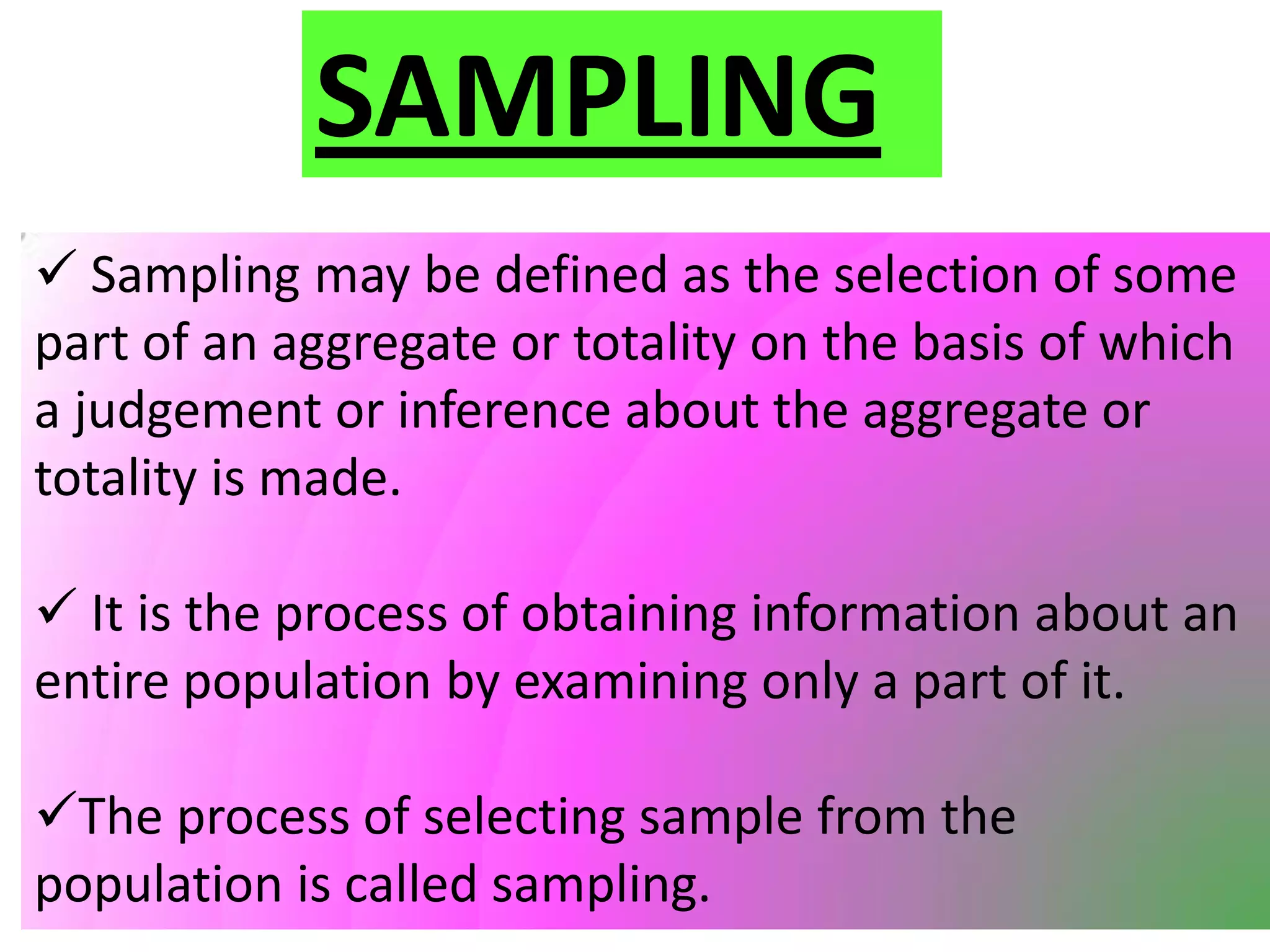
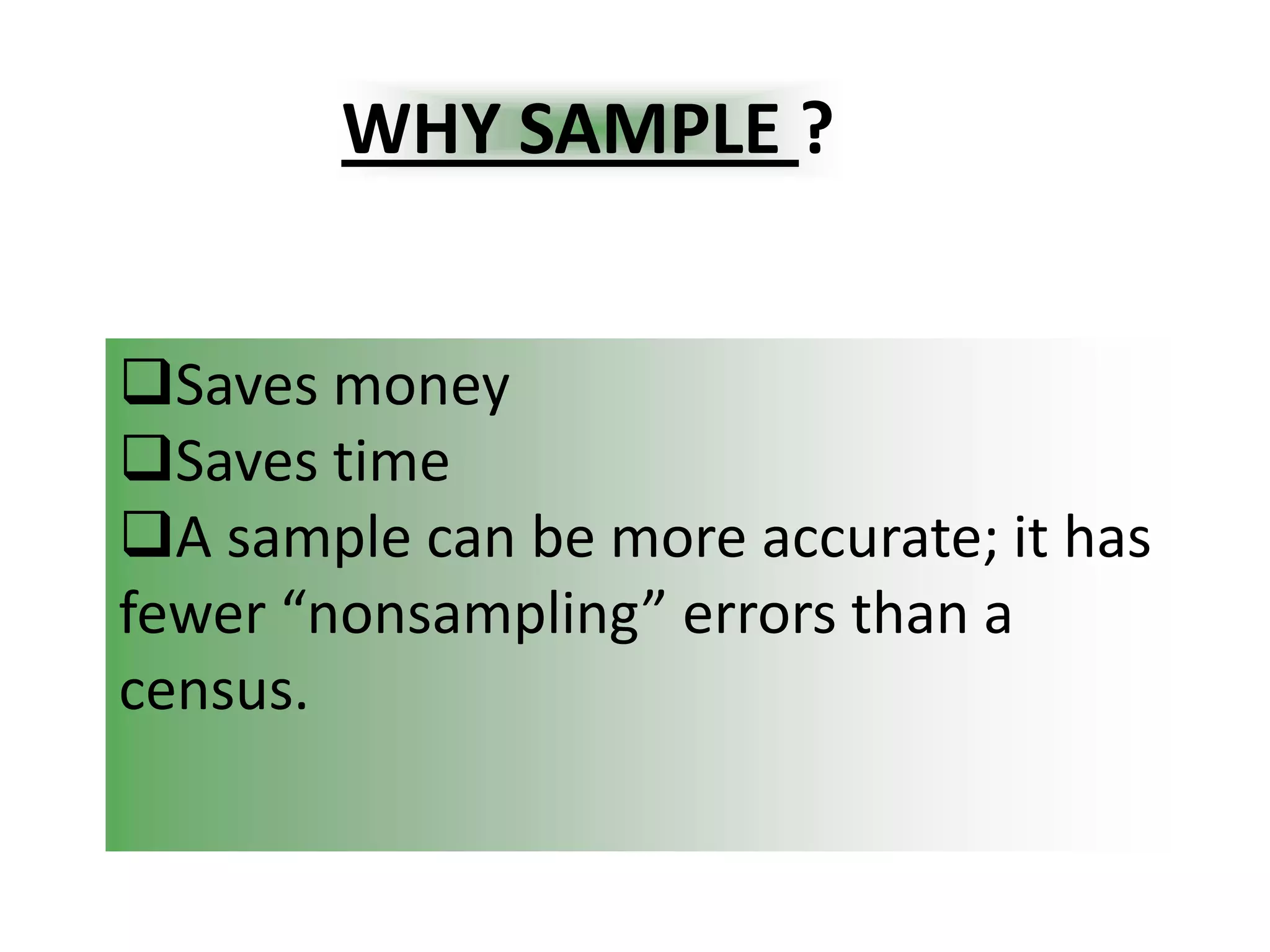
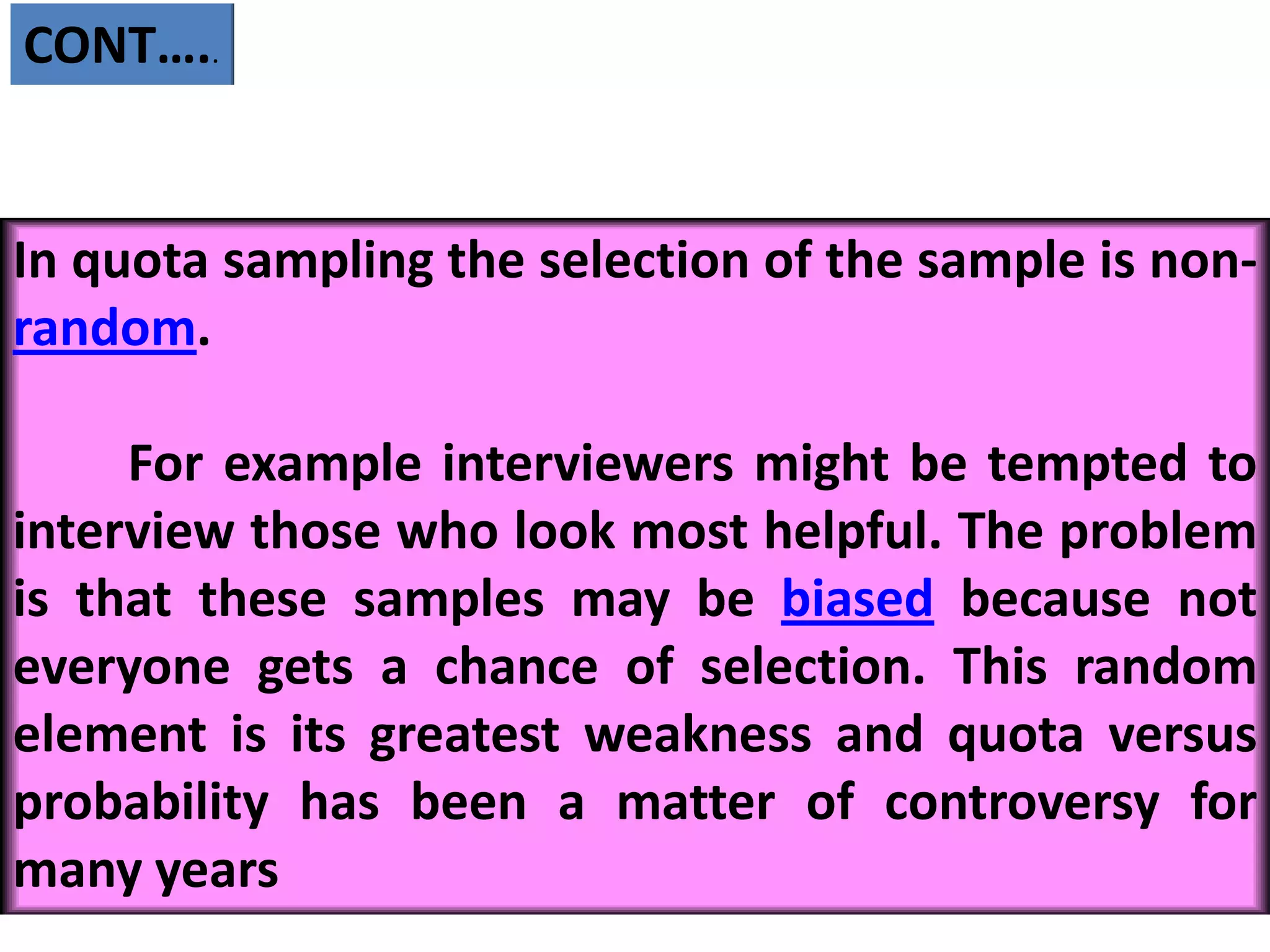
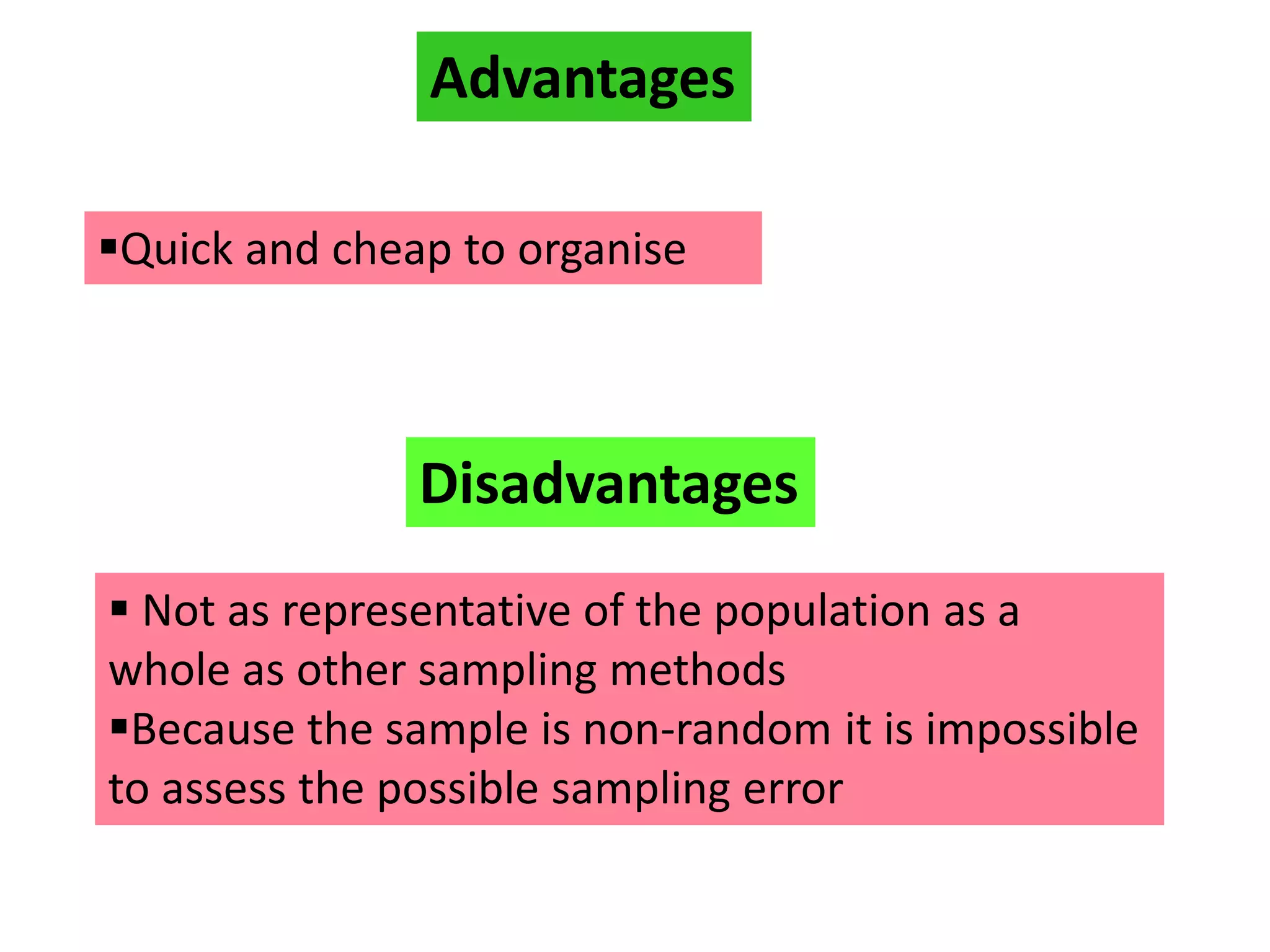
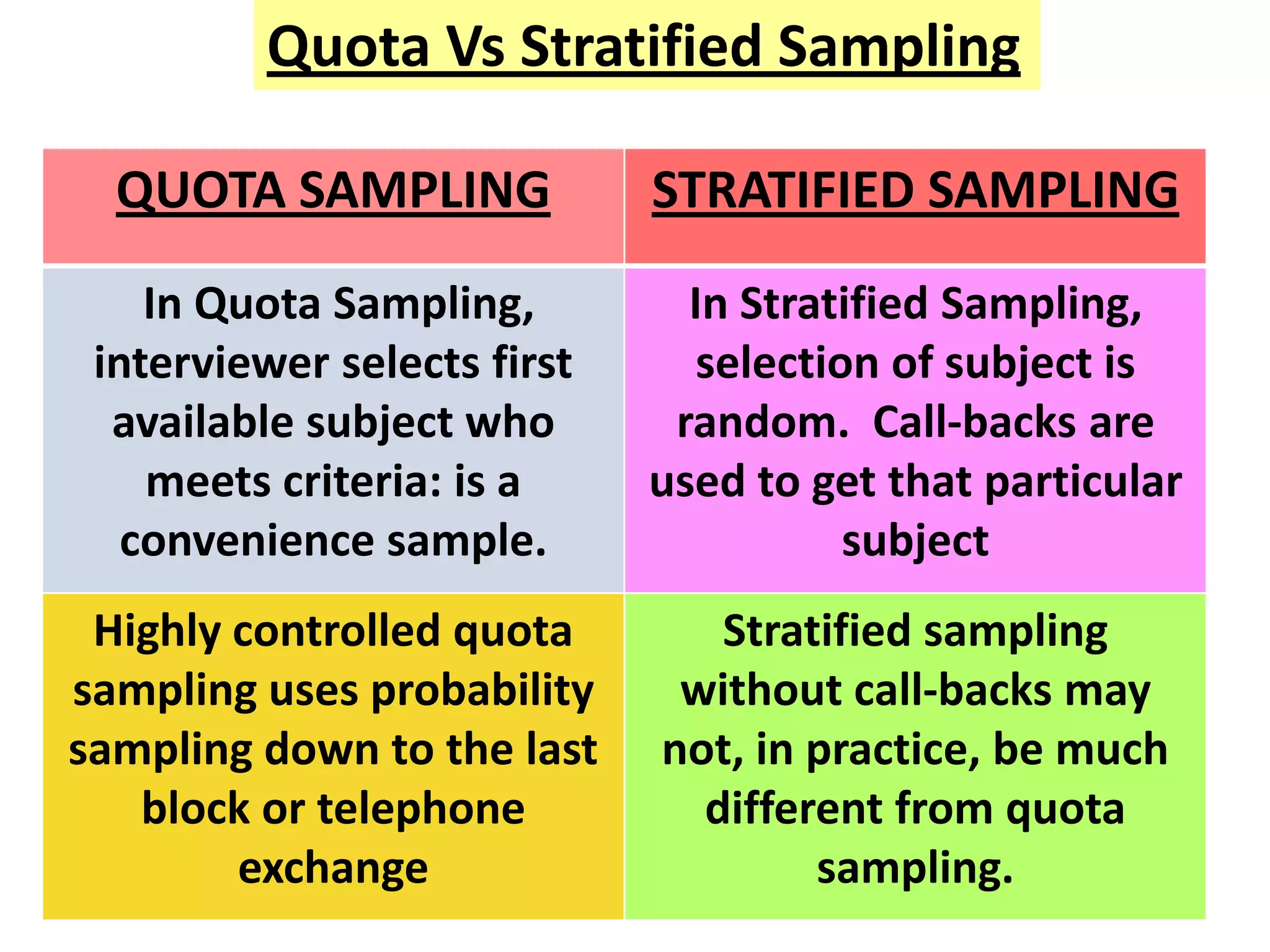
This document provides an overview of quota sampling. It defines sampling and explains why samples are used instead of censuses. Quota sampling involves selecting a sample based on predefined quotas for certain subgroups of the population. For example, quotas may be set to interview 50 females ages 45-60. Quota sampling is a non-probability method that relies on the interviewer's selection of subjects within each quota, which can introduce bias if not chosen randomly. While quick and cheap, it is not as representative as probability methods that ensure all subgroups have a chance of selection.