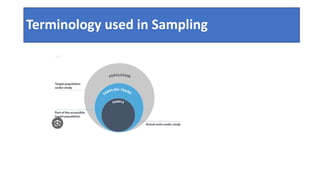
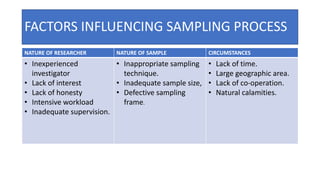
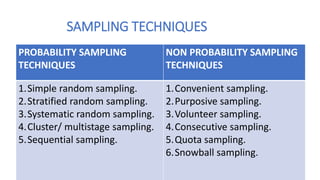
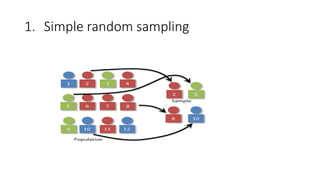
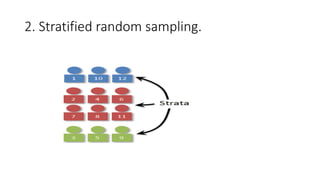
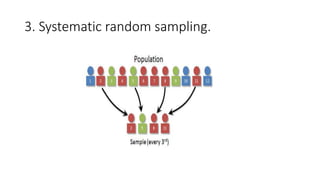
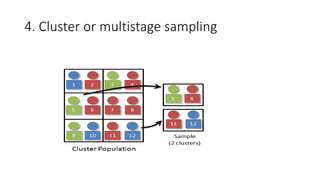
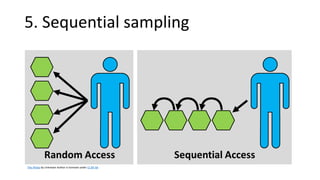
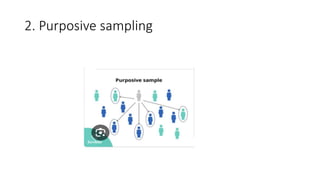
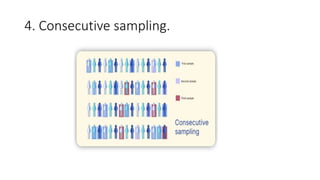
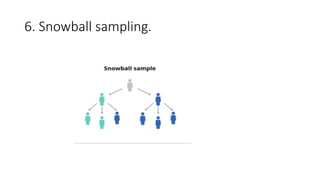
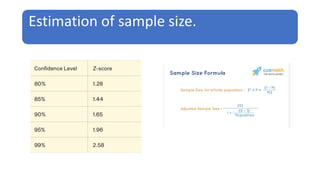
This document discusses sampling techniques used in research. It defines key terms like population, sample, and sampling. It describes probability sampling techniques like simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, systematic random sampling, cluster sampling, and sequential sampling. It also covers non-probability sampling techniques such as convenience sampling, purposive sampling, volunteer sampling, quota sampling, snowball sampling, and consecutive sampling. The document explains when and how to use different sampling techniques and notes important factors to consider in the sampling process.