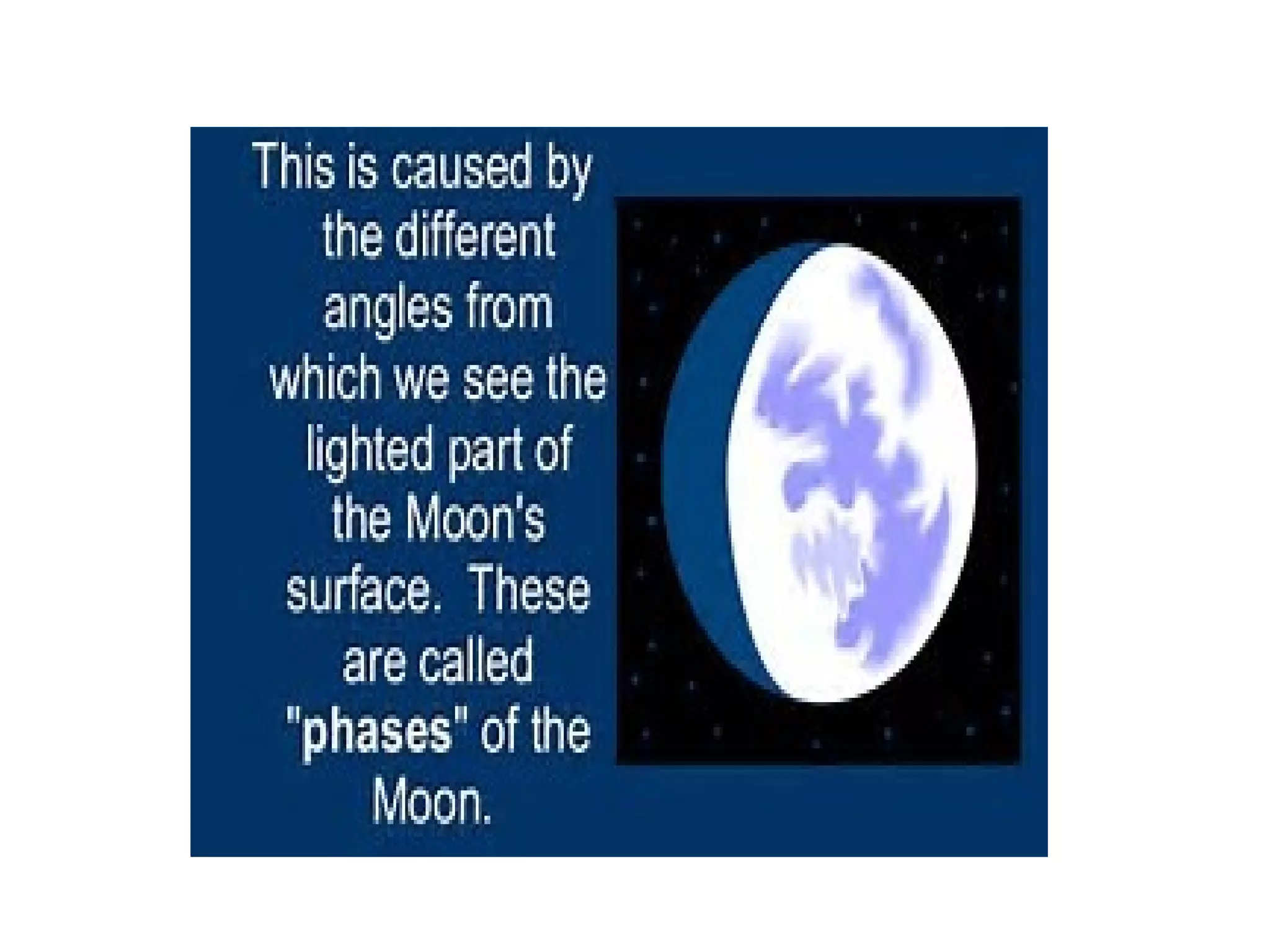
This document discusses the relationships between the Earth, Sun, and Moon, and how they affect day and night, years, and seasons. It explains that the Earth's rotation on its axis causes day and night, with a full rotation taking 24 hours. It also explains that the Earth revolves around the Sun over the course of 365 days, which divides the year into four seasons due to the tilt of the Earth's axis. Finally, it discusses how the Moon revolves around the Earth over 29 days, and how the changing positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon cause the Moon's phases.