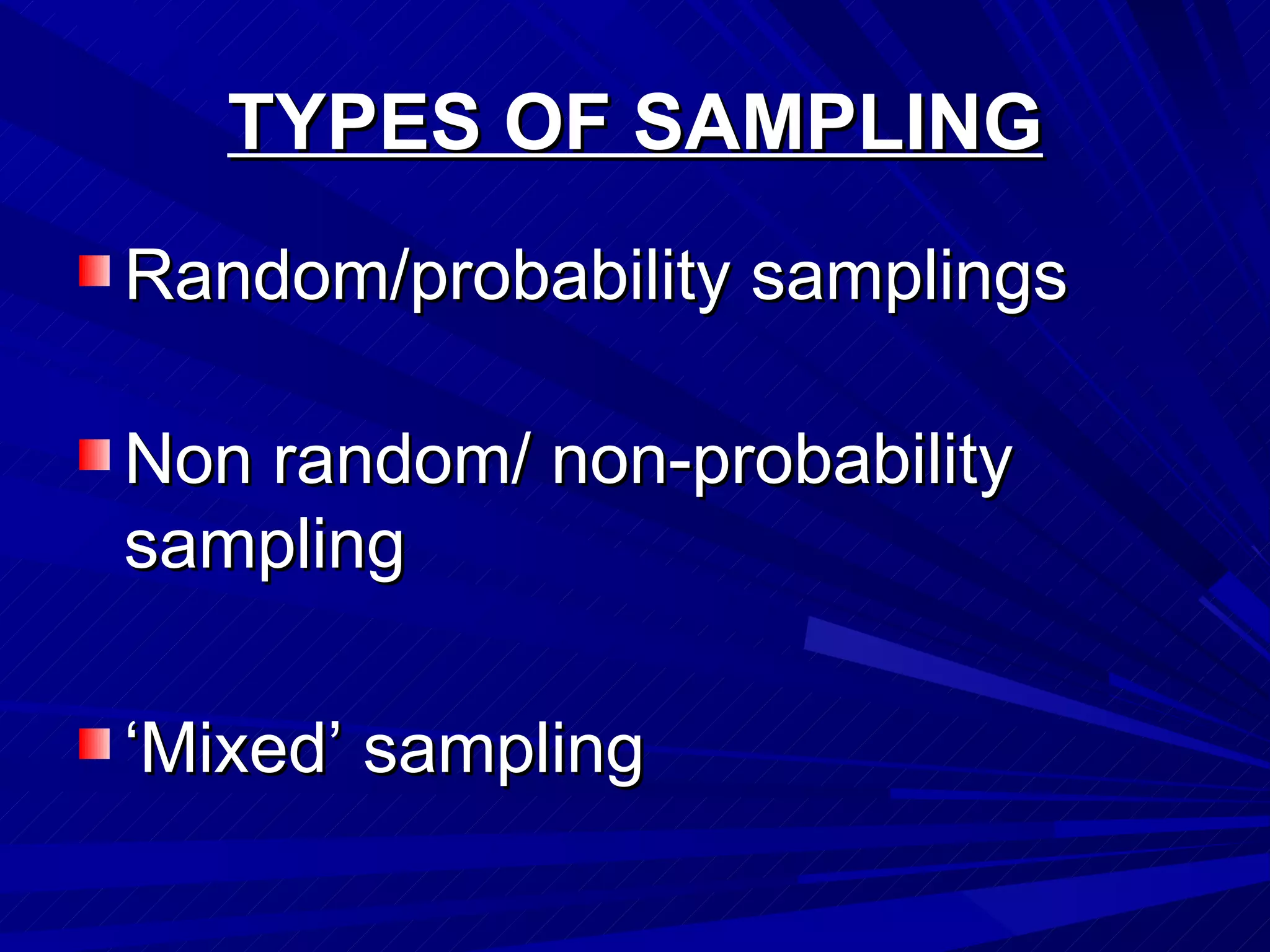
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of a population to make inferences about the whole population. It allows researchers to study populations that would be too large or impractical to study in their entirety. There are two main types of sampling - probability sampling, which allows results to be generalized to the larger population, and non-probability sampling, which is typically used for qualitative research where generalizability is not the goal. Sample size and how representative the sample is of the overall population impacts how well results can be generalized.




















![Sampling1[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sampling11-120509162836-phpapp02/75/Sampling1-1-22-2048.jpg)