Here are potential responses to the questions:
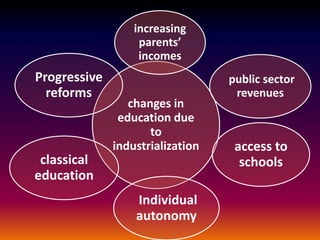
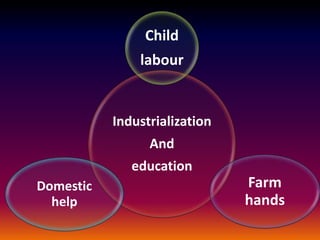
Industrialization led to changes in education by increasing access through higher parental incomes and public funding. It decreased child labor as kids stayed in school. It led to more progressive reforms away from classical education focused on rote learning towards developing critical thinking skills.
Democracy impacted education by promoting equal opportunities, universal education, and consideration of individual differences. It led to more child-centered, social, cooperative learning approaches. Democratic methods of teaching and school administration were adopted. Education was seen as crucial for participation in a democracy by developing literacy, confidence, and democratic attitudes.
Education and democracy complement each other. Education provides the capabilities people need to participate in a democratic society like literacy, while democracy