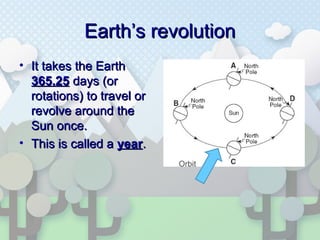
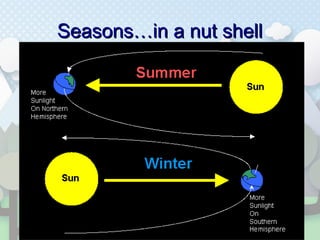
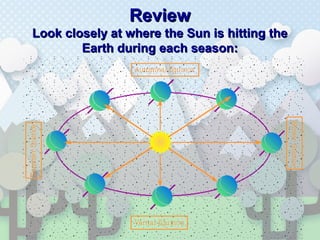
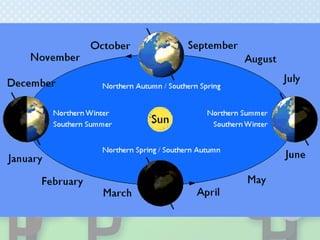
The document discusses the causes of seasons on Earth. Specifically, it explains that seasons are caused by the tilt of Earth's axis as it revolves around the sun, not by variations in Earth's distance from the sun. The tilt results in different parts of Earth receiving more or less direct sunlight throughout the year, causing the seasons of winter, spring, summer and fall in each hemisphere. Key concepts are that summer occurs when the sun's rays hit an area more directly, and winter occurs when the sun's rays hit an area at an extreme angle.