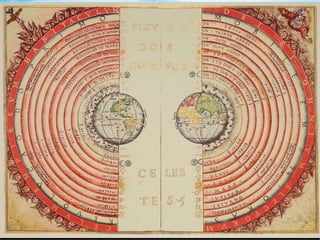
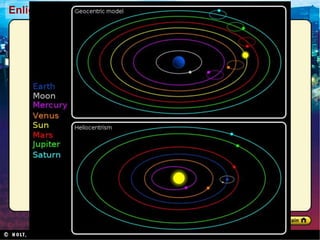
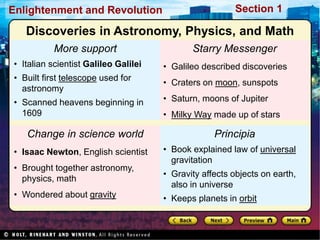
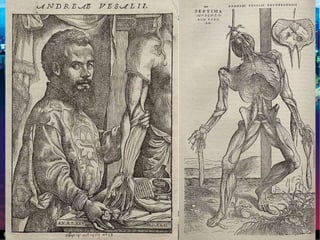
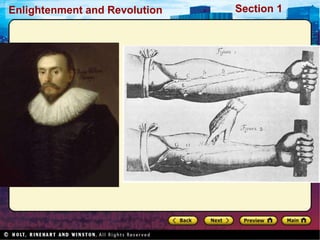
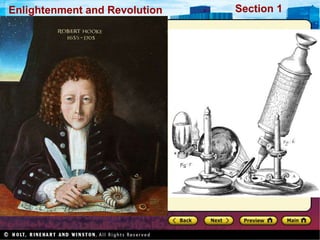
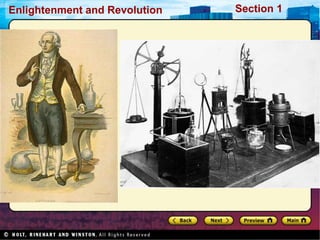
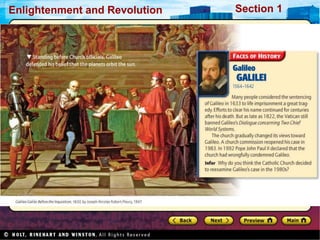
The Scientific Revolution involved a new way of thinking that challenged traditional views. Copernicus developed a heliocentric model of the solar system that placed the Sun, not Earth, at the center. Kepler later proved that planets orbit in ellipses, not circles. Galileo used a telescope to observe craters on the Moon and moons orbiting Jupiter, supporting Copernicus' theory. Newton later published Principia, explaining gravity and its effects on planetary motion. Discoveries were also made in biology through anatomy studies and microscopy, and in chemistry through experimentation and precise measurements. While the Catholic Church initially opposed challenges to its authority, it benefited from advances that enabled Renaissance art and architecture.