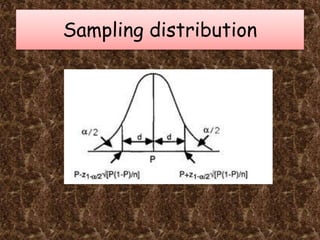
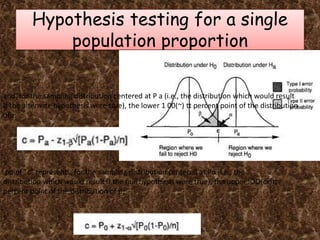
This document discusses sample size calculations for estimating population proportions and conducting hypothesis tests about population proportions. It provides formulas and examples for determining the needed sample size based on desired precision or confidence level when estimating a proportion, and desired power when testing if a proportion is different than a hypothesized value. For example, it shows that a sample of 97 children is needed to estimate the proportion receiving vaccinations within 10 percentage points of the true value with 95% confidence. It also works through an example where the needed sample size is 384 to test if a new medical treatment has a success rate at least 10 percentage points higher than the reported rate of 70% with 90% power and a significance level of 5%.