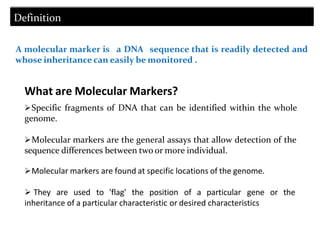
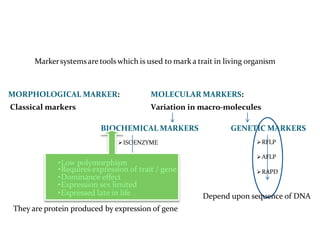
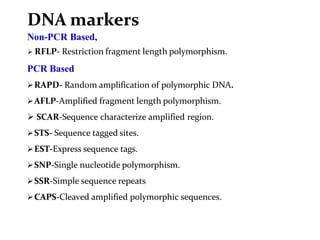
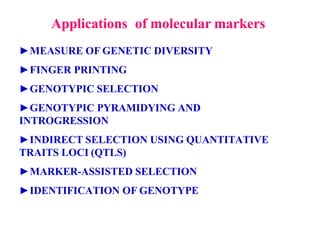
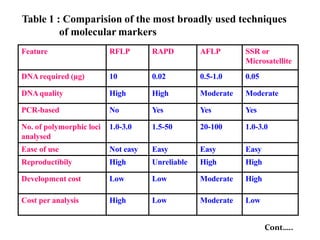
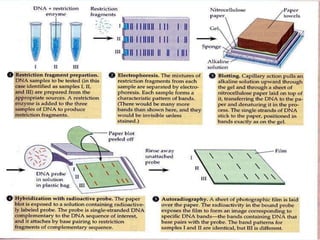
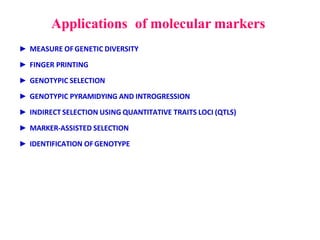
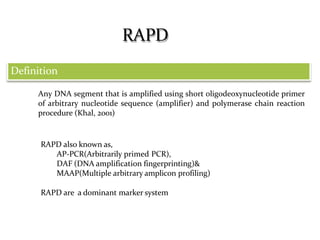
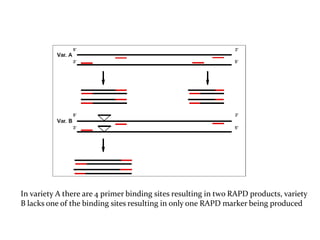
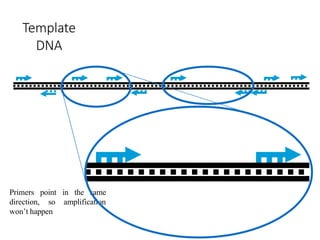
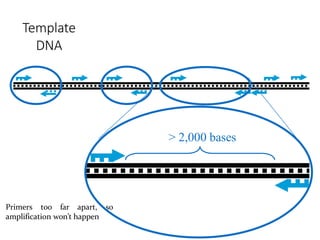
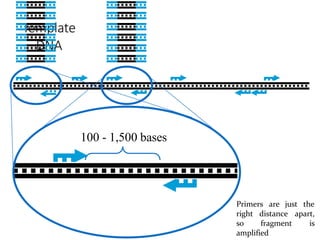
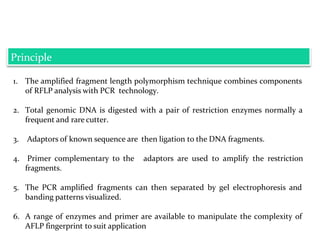
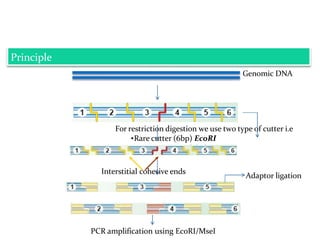
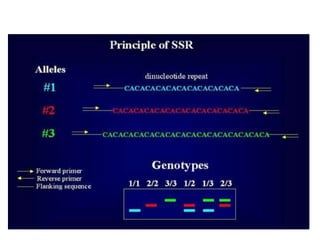
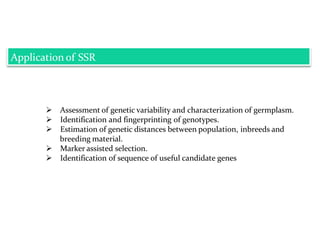
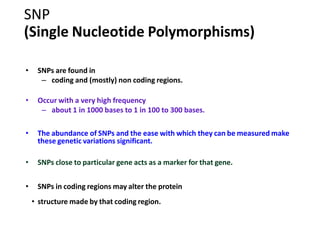
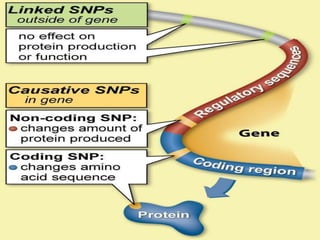
Molecular markers are DNA sequences that can be used to identify specific locations in the genome. They allow detection of differences between individuals. Common types of molecular markers include RFLP, RAPD, AFLP, SSR, and SNP. RFLP uses restriction enzymes and probes but requires a large amount of high quality DNA. RAPD uses PCR with random primers and needs little DNA but has low reproducibility. AFLP combines restriction enzymes and PCR for higher reproducibility. SSR and SNP detect differences in repetitive DNA sequences and single nucleotides, respectively. Molecular markers have various applications including measuring genetic diversity, fingerprinting, marker-assisted selection, and identifying genotypes.