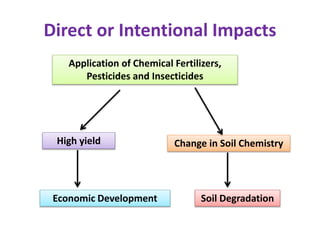
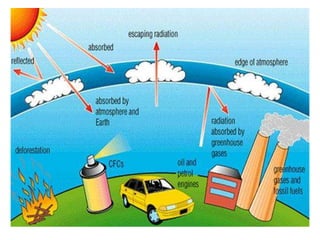
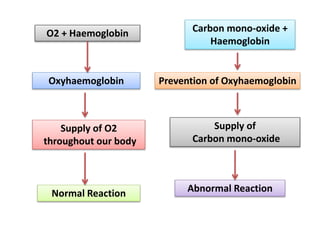
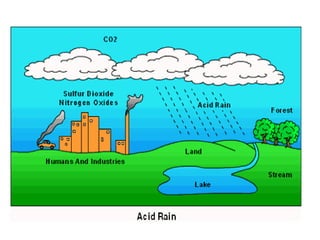
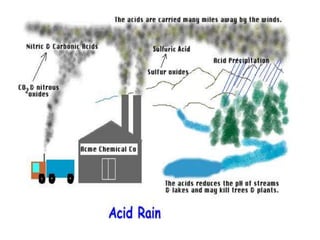
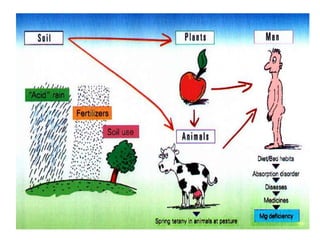
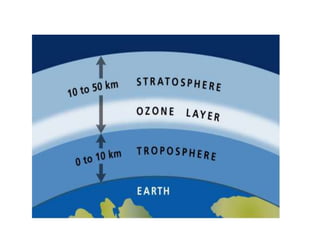
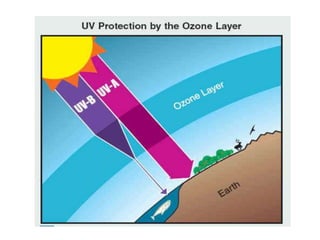
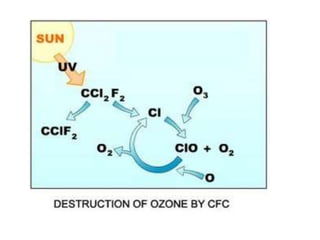
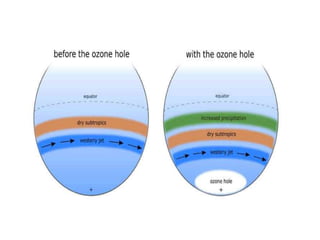
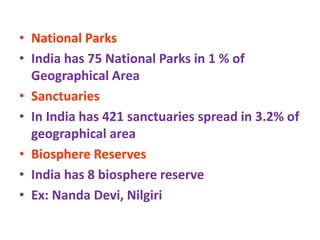
This document discusses environmental education, including its definition, meaning, need, importance, and scope. It defines environmental education as an interdisciplinary process that equips people with knowledge, attitudes, and skills to address environmental issues. The document emphasizes the need for environmental education to deal with pollution threats and educate about protecting air, water, land, and limiting noise pollution. It also outlines the role of teachers in raising awareness of environmental challenges and promoting conservation efforts.