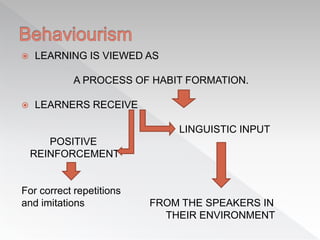
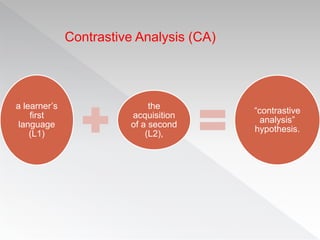
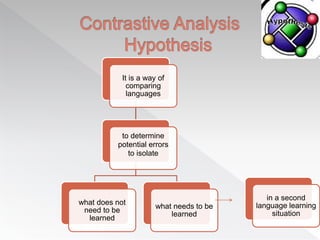
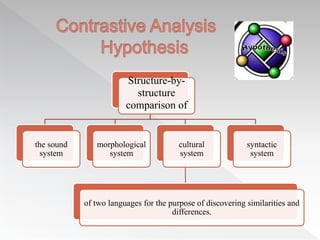
The document discusses several factors that influence second language acquisition, including the role of the learner's environment and innate characteristics. It describes learning as a process of habit formation, where learners receive positive reinforcement from speakers in their environment for correctly repeating and imitating the target language. The Contrastive Analysis Hypothesis proposes that learners will have an easier time acquiring aspects of the target language that are similar to their first language, and are more likely to make errors when the first and target languages have conflicting rules, known as negative transfer. However, later research found limitations to this hypothesis and determined that language acquisition is a more complex process than simple stimulus-response models suggest.