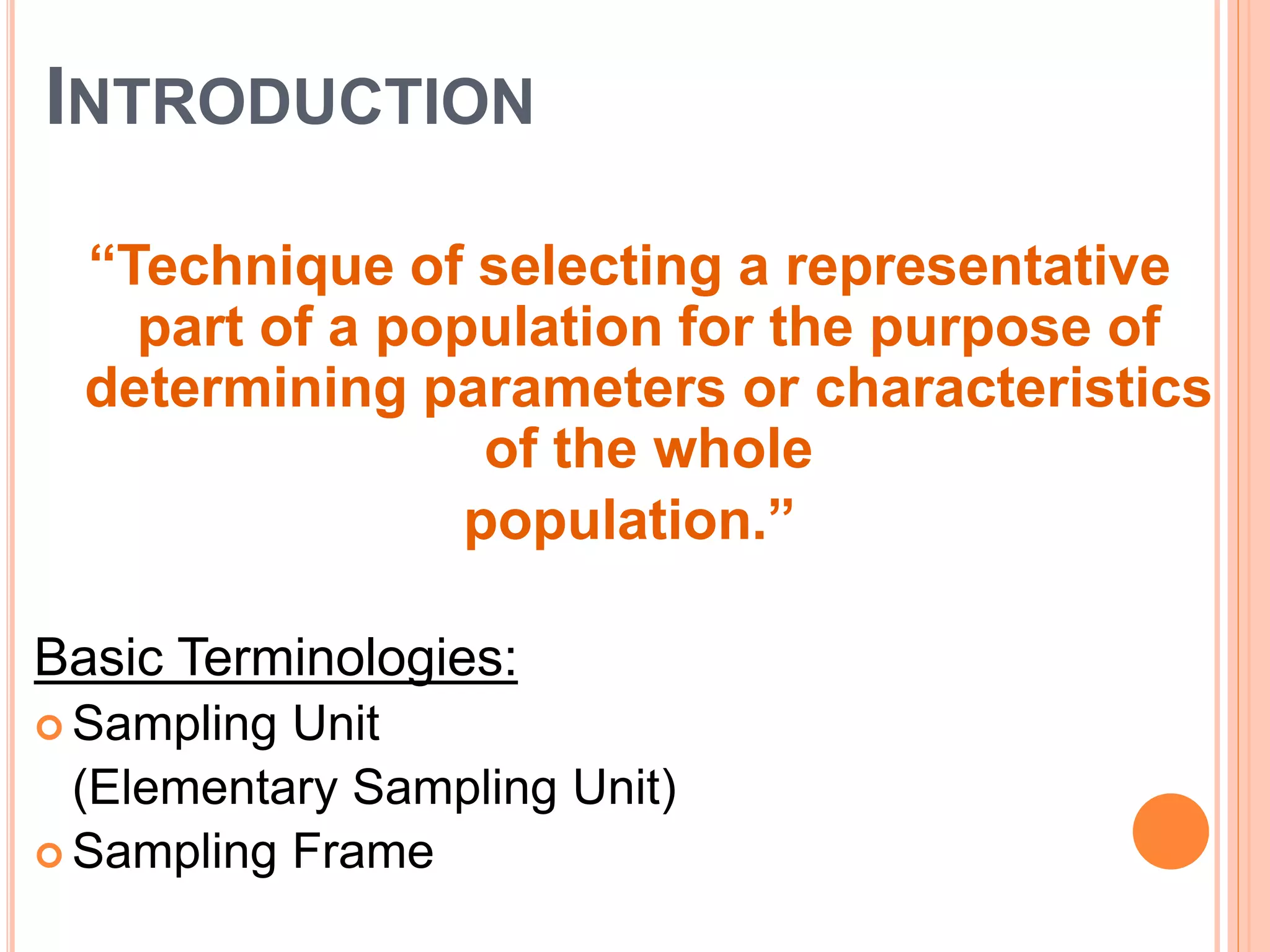
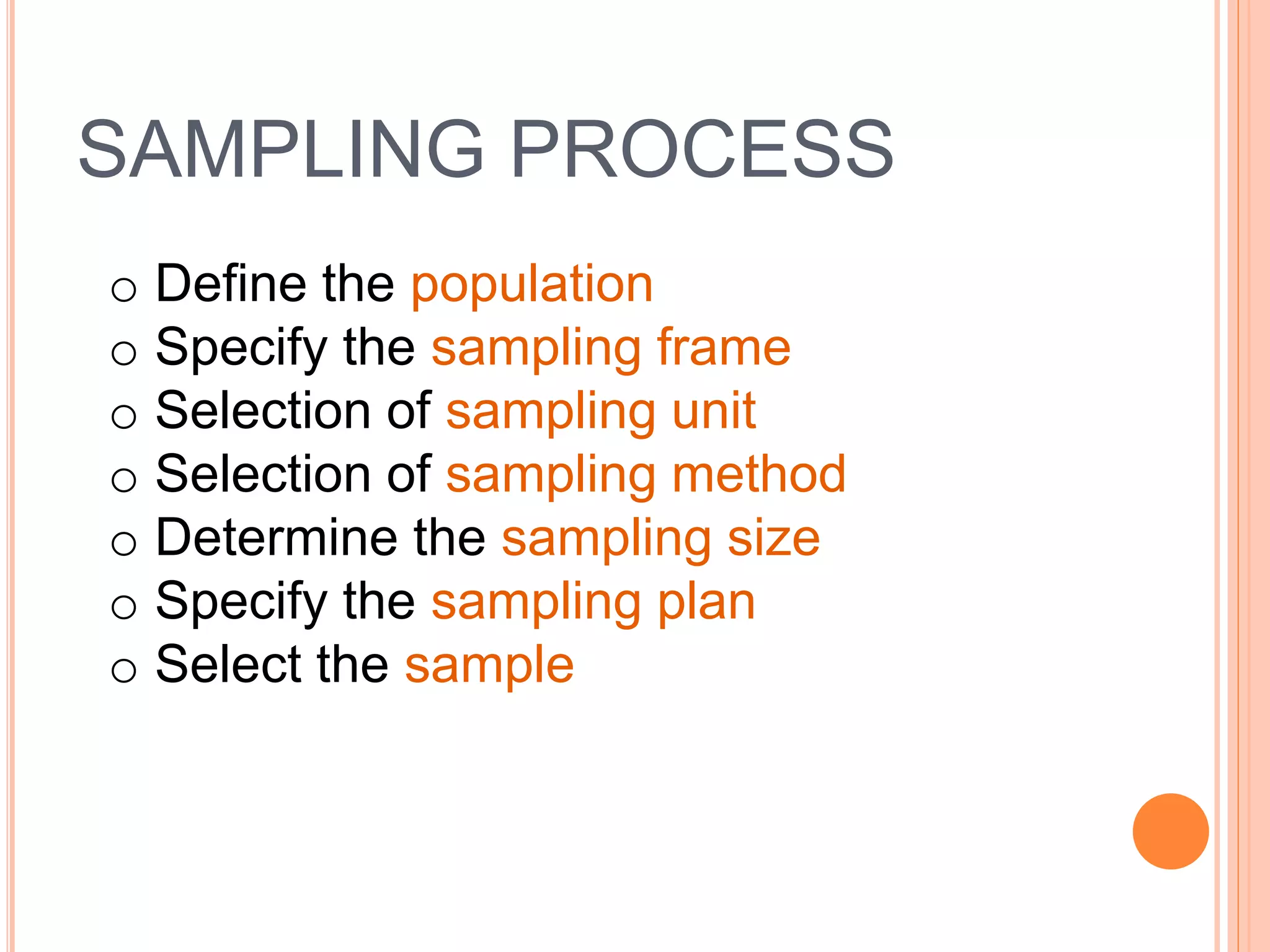
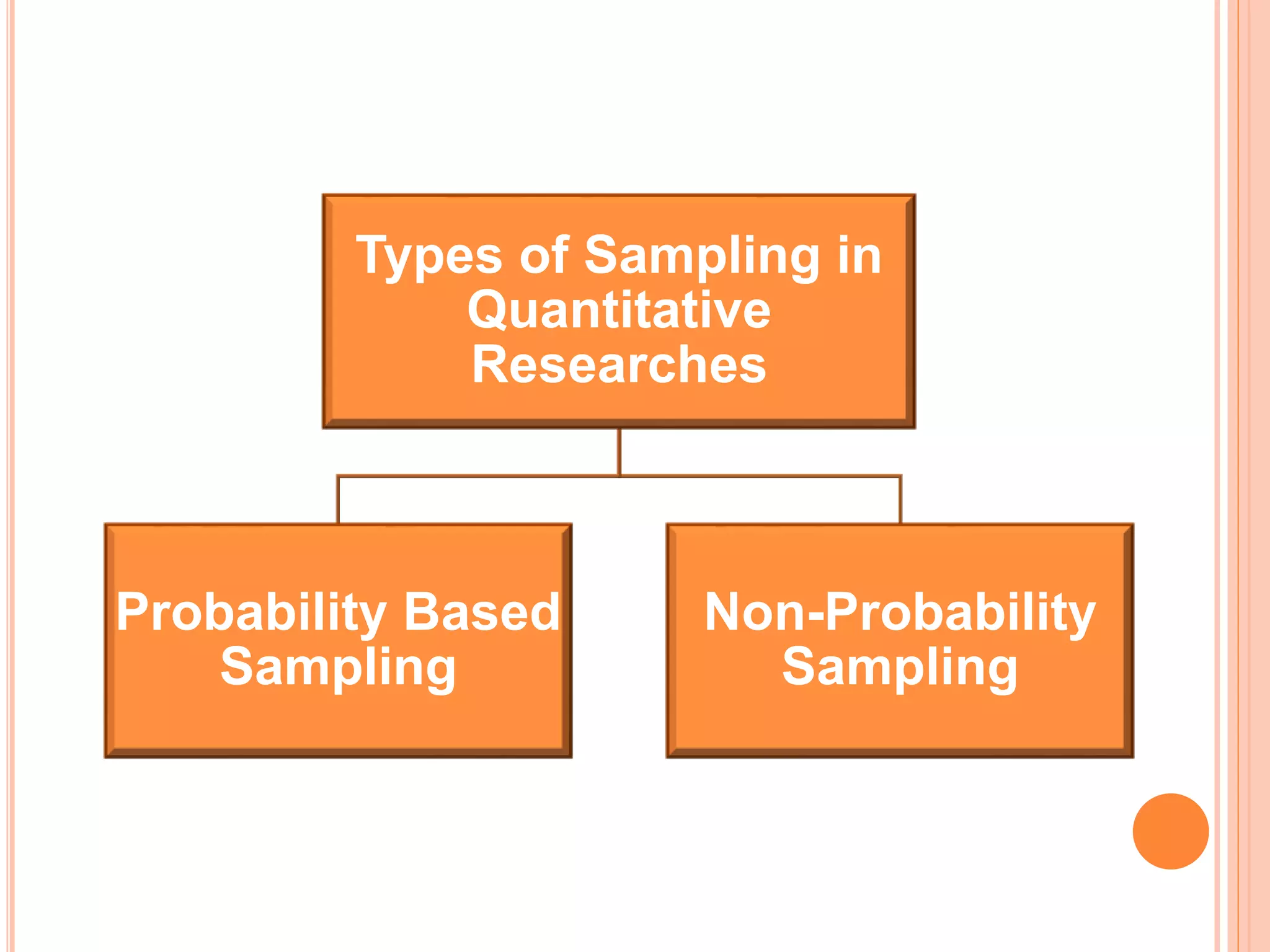
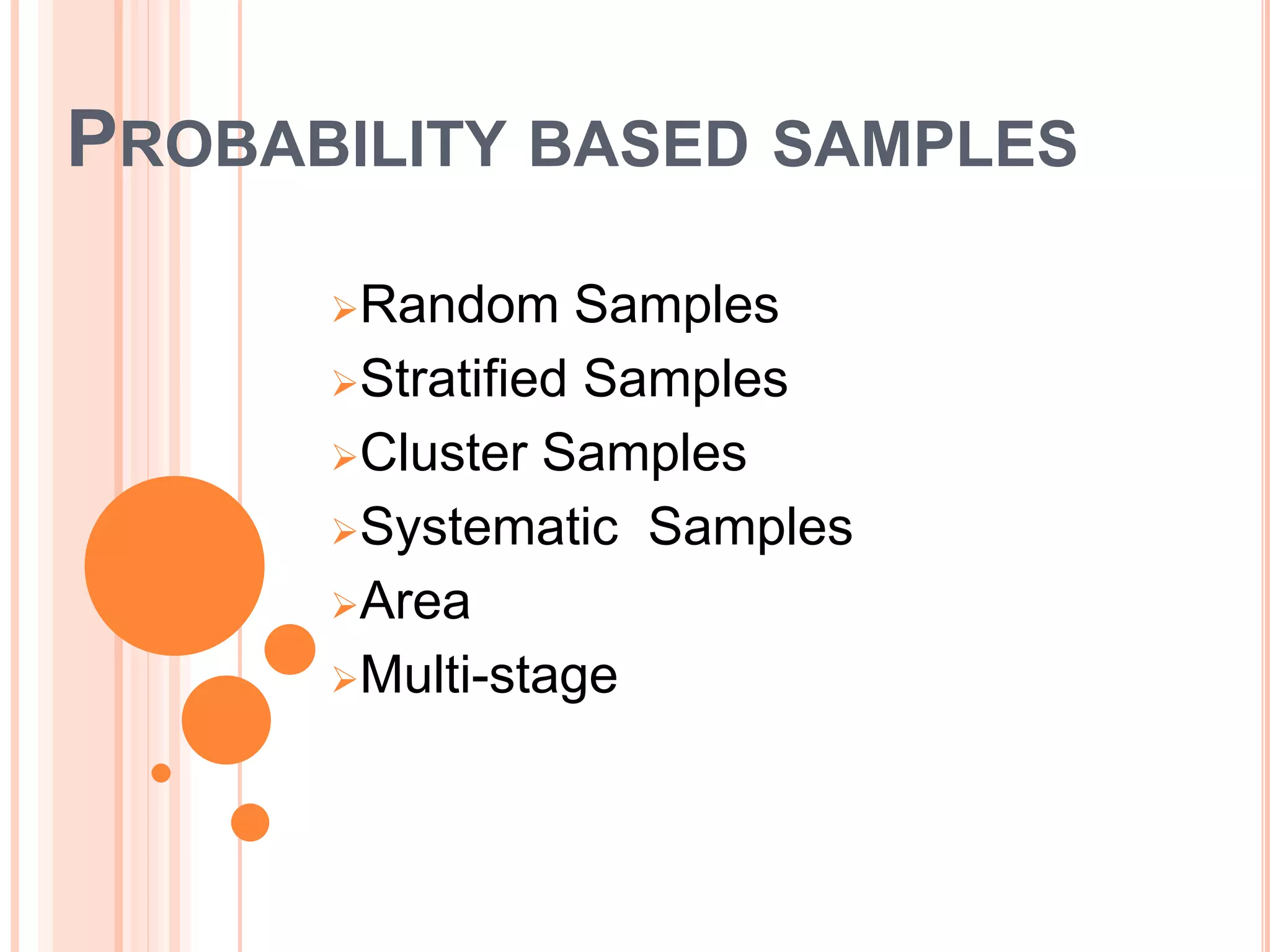
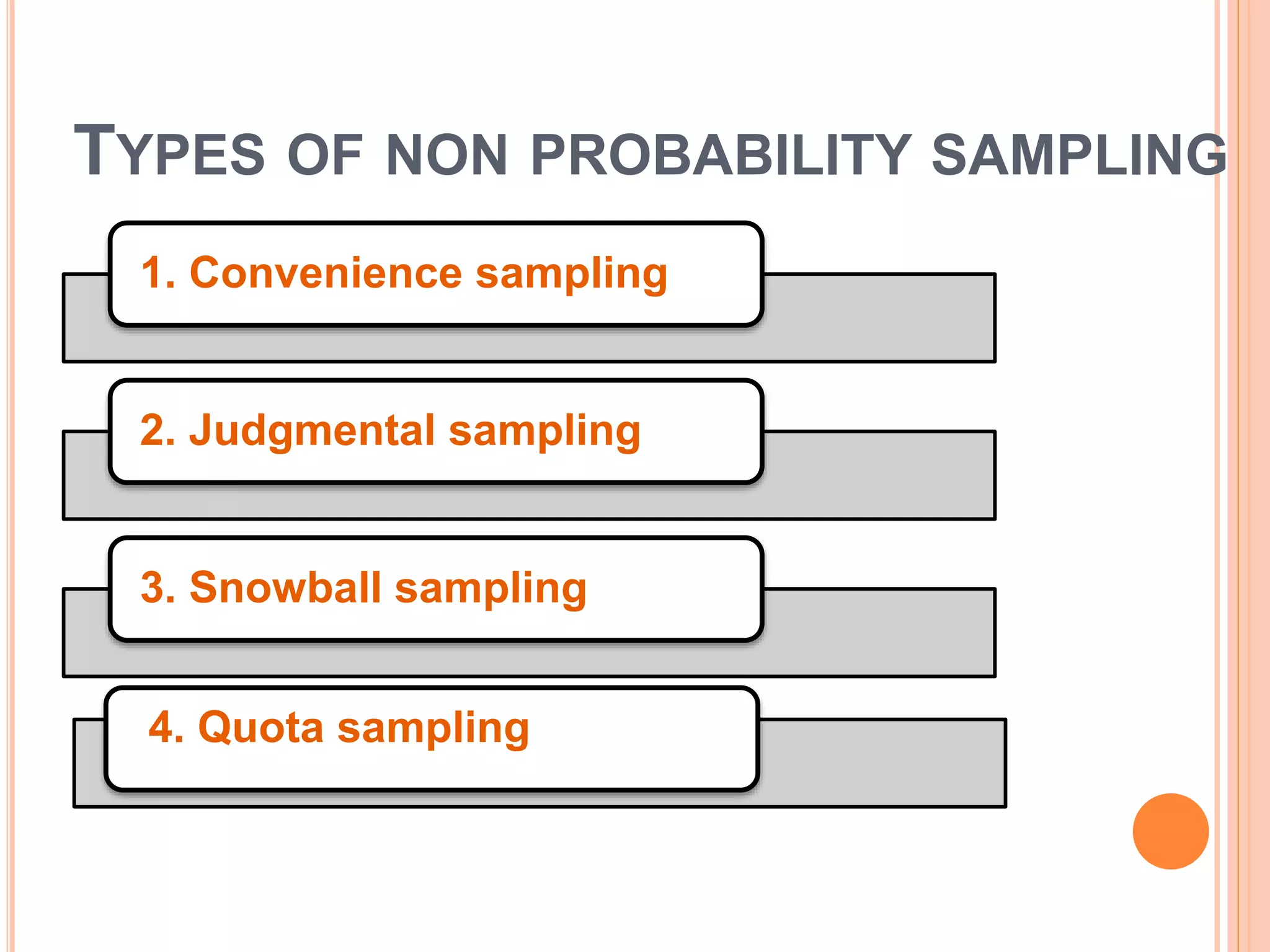
This document discusses different sampling methods used in research. It begins with defining sampling as selecting a representative part of the population to determine characteristics of the whole. The sampling process involves defining the population, selecting a sampling method, and determining sample size. Probability sampling methods like random, stratified, cluster and systematic sampling aim to give all units an equal chance of being selected. Non-probability methods like convenience, judgmental, snowball and quota sampling do not use chance and focus on easily available units. The document provides details on each sampling method and their advantages and disadvantages.