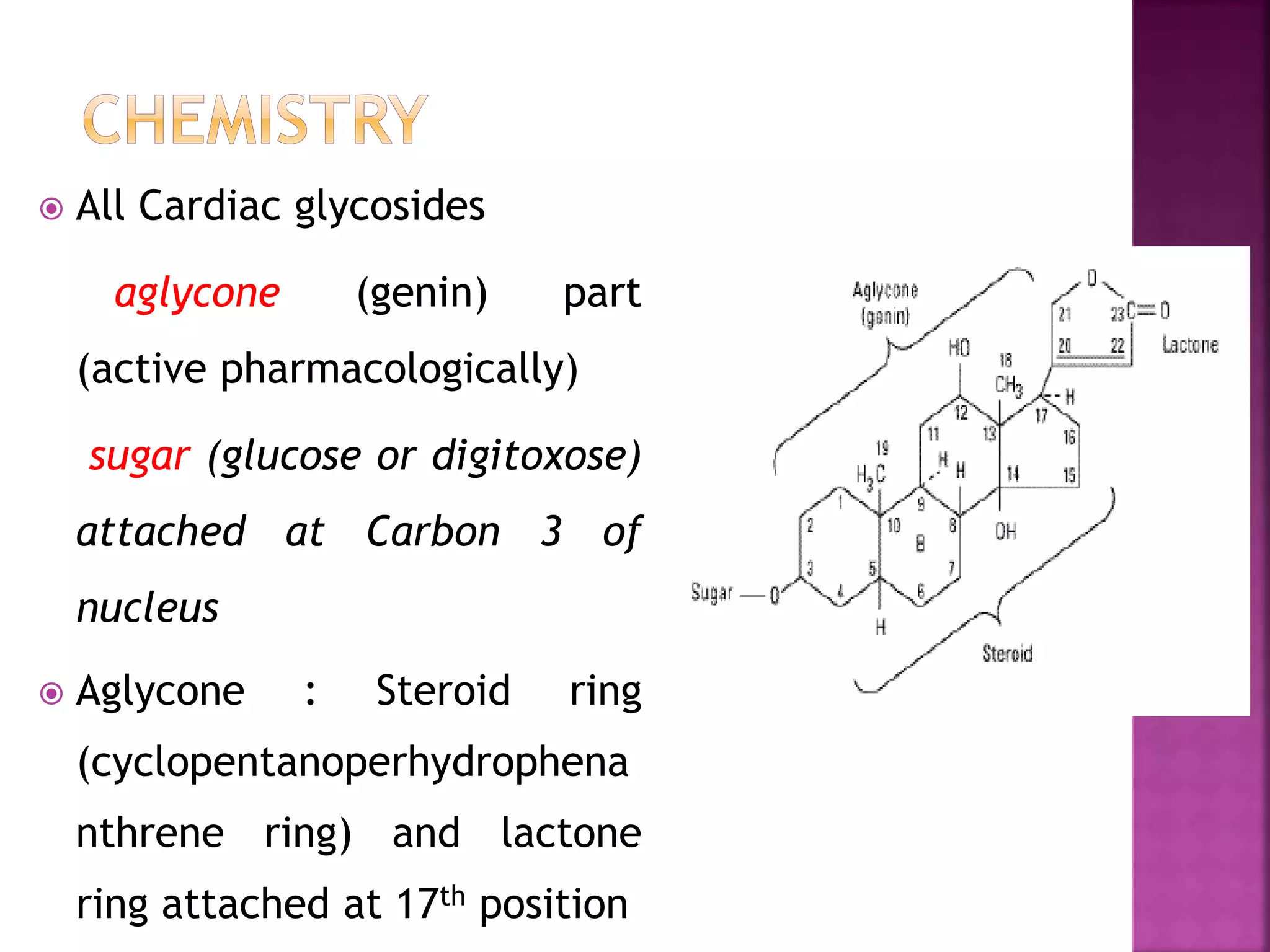
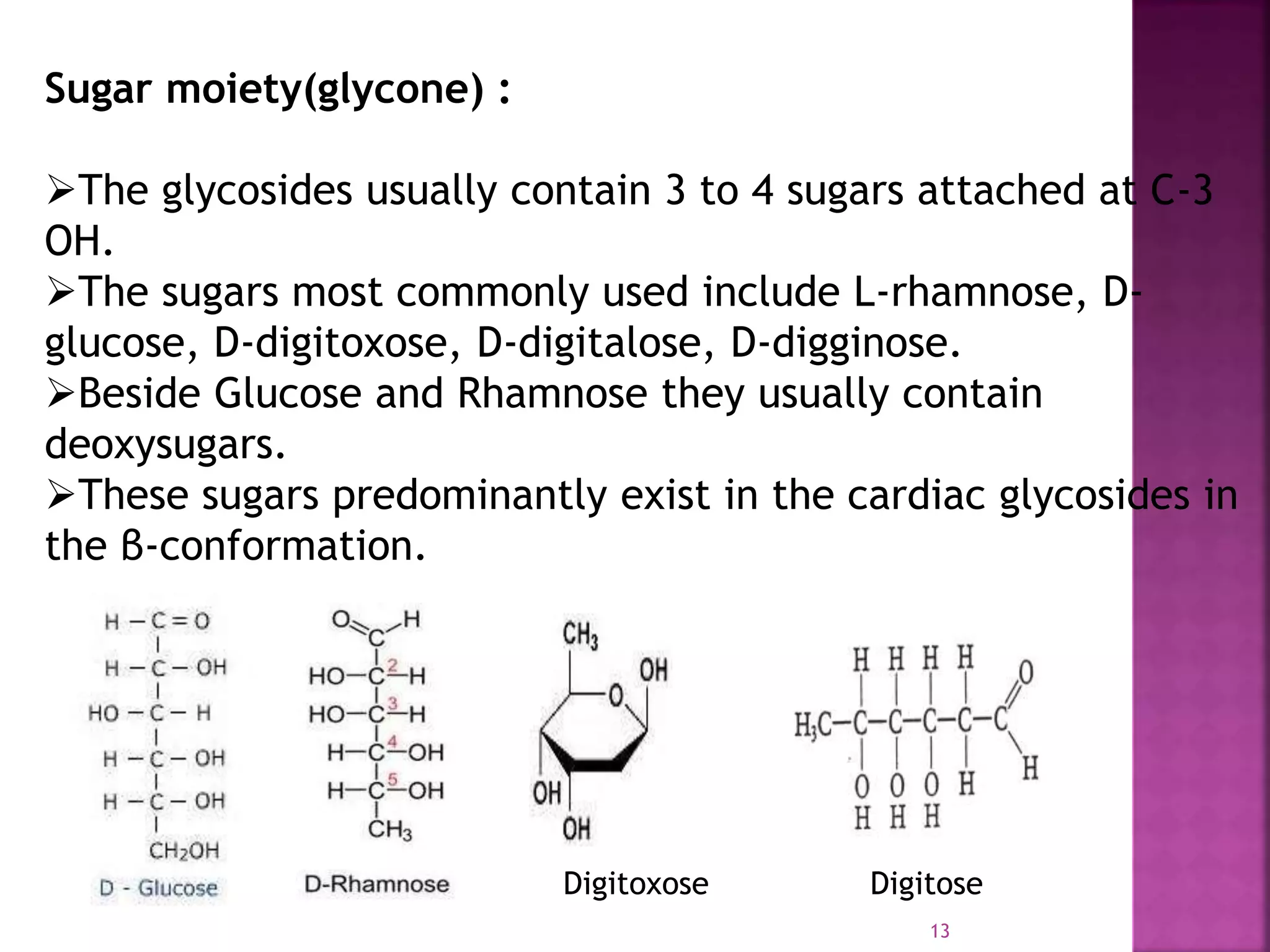
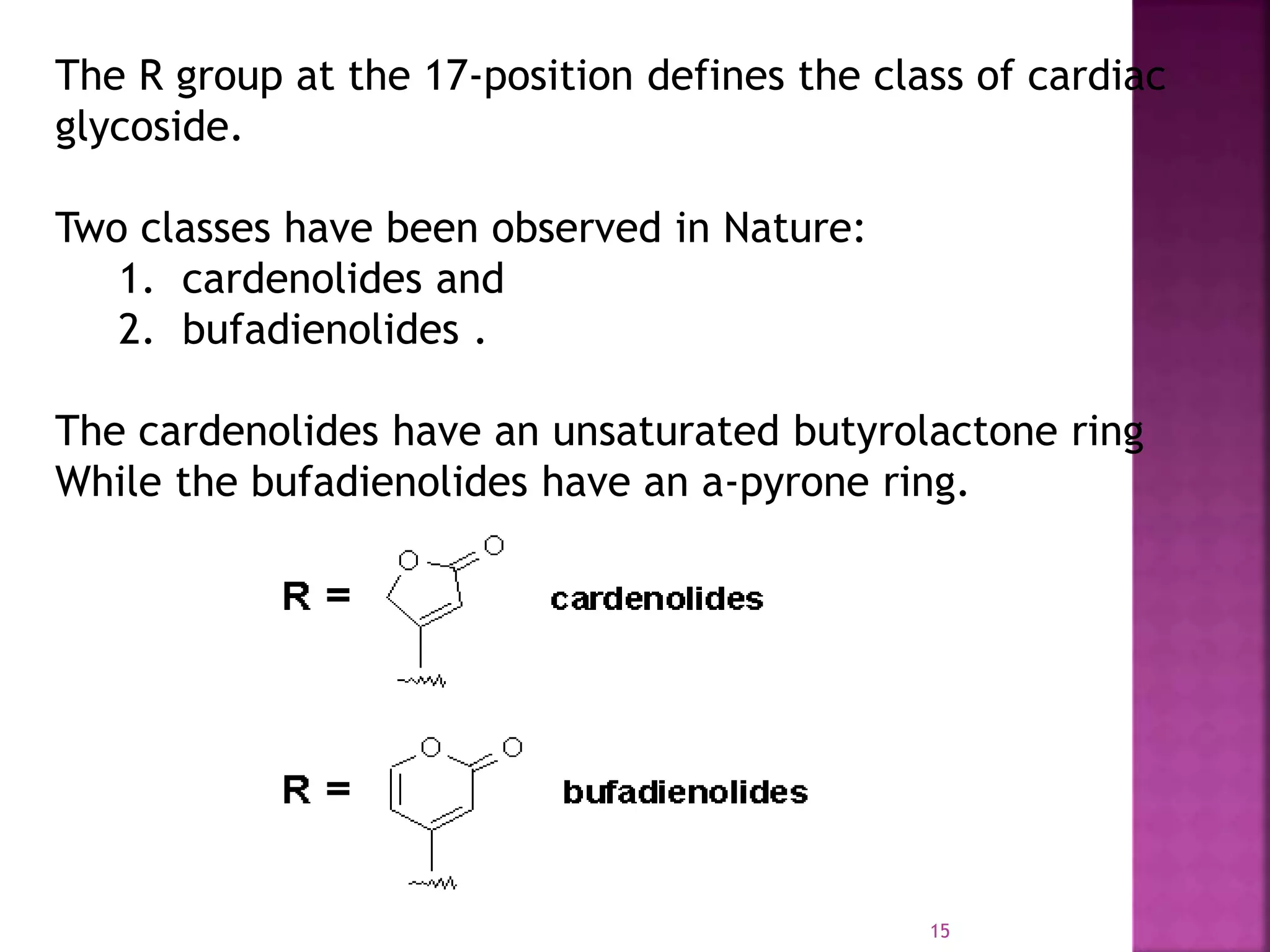
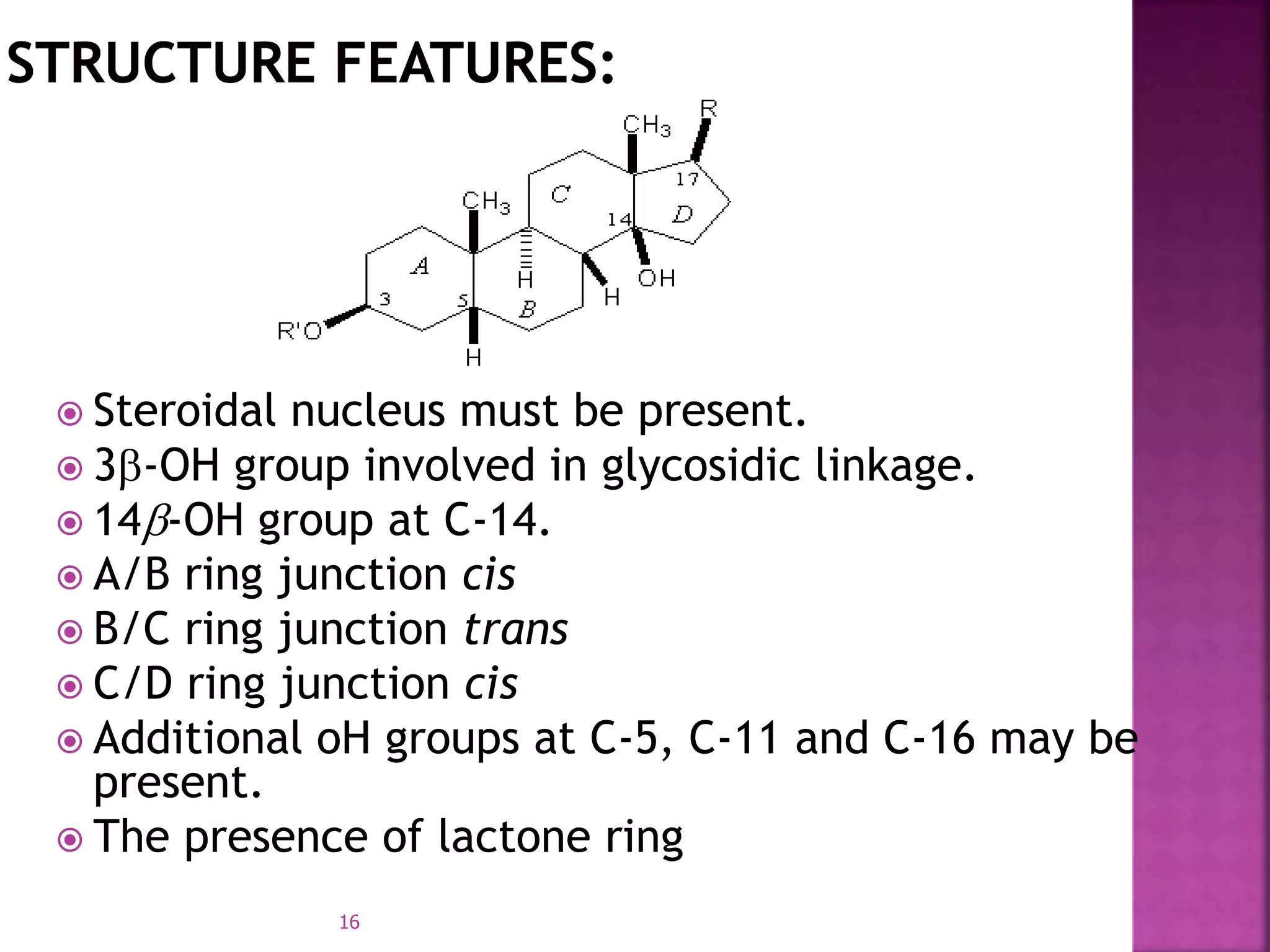
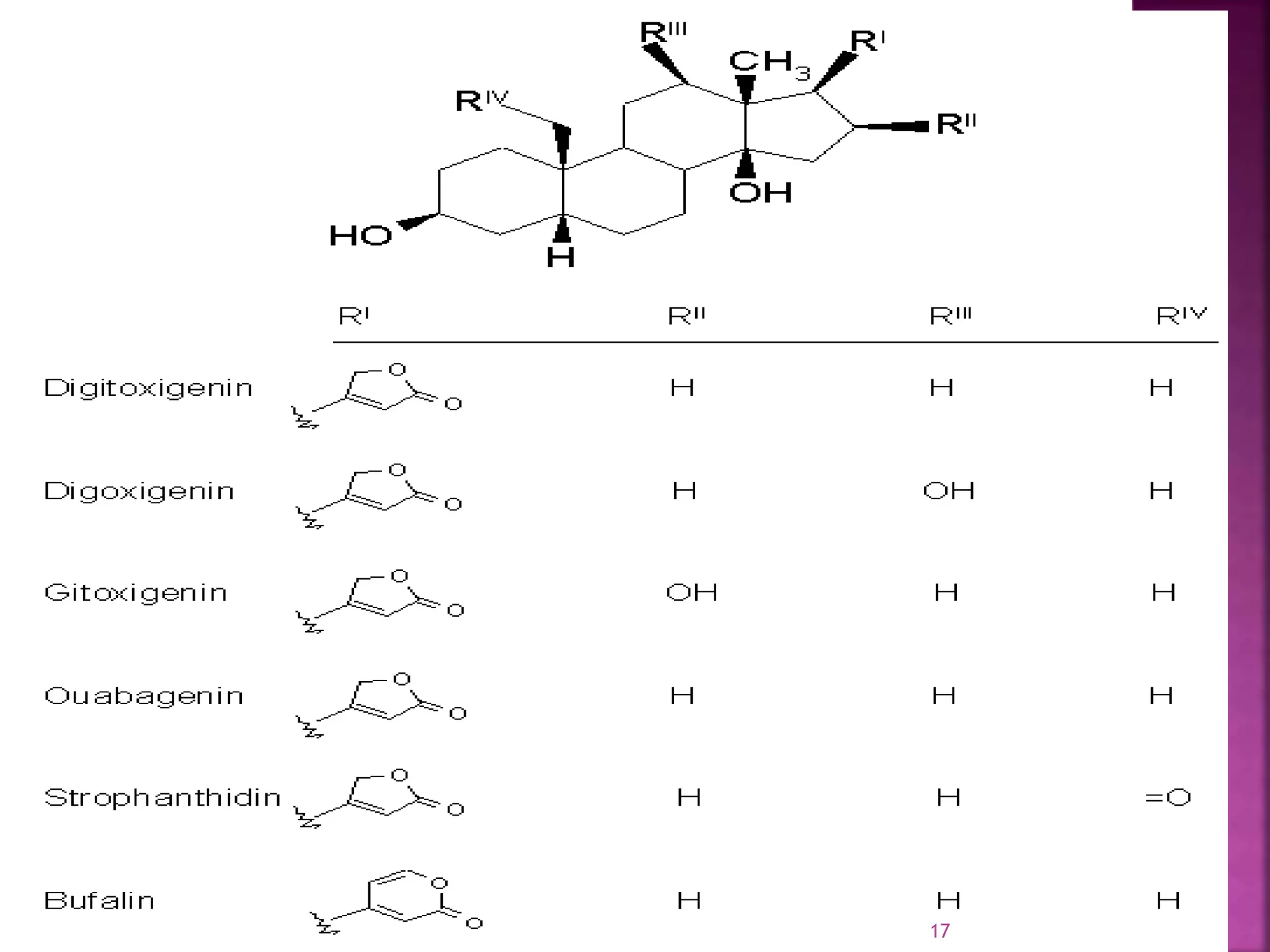
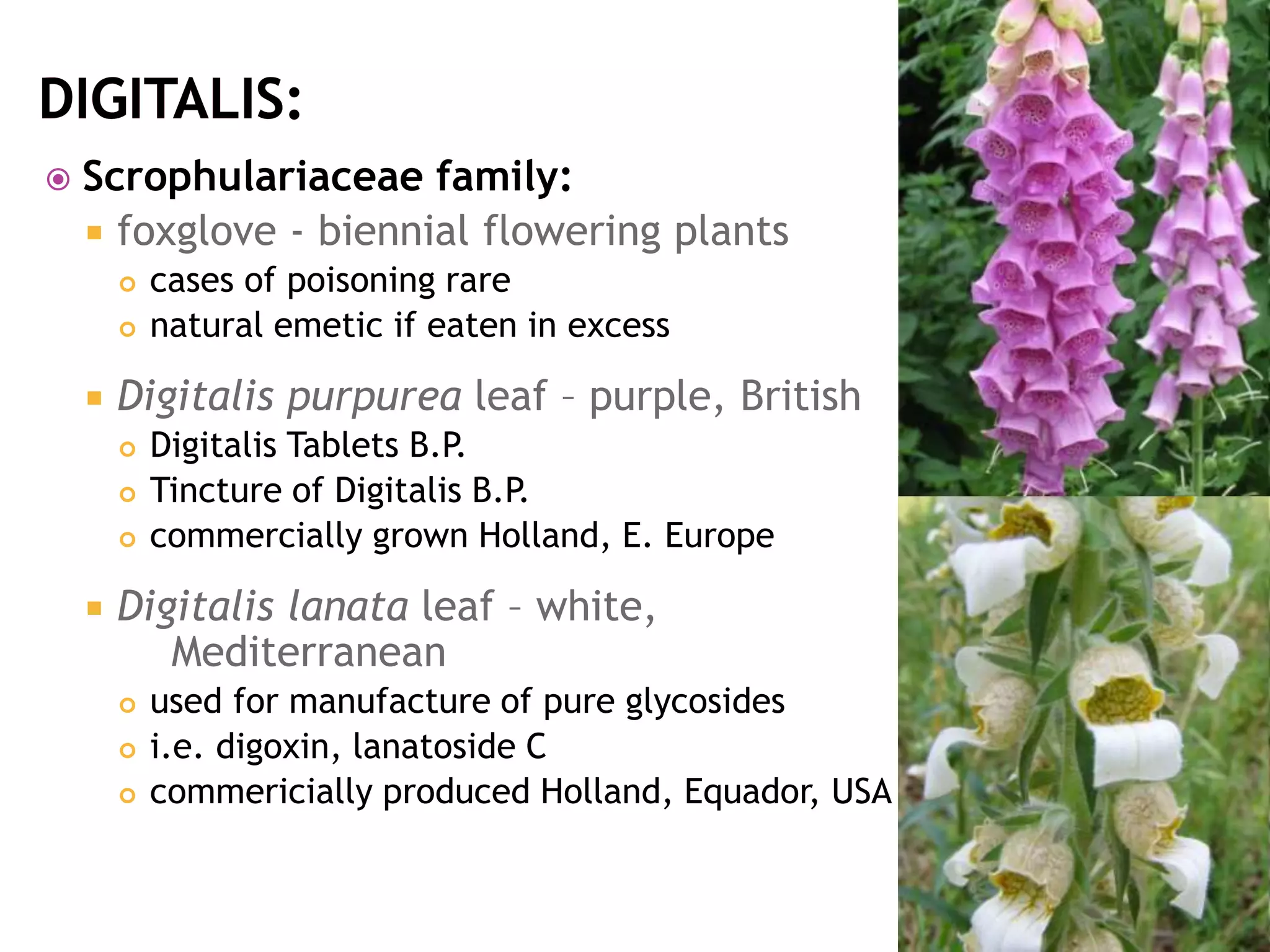
Cardiac glycosides are steroid compounds found in several plants that increase the force of contraction of the heart muscle. They increase cardiac contractility and output without increasing oxygen consumption or heart rate. Digitalis purpurea and Digitalis lanata are sources of medically important cardiac glycosides like digoxin and digitoxin. These glycosides have an aglycone steroid nucleus and sugars attached. They are used to treat congestive heart failure.














![ compounds belong to
cardenolide series
5 membered lactone ring
approx 96 compounds
[1930-1950 Stroll
worked on structures]
R1 R2 Names 1y 2y
H H digitoxigenin A A digitoxin
H OH gitoxigenin B B gitoxin
OH H digoxigenin C C digoxin
OH OH diginatigenin D D diginatin
H formylester gitaloxigenin E E gitaloxin
21
*
* Acetyl group
confers crystalline
properties - makes
compounds more
easily isolated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiacglycosides-230413062821-a41f8ce8/75/Cardiac-Glycosides-ppt-5th-sem-ppt-21-2048.jpg)




