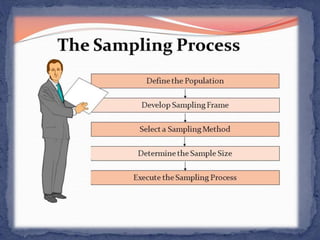
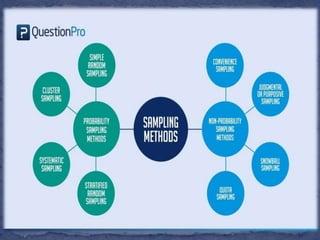
This document discusses various sampling methods used in research including probability sampling techniques like simple random sampling, cluster sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified random sampling. It also covers non-probability sampling methods such as convenience sampling, judgmental sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. The document explains how each method works with examples and concludes by defining sampling error and non-sampling error that can occur in research.