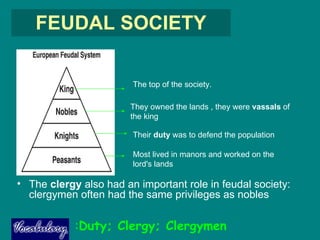
The feudal system that existed in Europe between the 11th and 13th centuries saw a hierarchical society develop. At the top was the king, who granted land to nobles in exchange for their loyalty and military service. These nobles then granted portions of their land to knights or clergy in exchange for their loyalty and labor. At the bottom were peasants, who lived and worked on the land, either as serfs bound to the manor or freemen who paid rent. This system provided for military protection and governance in a decentralized period after the fall of the Carolingian Empire.