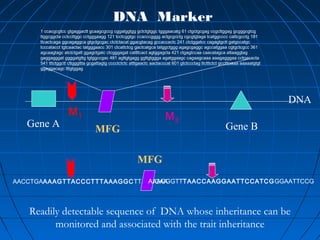
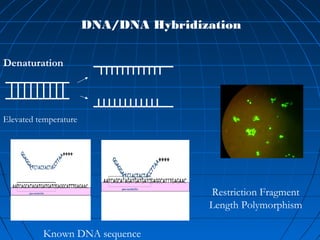
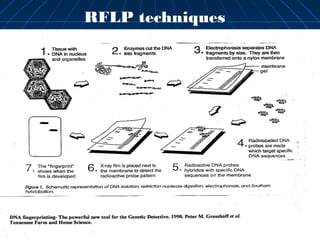
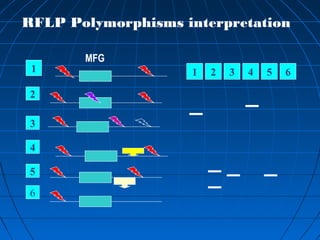
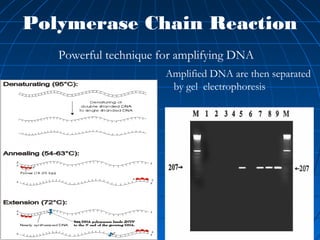
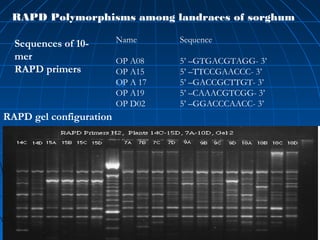
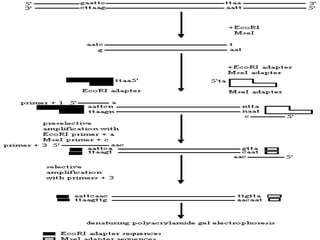
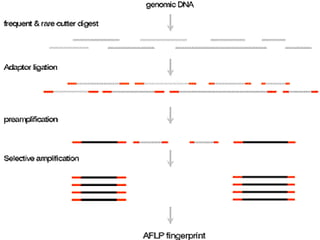
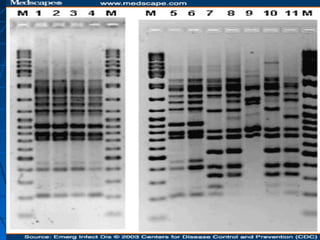
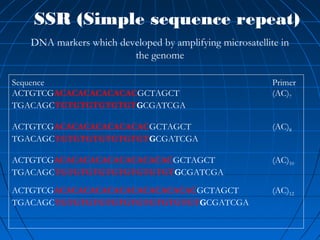
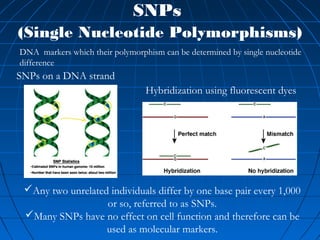
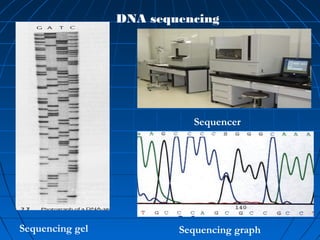
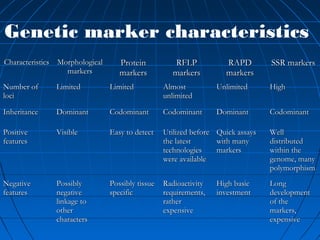
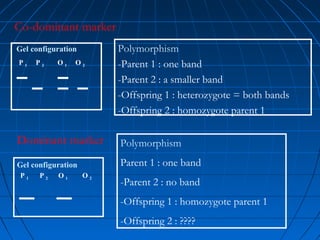
This document discusses genetic markers used in plant breeding. It defines genetic markers as any phenotypic difference controlled by genes that can be used to study inheritance or select for traits. The document describes two main types of genetic markers - morphological markers which are visible traits, and molecular markers which are detected at the DNA level. It provides details on various molecular marker techniques including RFLP, RAPD, AFLP, SSRs, and SNPs. It explains how each technique works and its advantages and disadvantages. The key information is that genetic markers are tools that allow studying inheritance of genes and selecting plants for breeding based on associated genetic differences.