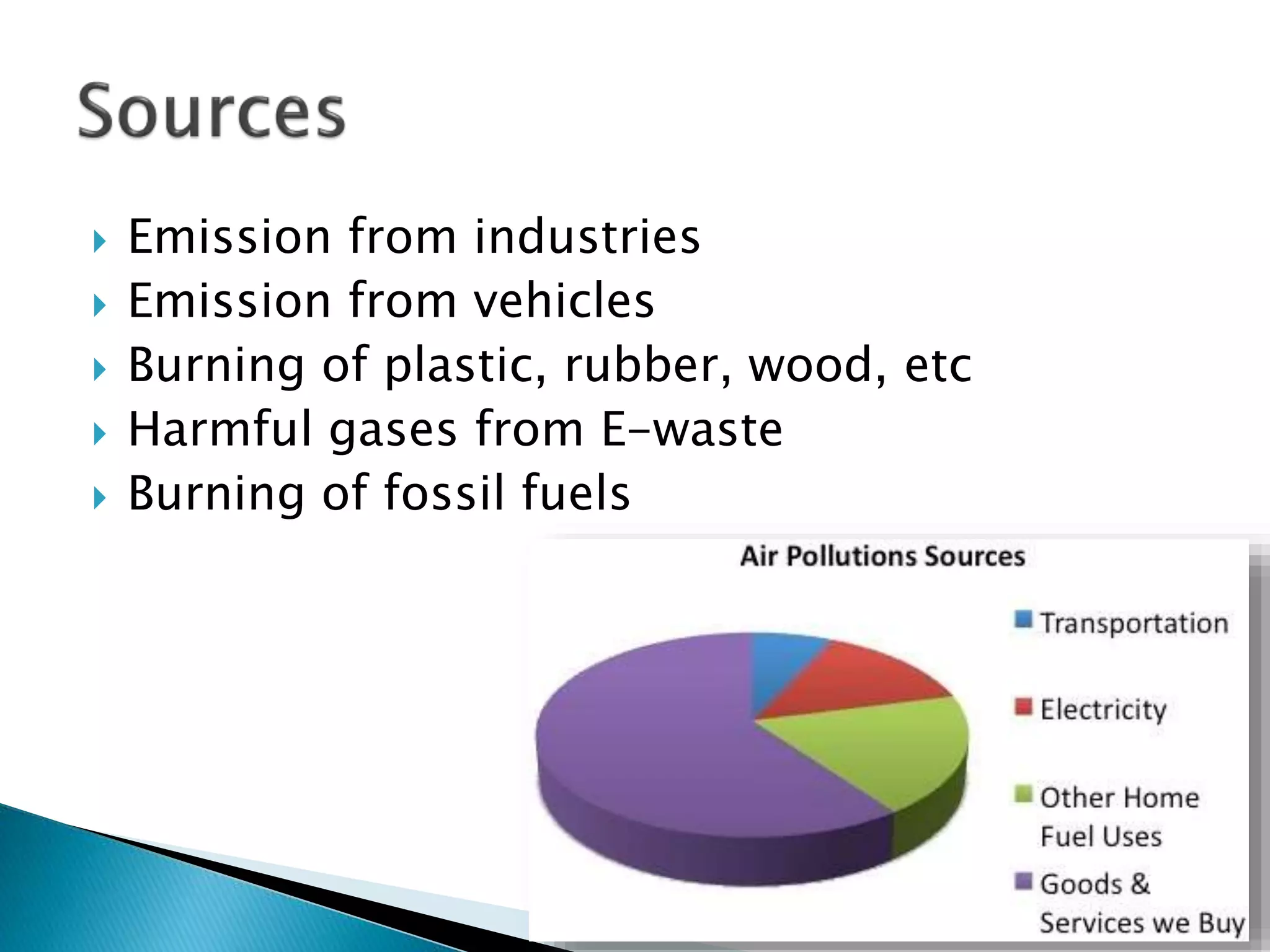
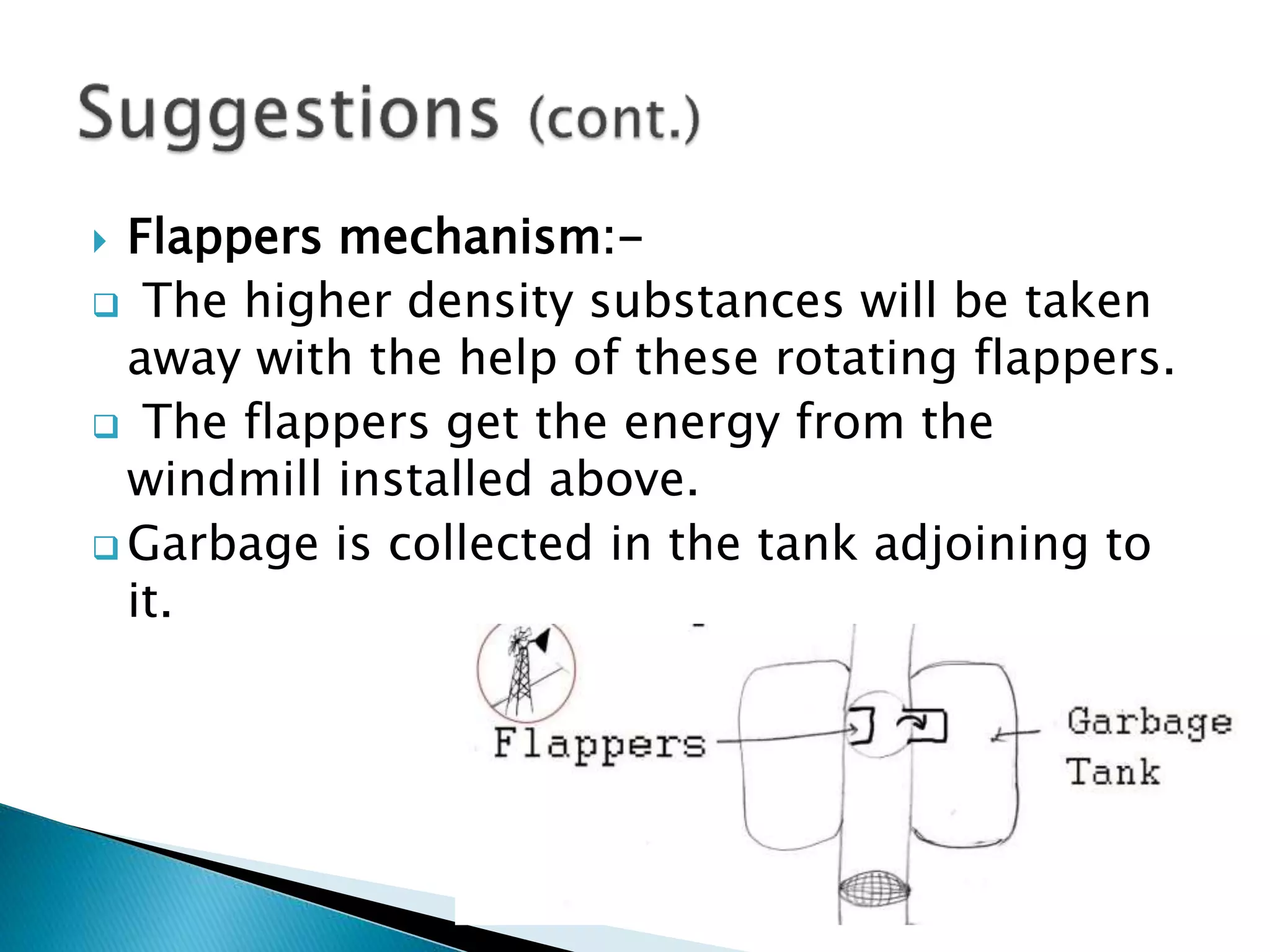
The document discusses different types of pollution including air, water, soil, noise pollution. It provides causes and effects of each type of pollution. It also suggests various solutions to tackle each type of pollution such as use of electric vehicles and catalytic converters for air pollution, rainwater harvesting and use of alum/chlorine for water pollution, reducing fertilizer use and reforestation for soil pollution, and using sound barriers and noise-proofing materials for noise pollution. The document emphasizes the importance of reducing all kinds of pollution for environmental protection and sustainability.