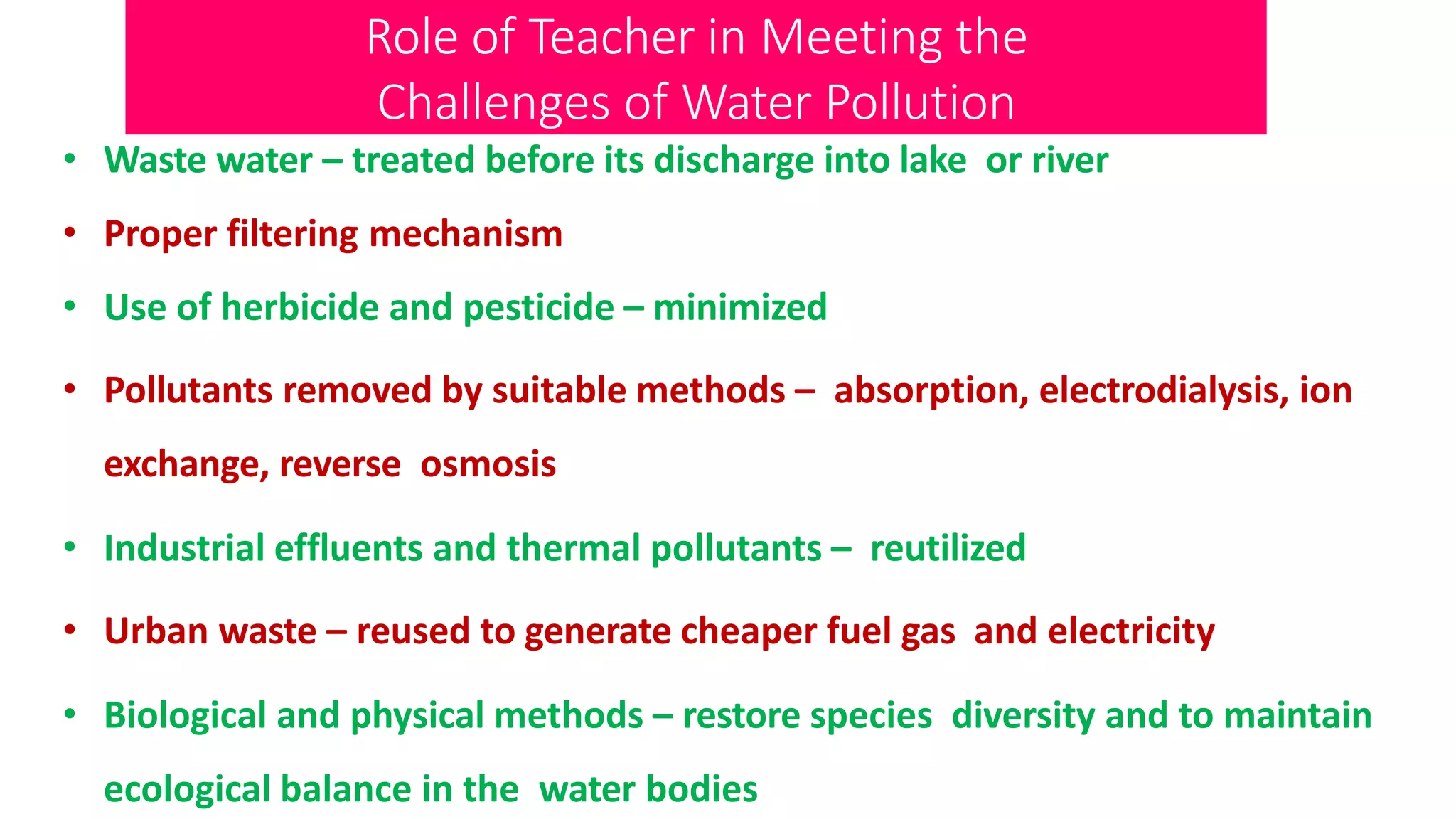
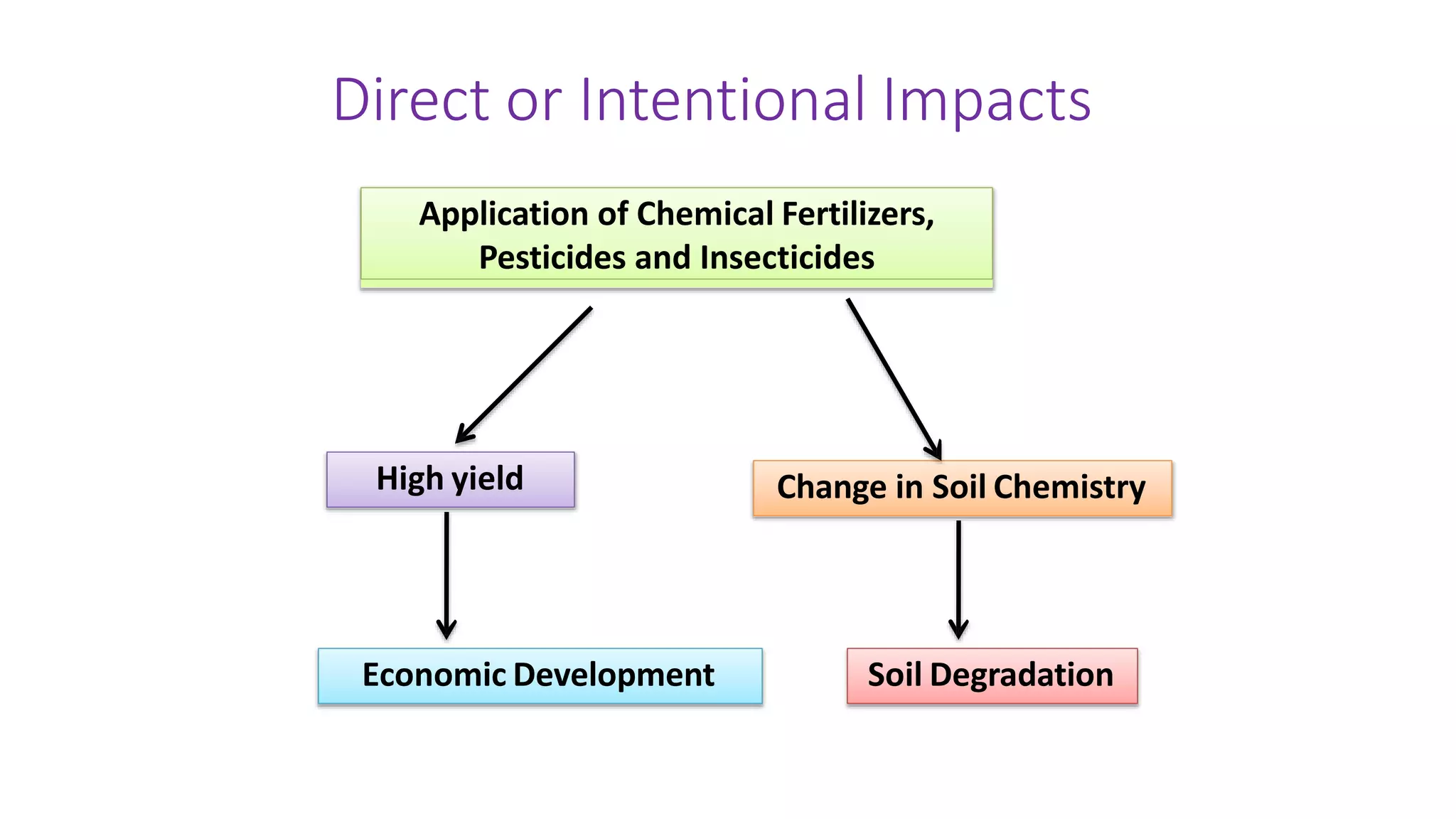
The document discusses the scope of environmental education, highlighting the teacher's role in addressing air, water, land, and noise pollution through various conservation strategies and community involvement. It outlines specific actions such as reforestation, reducing pesticide use, and promoting sustainable practices to combat environmental degradation. Additionally, it emphasizes the detrimental effects of pollution on health and the ecosystem, including respiratory disorders, soil degradation, and the greenhouse effect.